AAAP in the Media
Displaying 1 - 12 of 18
Global Leaders Rally Support and Finance for the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program to Tackle Climate Change in Africa
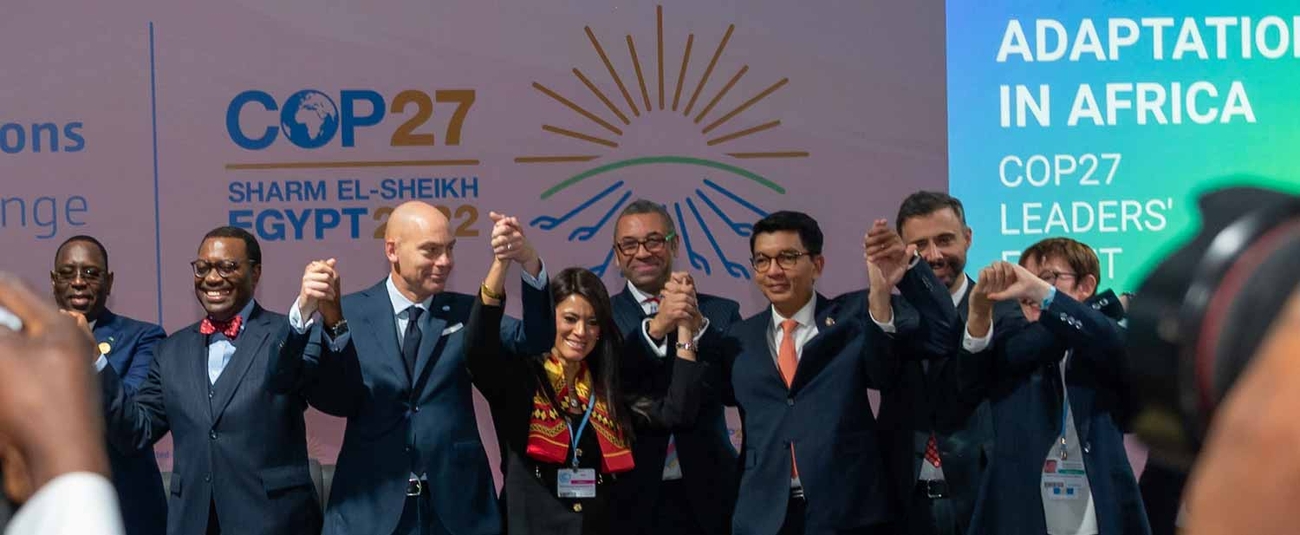

Global leaders on Tuesday rallied around climate adaptation for Africa. They attended the Africa Adaptation Leaders’ Event, convened by African Union Chair President Macky Sall of Senegal, Global Center on Adaptation CEO Patrick Verkooijen, and African Development Bank Group President Akinwumi Adesina.
The event took place at the global climate summit (COP27) in Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt. It underscored the critical need for climate adaptation in Africa and responded to the call for the capitalization of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP).
“This is a pivotal step in the fight against climate change,” African Union Chair President Macky Sall said. “The commitments made by Africa’s partners will give the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program the boost that it needs to transform the development trajectory of the world’s most climate exposed continent. I am confident in the ability of the AAAP to deliver results for Africa.”
The Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program is an Africa-owned and Africa-led initiative developed by the Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) and the African Development Bank (AfDB) in close collaboration with the African Union. It serves as the implementation of the Africa Adaptation Initiative (AAI) to mobilize $25 billion to implement, scale and accelerate climate adaptation across the Africa. Since 2021, AAAP has mainstreamed climate adaptation in over$3.5 billion of investments in 19 countries.
United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres said: “I want to express my total solidarity for the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program […] I urge the international community to support Africa to mobilize the technical & financial resources for scaling up transformative adaptation.”
