AAAP in the Media
Displaying 1 - 9 of 9
Staple Crops Processing Zone (SCPZ): funding proposal to the Green Climate Fund
The target countries of Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Togo and Zambia are regions experiencing high deforestation, poor agriculture yield and increasing poverty exacerbated by climate change. Across all four countries, climate variability and change has become a major threat to sustainable development.
As part of efforts to address these challenges, the four countries are implementing national projects to establish Staple Crops Processing Zones: initiatives designed to concentrate agro-processing activities within areas of high agricultural potential to boost productivity and integrate production, processing and marketing of selected commodities. These initiatives are purposely built shared facilities, to enable agricultural producers, processors, aggregators and distributors to operate in the same vicinity to reduce transaction costs and share business development services for increased productivity and competitiveness.
Developing adequate infrastructure (energy, water, roads, ICT) in rural areas of high agricultural potential should attract investments from private agro-industrialists/entrepreneurs to contribute to the economic and social development of rural areas.
The Staple Crops Processing Zone (SCPZ) development program aims to transform agriculture production in regions experiencing high deforestation, poor agriculture yield and increasing poverty exacerbated by climate change, including the target countries of Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Togo and Zambia.
The specific objectives of SCPZ are: (i) improving access to seed capital through grants and matching grants; (ii) supporting productivity enhancement through introduction of new technologies and agricultural inputs; (iii) improving access to infrastructure by supporting investment; (iv) improving the capacity of producer cooperative through training and TA, especially for targeted women and youth groups; (v) facilitating market linkages throughout-growers’ schemes; and (vi) facilitating on-farm value addition by targeting limited value chains and linking farmers to the supply chain.
GCF financing is sought to strengthen one of the project components of SCPZ in Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Togo and Zambia.
- Through the technical assistance program, AAAPwill accelerate the mobilization of adaptation finance.
- Increased carbon sinks in soil and above-ground biomass
- Reduced carbon dioxide/other greenhouse gas emissions from farms due to efficient energy use
- Increased renewable energy production from biomass, either as a substitute for fossil fuels or as a replacement for burning of fuel wood or crop residues
- Fewer incidents of bare soils, reduced soil erosion and increased water percolation.
- Reduced emissions through low-emission energy access and power generation
- Reduced emissions due to improved waste management, including by recycling waste and use of waste in biogas systems
- Reduction of emissions from land use and deforestation, and enhancement of forest carbon stocks.
-
Increased resilience, including to extreme events such as droughts and floods, and enhanced livelihood of about 55% of highly vulnerable people and communities
-
Increased access to better health and wellbeing, and food and water security to over 100,000 beneficiaries, in addition to provision of alternative sources of energy
-
Increased resilience of ecosystems and ecosystem services in forests and savannas
USD 427 million:
- Funding proposal to GCF seeking USD 174.02 million (USD 130.02 million grant and USD 44 million loan)
- AfDB providing USD 111.2 million (USD 85.2 million loan and USD 26 million grant)
- Co-financiers:
European Union, USD 10.4 million (grant)
BOAD, USD 17.6 million (loan)
Korea Exim Bank, USD 50 million (loan)
Korea Fund, USD 5 million (grant)
Islamic Development Bank, USD 31 million (loan)
Governments of target countries, USD 28 million (counterpart financing)
Digital Climate Adaptation Solutions Training – Southern Africa
Harnessing the power of technological innovations and digitalization to improve agricultural productivity and strengthen climate resilience has been recognized as one of the potential game changers to address many of pressing climate concerns and rural transformation challenges facing Africa today.
Digital climate-informed advisory services are tools and platforms that integrate climate information into agricultural decision-making. These services range from digital mobile apps, radio, and online platforms to digitally enabled printed bulletins based on climate models and extension services that utilize climate information platforms. DCAS offers crucial opportunities to build the resilience of small-scale producers in the face of worsening climate change impacts, particularly when bundled with complementary services (such as financing, input supply, market access, insurance).