“With this innovative program, Africa has developed a plan to grow, create jobs and opportunities for people, and to be resilient against the climate crisis,” said President Akufo-Addo of Ghana. “AAAP’s singular focus on the issue of climate adaptation will also contribute to greater stability and progress in Africa and around the world. AAAP is aligned with Ghana’s plans to address climate change as it chairs the Climate Vulnerability Forum (CVF) to lead efforts from the world’s most climate vulnerable countries to spur and mobilize investment through the Climate Prosperity Plans."
James Cleverly, Secretary of State for Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Affairs of the United Kingdom announced that the UK will provide £200 million to the African Development Bank’s Climate Action Window. This is in addition to the £20 million announced at COP26 in Glasgow to the AAAP Upstream Financing Facility.
Cleverly noted: “Climate change is having a devastating impact on countries in Sub-Saharan Africa facing drought and extreme weather patterns, which have historically received a tiny proportion of climate finance. This new mechanism […] will see vital funds delivered to those most affected by the impacts of climate change, much more quickly.”
Prime Minister Mark Rutte of the Netherlands followed through on the commitment made at the Africa Adaptation Summit held at the Global Center on Adaptation in September to confirm that the Netherlands will contribute EUR110 million to the AAAP, with EUR10 million in support for the Upstream Financing Facility hosted by GCA and EUR 100 million for the Climate Action Window of the African Development Fund at the African Development Bank as part of the Netherlands’ commitment to dedicate half of its climate funding, fully grant based, to climate adaptation, with a focus on Africa.
Norwegian Prime Minister Jonas Gahr Støre echoed African leaders’ calls for countries to rapidly scale up finance for climate adaptation, stating: “The climate crisis is here and now. Years of progress are at risk.”
“The AAAP Upstream Financing Facility is the delivery mechanism of adaptation and will use millions to leverage the billions that is required for adaptation,” he continued. “AAAP projects will generate effective climate adaptation outcomes. Adaptation is a growth agenda. A jobs agenda. And a prosperity agenda. On behalf of Norway, I am looking forward to continuing this partnership, investing in it, and supporting it with the Global Center on Adaptation.”
International Monetary Fund Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva emphasized the need to accelerate adaptation in Africa, stating: “It is paramount to support Africa’s adaptation because Africa will not reach its tremendous potential without it. AAAP complements the IMF’s Resilience and Sustainability Trust, which helps countries address external shocks such as climate change and ensure sustainable growth that can give Africa a chance to leapfrog outdated development models.”
African Development Bank Group President Dr. Akinwumi Adesina said: “Africa is suffering from the devastating effects of climate change. Our continent is being short changed by climate finance. The contributions towards the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program’s Upstream Financing Facility and the Climate Action Window – which the African Development Bank manages – will help capitalize the program. With increased capital, we can better deliver the investment needed to bridge the adaptation finance gap. We want to ensure that the most vulnerable communities can benefit from a sustainable and prosperous future.”
Endorsing the outcomes of the high-level meeting, Patrick Verkooijen, CEO of the Global Center on Adaptation, closed with a statement emphasizing the AAAP’s impact to date, noting that “there is no pause button on the climate crisis. Africa must adapt to the threat of climate change, and it must adapt now.”
“Through the AAAP,” he continued, “Africa has charted its path towards a climate-resilient future for its youth, its economic growth, and for its prosperity.”
About the Global Center on Adaptation
The Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) is an international organization which works as a solutions broker to accelerate action and support for adaptation solutions, from the international to the local, in partnership with the public and private sector, to ensure we learn from each other and work together for a climate-resilient future. Founded in 2018, GCA is hosted by the Netherlands, working from its headquarters in Rotterdam with a knowledge and research hub based in Groningen. GCA has a worldwide network of regional offices in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, Dhaka, Bangladesh and Beijing, China. Through this evolving network of offices and global and regional GCA teams, the organization engages in high-level policy activities, new research contributions, communications, and technical assistance to governments and the private sector.
About the African Development Bank
The African Development Bank Group is Africa’s premier development organization. Its overarching objective is to spur sustainable economic development and social progress in its regional member countries, thus contributing to poverty reduction across the continent.