The objectives of the DCAS trainings are as follows:
- Capacity enhancement for agricultural stakeholders across Southern Africa in DCAS
- Supporting trainees to improve their confidence and capacity to design and implement DCAS projects to reach the last mile and farmers for improved food security and climate resilience
- Facilitating knowledge/experience sharing of participants on contextual issues and approaches to scale up DCAS
- Increase the knowledge of stakeholders from across Southern Africa on opportunities and new approaches for the design, mainstreaming and use of digital tools and data-enabled agriculture to combat the effects of climate change
- enhancing capacity to use digital agriculture advisory services and solutions to ensure uptake by of DCAS among stakeholders in Southern Africa
- Over 50 Participants trained in digital agriculture and digital climate adaptation solutions
- A new cohort or platform of African public officials, researchers, farmers organizations leaders and agricultural NGO focal points with improved expertise in DCAS (for subsequent experience capitalization follow up and training)
- Training evaluation assessment report
- Improved understanding / knowledge of target stakeholders in Southern Africa through training and information sharing including lessons learned on the challenges, opportunities and new approaches to the design, mainstreaming and use of DCAS and data-enabled agriculture
- Enhanced capacity of selected agricultural stakeholders in public institutions and farmers groups across Southern Africa to use digital agriculture advisory solutions, implement digital climate smart advisory solutions, and train their members/colleagues to use DCAS tools
€100,000
Winners of the 2021 YouthADAPT Challenge acquire skills to accelerate climate adaptation innovation and create green jobs
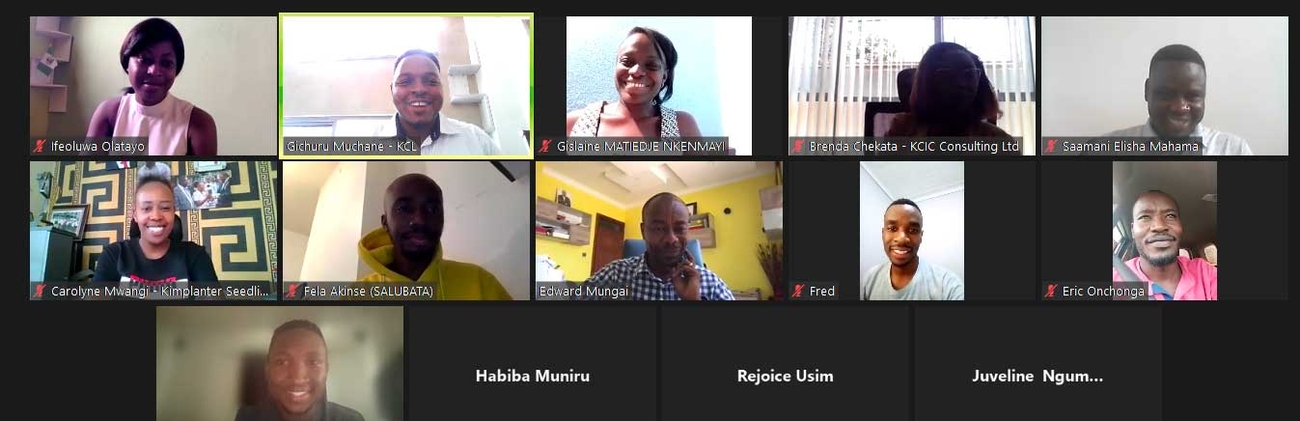
Winners of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program’s 2021 YouthADAPT Challenge have received training to equip them to produce and scale climate-related innovation and create green jobs.
The challenge competition awards business grants of up to $100,000 to young entrepreneurs and micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises in Africa to develop innovative solutions on climate adaptation and resilience.
During the three-day workshop, the 2021 winners – 10 representatives of enterprises from Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, Kenya and Zambia – received training in financial management and fundraising. Winning enterprises also received training on budgeting and cash flow projection, record keeping, and executing solid business plans.
The 10 entities are developing solutions in critical social and economic sectors affected by climate change, including agriculture; waste management; water resources and sanitation; renewable energy and energy efficiency; waste management and ecosystem restoration. Half of the enterprises are women-led businesses.
The training also instructed participants in how to position their enterprises in the market in order to offer an attractive funding proposition.
Ifeoluwa Olatayo of Soupah Farms-en-market in Nigeria, said she learned a lot during the training, including “how best to review the company’s finances and budget against unexpected shortfalls.”
Another participant, Juveline Ngum Ngwa of Mumita Holdings Limited in Cameroon, acknowledged the importance of budgeting in her enterprise’s overall success and security. “It allows us to better understand whether our business has enough revenue to pay its expenses,” Ngum Ngwa said.