The Bank Group achieves this objective by mobilizing and allocating resources for investment in African countries and providing policy advice and technical assistance to support development efforts.
In 2015, all multilateral development institutions agreed on the same set of objectives, the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Learn more: https://www.afdb.org/
About the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program
The Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP) is a joint initiative of the African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation (GCA). It aims to mobilize $25 billion, over five years, to accelerate and scale climate adaptation action across the continent. This ambition is delivered through the AAAP Upstream Financing Facility managed by the Global Center on Adaptation and the African Development Bank’s climate action window in the ADF replenishment. AAAP works across four pillars to achieve transformational results: Climate-Smart Digital Technologies for Agriculture and Food Security; African Infrastructure Resilience Accelerator; Youth Empowerment for Entrepreneurship and Job Creation in Climate Adaptation and Resilience and Innovative Financial Initiatives for Africa. AAAP has already guided over $3.5 billion of upstream investments in 19 countries with every dollar spent influencing $100 downstream.
COP27 - COP27 Leaders' Event, Accelerating Adaptation in Africa (DAY 2)
State and Trends on Adaptation Report 2021: Africa
Adaption is crucial for the continent that is the most vulnerable to climate change, but adapting successfully will bring enormous benefits.
Climate risk regulation in Africa’s financial sector and related private sector initiatives
Extreme weather phenomena such as rising temperatures and the increasing frequency of droughts and floods are affecting lives and livelihoods in Africa. According to the Global Climate Risk Index 2021,1 five African countries ranked among the 10 countries most affected by extreme weather in 2019: Mozambique (first), Zimbabwe (second), Malawi (fifth), South Sudan (eighth), and Niger (ninth).
State and Trends in Adaptation Report 2022
A year on from State and Trends in Adaptation 2021 (STA21) which set out our blueprint for adaptation action, the evidence of the impact of deepening, growing climate change daily invades our screens.
2022 has seen record-breaking extreme weather globally, with mighty floods, vast wildfires, enduring heatwaves, and drought on every continent. More frequent and intense extreme weather and climaterelated events are creating new and increasing risks everywhere.

20 young African entrepreneurs bag $100,000 each to boost their climate adaptation businesses
Africa Seeks Public-Private Investments to Help Combat Climate Change
Digital Climate Adaptation Solutions Training- North Africa
Harnessing the power of technological innovations and digitalization to improve agricultural productivity and strengthen climate resilience has been recognized as one of the potential game changers to address many of pressing climate concerns and rural transformation challenges facing Africa today.
Digital climate-informed advisory services are tools and platforms that integrate climate information into agricultural decision-making. These services range from digital mobile apps, radio, and online platforms to digitally enabled printed bulletins based on climate models and extension services that utilize climate information platforms. DCAS offers crucial opportunities to build the resilience of small-scale producers in the face of worsening climate change impacts, particularly when bundled with complementary services (such as financing, input supply, market access, insurance).
The objectives of the DCAS trainings are as follows:
- Capacity enhancement for agricultural stakeholders across North Africa in DCAS
- Supporting trainees to improve their confidence and capacity to design and implement DCAS projects to reach the last mile and farmers for improved food security and climate resilience
- Facilitating knowledge/experience sharing of participants on contextual issues and approaches to scale up DCAS
- Increase the knowledge of stakeholders from across North Africa on opportunities and new approaches for the design, mainstreaming and use of digital tools and data-enabled agriculture to combat the effects of climate change
- enhancing capacity to use digital agriculture advisory services and solutions to ensure uptake by of DCAS among stakeholders in North Africa
- Over 50 Participants trained in digital agriculture and digital climate adaptation solutions
- A new cohort or platform of African public officials, researchers, farmers organizations leaders and agricultural NGO focal points with improved expertise in DCAS (for subsequent experience capitalization follow up and training)
- Training evaluation assessment report
- Improved understanding / knowledge of target stakeholders in North Africa through training and information sharing including lessons learned on the challenges, opportunities and new approaches to the design, mainstreaming and use of DCAS and data-enabled agriculture
- Enhanced capacity of selected agricultural stakeholders in public institutions and farmers groups across North Africa to use digital agriculture advisory solutions, implement digital climate smart advisory solutions, and train their members/colleagues to use DCAS tools
€100,000
High-level remarks of the Global Center on Adaptation CEO, Prof. Patrick Verkooijen, at the meeting on the 16th replenishment of the African Development Fund

Dr. Akinwumi Adesina, President of the African Development Bank Group, ADF Deputies, Executive Directors, other members of the African Development Bank’s Senior Management, distinguished Ladies and Gentlemen.
Thank you for the opportunity to address you today at this crucial meeting on the 16th replenishment of the African Development Fund (ADF). My name is Patrick Verkooijen, CEO of the Global Center on Adaptation. I’m joining you today from our headquarters in Rotterdam, on the world’s largest floating office.
It is an honour for GCA to work on climate adaptation with the African Development Bank under the leadership of my big brother and friend Dr. Akinwumi Adesina, Africa’s “Optimist-in-Chief.”
Today, I want to deliver three messages.
First, climate adaptation is not an independent challenge that Africa must tackle separately. It is not an “either/or” question but an opportunity for “and.” An opportunity for leverage.
Second, the needs for climate adaptation are enormous but African countries themselves are already moving forward and financing a portion of those needs. They have no option. But they need partners. They need you.
Third, GCA and the Bank are not waiting. There is an African-owned and Africa-led program for investments in climate adaptation – the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP). Action is already happening on the ground. But that initial action is not nearly enough.
For all these three reasons the proposed increase in ADF resources and the climate set aside are critical for the continent today.
First, climate adaptation is not an “either/or” challenge. The Sustainable Development Goals can only be achieved if education, health, and infrastructure services like water are adapted to the increasing shocks of climate change.
Adaptation is critical for private sector development. Last year, we interviewed SMEs from all over Africa. More than three quarters said that they have been directly impacted by climate change, by losing their assets or their customers. Africa needs private sector development and adaptation.
The world watches in horror at the war in Ukraine. Food prices are increasing rapidly with direct impacts on African economies and households. But I don’t want to imagine if the crops this year in the region are impacted by climate shocks like droughts or floods. If farmers’ work is lost because of the common climate shocks suffered by Africa every year, then farmers, households and countries will face a triple shock: the COVID economic crisis, the implication of the Ukraine war, and the climate shocks of 2022 and 2023. So, it is not Ukraine or adaptation. It should be Ukraine and adaptation.
Finally, it is not climate adaptation or mitigation. The world must stay within 1.5 degrees warming. The recent IPCC report is the loudest alarm siren we are hearing. This target is possible. But if the world does not achieve it, large parts of Africa will cross the threshold of financially and economically viable adaptation. Large portions of drylands in many Africa countries will become uninhabitable. So, it is not adaptation or mitigation. It is adaptation and mitigation.
Ladies and Gentlemen, let me discuss my second point. The needs are enormous. GCA calculations made as part of the State and Trends in Adaptation 2021 report focused on Africa show that the continent needs $330 billion between now and 2030 to achieve its NDC targets. But this is not what the African countries are asking for. African governments already committed in those NDCs to put $66 billion of their own funds. They have no choice. Africa must adapt. But it cannot adapt alone. The financing gap is enormous.
Adaptation should not be seen as a cost, but as an investment. Our State and Trends in Adaptation 2021 report also shows that, in Africa, adaptation pays off. Adaptation is good business. For example, investments in climate-smart agriculture can give as much as four dollars in benefits for every dollar invested. Moreover, the costs of inaction are ten times higher than the cost of action. Adaptation is a smart investment.
African nations are already investing and have committed to invest more. But they cannot do it alone. They need the world to partner with them. ADF16, and its climate set aside, are part of the partnership Africa needs.