Carolyne Mukuhi of Kimplanter Seedlings in Kenya said: “We look forward to this great journey towards a successful, impactful climate-adaptable business. A great world together.”
In addition to the training, the winning enterprises will be provided with mentorship and support to expand partnerships, knowledge sharing and learning through a network of young entrepreneurs in climate adaptation. The challenge also offers its winners an opportunity to participate in a 12-month business accelerator program to help them scale up their businesses, deepen their impact and create decent jobs.
An annual competition, the challenge falls under one of the pillars of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program, namely empowering youth for entrepreneurship and job creation in climate adaptation and resilience. The strategic goal is to strengthen inclusive growth and broaden investment and economic opportunities for youth in Africa by providing training, mentorship, and financing to youth-led businesses.
The Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program is a partnership between the African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation.
The African Development Bank’s contribution to the YouthAdapt Challenge was sourced from the Youth Entrepreneurship and Innovation Multi-donor Trust Fund.
AAAP Webinar: Adaptation financing must go to those who need it most
The Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP) hosted a session titled, “AAAP: Transformative Adaptation to Accelerate and Scale Climate Action” at the Virtual Gobeshona Global Conference on 29 March. The session focused on policy shifts, the enabling environment, financing, community engagement and private sector involvement to accelerate and scale climate adaptation in Africa.
The session brought together policy makers, sustainable financiers, climate resilience experts and youth advocates to discuss the latest report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) that calls for increased speed and scale in implementing adaptation actions.
“Climate change impacts are already occurring, faster and more severely than previous IPCC reports indicated,” said Dr. Rebecca Carter, the Acting Director, Climate Resilience Practice at the World Resources Institute, setting the scene for the session. “This new report makes it clear that we are already facing irreversible losses and damages to human societies and ecosystems around the world, “Carter added.
Prof. Philip Antwi-Agyei, an Associate Professor at the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology and Lead Author of IPCC’s special report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5 °C said there is the need to incorporate indigenous knowledge with scientific knowledge to develop the most effective adaptation interventions and solutions. Farmers, use indigenous knowledge to predict drought and rainfall and this knowledge is important for adaptation action, Antwo-Agyei added.
Zambia Ministry of Green Economy and Environment official Chitembo Kawimbe Chunga said adaptation should be integrated into local and national development plans.
She added that laws, policies and regulations on adaptation exist in Zambia that show where and how to adapt. Zambia is working with development partners including the African Development Bank to explore best practices for adaptation and resilience building among communities. Chunga is also the National Coordinator of both the Transforming Landscapes for Resilience and Development and the Zambia Strengthening Climate Resilience projects.
The audience followed presentations on different funding sources, including green bonds and blended finance to mobilise finance for adaptation.
According to Peter Wamicwe, a Sustainable Finance Specialist at the CGIAR, “investors need to come in in numbers and have different areas of focus. Some can focus on financial returns while others on environmental and social impact.”
Crowding in different types of investors can reduce risk and achieve impact, Wamicwe said.
AAAP – a joint initiative of the African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation – aims to mobilise $25 billion to drive adaptation across the African continent to strengthen food security for at least 10 million people, support one million youth with entrepreneurship skills and job creation, and integrate climate resilience into about $7 billion worth of infrastructure investments, among other results.
Speaking during the session, Senior Director for Africa at the Global Center on Adaptation, Prof. Anthony Nyong said that AAAP is a strong response to another crisis: climate change.
“What is crucial is that this program is an Africa-owned and Africa-led response to the continent's vulnerabilities and opportunities,” Nyong said.
In a panel discussion on the role of youth in climate adaptation, Aramide Abe, Regional Manager, Youth Jobs and Entrepreneurship, Global Center on Adaptation said youth have demonstrated ingenuity to drive adaptation solutions.
She added that youth-led start-ups on the continent are creating solutions and mobilising financing, and that “AAAP is supporting youth-led businesses on the continent to avoid the ‘valley of death’ that the majority of businesses on the continent go through due to lack of skills and funding.”