Dear ADF Deputies, my third point is that Africa, the Bank and GCA are not waiting. African nations have called for an ambitious Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program. This is an Africa-owned and Africa-led program. It aims to deliver
$25 billion of investments adapted to the rapidly changing climate. GCA, together with the African Development Bank and the African Union, and other partners like the World Bank, EIB and IFAD, are moving forward with the implementation of AAAP investments.
GCA is mobilizing $250 million for the AAAP Upstream Financing Facility. The initial contributions from development partners have helped us bring the best science and global adaptation practice to more than $3 billion of investments already approved by the AfDB’s Board of Directors. The leverage of 1 to 100 of the Upstream Facility is real.
First, the Bank is financing a $350 million project to build resilience for food and nutrition security in the Horn of Africa. GCA experts worked with the Bank team to bring the best models of digital climate information systems to ensure the project activities and the beneficiary farmers have the tools to adapt and build more resilient food systems.
In another example, the Bank is financing an $80 million Youth Enterprise Development program for South Sudan. GCA adaptation specialists are working with the Bank experts to help create the skills, jobs, and SME for adaptation businesses in areas such as agriculture or infrastructure.
Honourable ADF Deputies. Africa cannot wait to invest in adaptation. Africa and its partners like the Bank and GCA are not waiting.
And I hope you do not wait. The mobilization of resources for ADF16 and its climate set aside are urgent for the continent. We hope you hear the voices of African leaders.
At “the African COP”, at COP27, President Adesina, President Macky Sall, as Chairperson of the African Union, and I will convene a High-level gathering of African and world leaders. The continent needs your support. A clear commitment at COP27 for ADF16 and its climate set aside is the response Africa needs.
Africa has the plan. Africa has the commitment. Now, with a fully capitalized ADF16, it will have the vehicle. Let’s make it happen. Thank you.
Global and African Leaders Welcome Launch of GCA Africa as “Historic Moment to Accelerate Adaptation” on the Continent

The Global Center on Adaptation today announced the launch of its regional office in Côte d’Ivoire.
Hosted by the African Development Bank at its headquarters in the Ivorian capital Abidjan, GCA Africa will work with partners across the continent to scale and accelerate adaptation action that protects African communities from the impacts of climate change.
GCA Africa will focus on programs and action, knowledge acceleration and capacity building and agenda-setting that respond to the acute challenges from the changing climate facing African countries.
The GCA Africa programs include improving the food security of one billion people in Sub-Saharan Africa by 2030 through a program on rural well-being and food security, as well as projects to support communities through water for urban growth and resilience; using nature for more resilient infrastructure; adaptation finance and building youth leadership.
Commenting on the launch, Ban Ki-moon, Co-Chair of the Board of the Global Center on Adaptation and 8th Secretary-General of the United Nations said:
“This is a historic moment to accelerate adaptation in Africa. Nowhere is the challenge of achieving sustainable development in the face of a changing climate more acute. Our new regional office will support regional and national adaptation efforts by emphasizing and spreading existing best practices on the continent and ensuring their fully fledged integration into broader international adaptation efforts”.
Dr. Akinwumi Adesina, President of the African Development Bank said:
“I am delighted with the launch today of the Global Center on Adaptation for Africa (GCA) hosted by the African Development Bank. The Bank has committed to doubling its financing for climate to $25 billion by 2025, with over 50% devoted to climate adaptation. Africa must not be short-changed by global climate finance. We will partner with the GCA to mobilize more resources for climate adaptation in Africa.”
Ali Bongo Ondimba, President of Gabon and Chair of the African Adaptation Initiative said:
“The devastating effects of climate change, which include severe droughts, floods, reduced agricultural yields, sea-level rise, and other climate-related disasters, are on the rise. The launch of GCA Africa is a bold and innovative initiative to galvanize the support needed to significantly scale up adaptation on the continent, identify gaps and connect regional partners to find solutions.”
Quotes from other partners:
Kristalina Georgieva, Managing Director, International Monetary Fund said:
“More than any other region, sub-Saharan Africa is vulnerable to the impact of climate change, which threatens lives and livelihoods and undermines economic growth. After the current crisis, boosting resilience is an urgent priority so it’s vital we share the knowledge and best practice that can help accelerate climate adaptation.”
Amina J. Mohammed, Deputy Secretary General of the United Nations said:
“There is an urgent need to step up the support for people in Africa, and around the world, affected by climate change. I welcome the Global Center on Adaptation Africa as a crucial partner in delivering the elevated ambition and enhanced action that is needed to make this shift towards a resilient future.”
Feike Sijbesma, Co-Chair of the Board of the Global Center on Adaptation and Honorary Chairman of Royal DSM said:
“Millions of lives depend on Africa’s agricultural sector. Adapting and improving its resilience to climate change is therefore a must. By investing in African local food systems we catalyze sustainable value chains and support the vulnerable but small-scale often female producers.”
Nana Akufo-Addo, President of Ghana said:
“Adaptation to the impact of our changing climate is essential if Ghana is to continue to grow and prosper. We look forward to working with GCA and its partners to meet the challenge of climate change and ensuring resilience is built into Africa’s economic recovery plans.”
Dag-Inge Ulstein, Minister of International Development for Norway said:
“Climate change is not only damaging for the environment, but devastating also for development. It is important that countries around the world, especially our partners in Africa, work together to address these global challenges. Norway is pleased to be able to support GCA Africa in accelerating this agenda.”
Peter Eriksson, Minister for International Development Cooperation for Sweden said:
“GCA is a key solutions broker and center of excellence with a holistic approach that aims to accelerate adaptation solutions for a climate-resilient future in Africa. By working with GCA Africa we will intensify climate adaptation efforts to ensure we integrate solutions to have a coherent response to our climate emergency.”
Patrick Verkooijen, CEO of the Global Center on Adaptation said:
“The impacts of climate change are already being felt across Africa and will only increase in magnitude. Adaptation is not a nice-to-have, it’s a necessity. Through our role as a solutions broker, GCA Africa will work closely with partners in every sector to ensure the most effective adaptation measures are shared and scaled across the continent, responding to the growing demand for strengthening resilience to the impacts of our changing climate.”
The launch of GCA Africa comes shortly after the launch of its South Asian office in Dhaka by Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina in September 2020. Its first regional office was launched in Beijing by Premier Li Keqiang in June 2019.
In May 2020, GCA Africa published a GCA policy brief(link is external), with the African Adaptation Initiative and endorsed by 54 Heads of State and Government, which recommended focusing stimulus investment in Africa on resilient infrastructure and food security to overcome the COVID-climate crisis.
The GCA is the lead partner institution for the Climate Adaptation Summit in the Netherlands – the first major gathering of international leaders dedicated entirely to adaptation. The summit takes place on 25 January 2021 and is hosted by Prime Minister Mark Rutte of the Netherlands. The GCA is also the Managing Partner to the Climate Vulnerable Forum and Vulnerable Twenty (V20) Group of Ministers of Finance, a group of 48 developing countries highly vulnerable to climate change.
Watch the launch at the following links:
About the Global Center on Adaptation
The Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) is an international organization which works as a solutions broker to accelerate action and support for adaptation solutions, from the international to the local, in partnership with the public and private sector, to ensure we learn from each other and work together for a climate resilient future. Founded in 2018, the GCA is hosted by the Netherlands. Through an evolving network of offices and global and regional GCA teams including a global innovation hub for climate adaptation launched by Premier Li Keqiang in Beijing, the organization engages in high-level policy activities, new research contributions, communications, and technical assistance to governments and the private sector.
Event page
Bizerte city climate stress test
Currently, Africa’s infrastructure needs are around USD 130–170 billion a year, with an investment gap of over 50–60% of that amount. Making Africa’s infrastructure resilient adds only an average of 3% to total costs, but every $1 spent could yield $4 of benefits.