Alphaxard Gitau, a youthful dairy farmer in Kenya and market value chain specialist, said that while financing is available it needs to be structured in a way that meets the needs of youth
The panelists recommended putting adaptation finance in the hands of those who bear the brunt of climate change. They urged the use of a blend of public and private finance to target and tailor interventions and that the potential of youth should be harnessed in practical ways to effect change, and to scale and sustain adaptation actions across all spheres.
Click here to view a recording of the session
Programme for Integrated Development and Adaptation to Climate Change in the Zambezi River Basin (PIDACC Zambezi)
Zambezi River Basin, in Southern Africa Region, has the largest drainage basin (1.4 million km2) with rich variety of natural resources, covering parts of eight riparian states namely Angola, Botswana, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Despite this potential, riparian states are struggling to cope up with worsening ecological circumstances, environmental degradation, global warming, and climate change, which have created conditions of chronic vulnerability, food insecurity, and economic hardships
The objective of the project is to strengthen regional cooperation in building the resilience of the Zambezi River Basin communities to climatic and economic shocks, through promoting inclusive, transformative investments, job-creation, and ecosystem-based solutions.
- Identified climatic risks to major agricultural value chains and digital technologies that have the potential to accelerate climate adaptation in the Zambezi River Basin
- Prepared national profiles on digital adaptation in agriculture for the various countries of the Zambezi River Basin, a summary of the prevalent adaptation techniques among smallholder farmers, and the key institutional, policy and human capital challenges to digitization
- Actionable design and engagement opportunities, which will mainstream digital climate advisory services into the implementation of the PIDACC program
- Benefit about 800,000 (60% women and 10% youth) within hotspot areas, and indirectly the whole population
- Improved access to water, climate smart agricultural technologies, and community-level infrastructure for irrigation and markets
- Associated benefits include multi-sectoral utilization of shared water resources within the context of integrated land and water resources development and management, gender equality and social inclusion
- Strengthened institutional capacities and mechanisms for coordination of Basin monitoring, planning, and management
- Increased demand-driven community-level feasible climate resilient infrastructure that would support livelihoods
- Reinforced inclusive and diversified climate resilient livelihoods support through enhanced agribusiness and small & medium enterprises (SME) development
- Developed and improved livelihoods, including job creation by enhancing agribusiness through investments in water, sanitation, energy, human capital, and agriculture sectors
- Support adaptive capacity of communities with a view to avoid, reduce and reverse land degradation and effectively manage water
AfDB Investment of USD16.7 million of total USD19.4 Million
Session on Water Solutions for Climate Adaptation: lessons to scale up impactful delivery during the 2023 UN Water Conference
What: Session on Water Solutions for Climate Adaptation: lessons to scale up impactful delivery during the 2023 UN Water Conference
Who: Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program of the African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation
When: 22 March 2023, 18:30 EST
Where: United Nations Headquarters, Conference Room 9
Event description:
The Global Center on Adaptation and the African Development Bank are co-convening a high-level event at the UN 2023 Water Conference. This is the first event of its kind in nearly five decades. It places water at the center of a robust global response to climate change.
The session will dwell on the need to build resilience to climate change across Africa, developing states and vulnerable nations. It will propose proven water solutions for a warming world to advance climate adaptation and a model of delivery to achieve impact at scale. Furthermore, it will share lessons from the model of implementation in the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program.
It will also serve as a launch pad to highlight the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program’s achievements within its Water-Urban sub-program and seek its replication as a model in other regions, particularly Asia and small island states.
The high-level dialogue will feature statements and contributions from invited leaders across the fields of global politics and international finance.