The Africa Infrastructure Resilience Accelerator (Pillar 2 of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP)) focuses on accelerating infrastructure resilience efforts on the continent. It will strengthen the enabling environment and provide the technical support to scale up investment in resilient infrastructure. It will also ensure that new and existing infrastructure uses nature-based solutions and create positive socioeconomic impacts and green jobs. By 2025, Pillar 2 of the AAAP aims to scale up investment at national and city level for climate-resilient infrastructure in key sectors such as water, transport, energy, and waste management, and integrate resilience in up to 50% (by value) of new infrastructure projects.
The City Adaption Accelerators (CAAs) are carrying out Rapid Climate Risk Assessments in target cities, which aim to improve climate adaptation and build resilience in urban areas.
The primary purpose of the RCRAs is to inform the identification and preparation of AfDB projects.
The RCRAs will inform the development of a comprehensive climate adaptation strategy and prioritization plan and are a crucial step towards the development of the CAA for each of the target cities. The overarching objective of the CAA is to create a shared strategic framework for GCA’s engagement in climate adaptation and resilience building in urban areas. The development objective of the CAA is to support cities and countries to strengthen their urban climate adaptation and resilience outcomes through enhanced (1) understanding; (2) planning; (3) investments; and (4) governance and capacity building.
- Outputs will inform future discussions surrounding climate adaptation investments
- GCA is demonstrating its unique value add in its ability to provide technical guidance to firms towards developing well-informed analyses
- Literature review of vulnerability and adaptive capacity assessments of cities to climate change
- Scoping of past and current initiatives and key stakeholders relevant for adaptation and resilience building in cities
- City Scan: rapid review of actions around climate hazard and risk assessments and more locally focused assessments of vulnerability and adaptive capacity
- Rapid Climate Risk Assessment: an overview of the key climate hazards and associated risks; will indicate whether an in-depth climate risk assessment is required
- City Scoping: provides insight into past and current initiatives relevant for adaptation and resilience building and identifies key stakeholders and relevant initiatives
As part of the CAA, the RCRAs will contribute to the following impacts:
- Strengthened urban climate risk management in cities and their hinterlands
- Improved climate adaptive spatial planning at the municipal and regional levels
- Enhanced water resources management for more equitable access to ecosystem benefits
- Enhanced resilience, consistency, inclusiveness and integration of urban drinking water, sanitation and solid waste management services
- Improved urban liveability and public health due to a reduction in climate risks stemming from heat stress and disease
African Youth Adaptation Solutions Challenge – Cycle 1
Through the African Youth Adaptation Solutions (YouthADAPT) Challenge, the AAAP aims to inspire and support the commercialisation of climate change adaptation solutions, driven by African youth entrepreneurs. The YouthADAPT Challenge is open to solutions (products, services, tools, or ideas) targeted at climate change adaptation and increasing resilience.
Admissible solutions can represent:
- An adaptation solutions business that has not been scaled and is not in widespread use
- An existing resilience and adaptation solutions business or product
- A commercially viable means to raise awareness or scale uptake of specific adaptation solutions.
Applicants must be 18–35 years old and registered and operating in Africa. Their venture must be youth-led while delivering climate adaptation or resilience solutions addressing a real-life challenge. 50% of the finalists will be women-owned or women-led enterprises. Winners will receive a business grant of up to $100,000 and the opportunity to further develop their ventures through business support and acceleration.
The Cycle 1 (2021) winners were unveiled at COP26 in Glasgow, United Kingdom, in a ceremony held at the Africa Pavilion. They include Mumita Holdings Limited, Cameroon, Salubata Technological Innovations Limited, Nigeria, Sustainable Builders, Zambia, Global Farms and Trading Company Limited, Ghana, Miama General Dealers Limited, Zambia, Kimplanter Seedling and Nurseries Limited, Kenya, Irri Hub Ke Limited, Kenya, Soupah Farm en- Market Limited, Nigeria, Simkay Green Global Ventures, Nigeria and Bleaglee Waste Management Limited, Cameroon.
The YouthADAPT Challenge aims to support youth-led enterprises to accelerate and scale-up innovative solutions for climate adaptation and resilience that will also lead to decent jobs for youth. The solutions target key environmental, social, and economic sectors affected by climate change, with a clear value proposition to scale up for greater impact and to create specified direct jobs.
The Challenge aims to strengthen inclusive growth and broaden investment and economic opportunities for youth in Africa through entrepreneurial skills development by providing training, mentorship, and financing to youth-led businesses (50% women-owned). The first edition of the awards was launched on 06 September 2021.
- Provide a financial contribution to cover the cost of program implementation and 50% of grant funding
- Participate in project missions and field visits to review progress with select beneficiary enterprises
- Support the project team to provide clarity on climate change adaptation and resilience in the training component, including tracking the creation of adaptation jobs
- Coordinate project monitoring and evaluation.
- The most innovative youth-owned enterprises on the continent are scaled up
- The viability of selected businesses is improved, to help sustain their impact on climate change adaptation
- Inclusiveness promoted through 50% of the selected businesses being led by women.
- Young innovators and MSMEs equipped with customised business development skills and resources;
- The short-term growth of youth-owned enterprises supported, with links to private equity and loan products for longer term growth.
- Expansion of partnership, knowledge sharing, exchange and learning created through a network of youth entrepreneurs in Africa.
- Inclusive growth, investment and economic opportunities for youth are strengthened through entrepreneurial skills development;
- Adaptation, innovation and jobs integrated and for jobs;
USD 1,000,000
Rapid Climate Risk Assessments for Five African Cities (Batch II)
Currently, Africa’s infrastructure needs are around USD 130–170 billion a year, with an investment gap of over 50–60% of that amount. Making Africa’s infrastructure resilient adds only an average of 3% to total costs, but every $1 spent could yield $4 of benefits.
The Africa Infrastructure Resilience Accelerator (Pillar 2 of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP)) focuses on accelerating infrastructure resilience efforts on the continent. It will strengthen the enabling environment and provide the technical support to scale up investment in resilient infrastructure. It will also ensure that new and existing infrastructure uses nature-based solutions and create positive socioeconomic impacts and green jobs. By 2025, Pillar 2 of the AAAP aims to scale up investment at national and city level for climate-resilient infrastructure in key sectors such as water, transport, energy, and waste management, and integrate resilience in up to 50% (by value) of new infrastructure projects.
The City Adaption Accelerators (CAAs) will conduct Rapid Climate Risk Assessments (RCRAs) in target cities, which aim to improve climate adaptation and build resilience in urban areas.
The primary purpose of the RCRAs is to inform the identification and preparation of AfDB projects.
The RCRAs will inform the development of a comprehensive climate adaptation strategy and prioritization plan and are a crucial step towards the development of the CAA for each of the target cities. The overarching objective of the CAA is to create a shared strategic framework for GCA’s engagement in climate adaptation and resilience building in urban areas. The development objective of the CAA is to support cities and countries to strengthen their urban climate adaptation and resilience outcomes through enhanced (1) understanding; (2) planning; (3) investments; and (4) governance and capacity building
- informed future discussions surrounding climate adaptation investments
- technical guidance to firms towards developing well-informed analyses
- Literature review of vulnerability and adaptive capacity assessments of cities to climate change
- Scoping of past and current initiatives and key stakeholders relevant for adaptation and resilience building in cities.
- City Scan system established for a rapid review of actions around climate hazard and risk assessments and more locally focused assessments of vulnerability and adaptive capacity.
- Rapid Climate Risk Assessments prepared: readily available and accessible information on key climate hazards and associated risks; will indicate whether an in-depth climate risk assessment is required.
- City Scoping system established that provides insight into past and current initiatives relevant for adaptation and resilience building and identifies key stakeholders and relevant initiatives.
- Strengthened urban climate risk management for resilient cities;
- Equitable access to water resources that are well and sustainably managed created; Improved urban liveability and public health due to a reduction in climate risks stemming from heat stress and disease
~€45,000 per city (~€225,000 total)