African, other world leaders gather for largest summit on climate adaptation at COP26
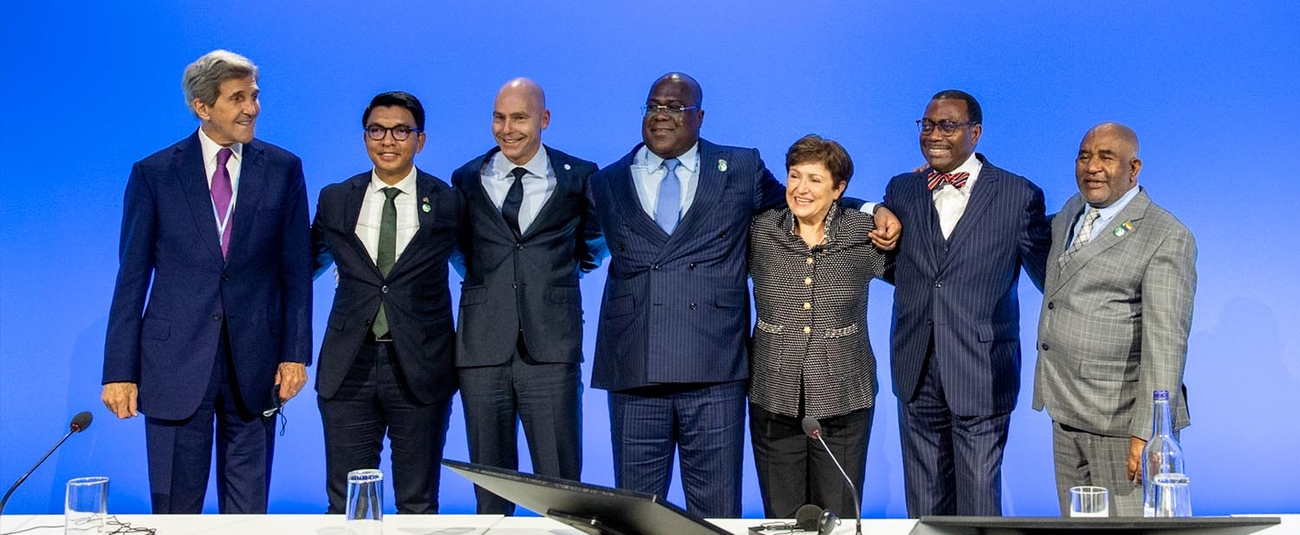

African and other global leaders came together at COP26 in Glasgow yesterday for the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Summit, the largest summit to date on climate adaptation.
The summit called for the rest of the world to ramp up its support for the African continent as it adapts to the adverse effects of climate change, including devastating human impacts in Madagascar, where 1.3 million people live under food distress following four years of no rain. Madagascar’s situation has been described as the first climate induced drought.
President Félix Tshisekedi of the Democratic Republic of Congo and Chairperson of the African Union led Tuesday’s event. He highlighted the $6 billion in financial commitments for climate adaptation that African countries had put forward in their nationally determined contributions (NDCs) and called for increased funding to produce the additional $27 billion a year that the continent requires.
President Tshisekedi said: “Adaptation finance flowing to Africa is grossly insufficient compared to the enormous resources needed for the continent to adapt to climate change. That is why African countries, working with the Global Center on Adaptation, the African Development Bank, and other partners, launched the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP). The program lies at the heart of Africa’s climate change needs. It is Africa-owned and Africa-led. African nations have endorsed it as Africa’s preferred mechanism to deploy adaptation finance for adaptation projects in Africa.”
African Development Bank Group President Dr Akinwumi A. Adesina said: “The Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program is a game changer for Africa to deliver results and impacts on adaptation, fast and at scale. It will support 30 million farmers with digital climate advisory services. The Technologies for African Agricultural Transformation program supported by the African Development Bank and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation has already delivered climate resilient technologies for 11.2 million farmers in just two years.”
He added: “With the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program, we expect to reach 40 million farmers. We plan to support farmers in producing 100 million metric tons of food, which will be enough to feed 200 million people and reduce hunger by 80%.”
Moderating summit proceedings, Patrick Verkooijen, CEO of the Global Center on Adaptation, underscored the urgent need for accelerated climate adaptation action across the continent: “COP26 must deliver on the promises of Paris,” he said. “We are failing and we are failing Africa. We must bring more ambition and more finance to help Africa adapt to the pace of a climate emergency devastating the continent with increasingly serious consequences for the world’s poorest and most vulnerable,” the GCA CEO added.
COP26 President Alok Sharma announced $197 million in new funding for adaptation for Africa from the UK government. Of this amount, $27 million will support the Africa Adaptation Accelerated Program upstream facility to deliver technical assistance and a pipeline of bankable projects. The package is expected to unlock almost $1.2 billion for climate adaptation in Africa. Sharma said there will be more to come.
US Secretary of State Antony Blinken also announced new funding for climate adaptation from the United States government. He said the US President would work with the US Congress to dedicate $3 billion annually in adaptation finance by the year 2024. This is the largest commitment ever made by the US to reduce the impact of climate change in those most endangered by it around the world.

