AAAP in the Media
Displaying 1 - 11 of 11
The Gambia: African Development Bank commits grants of $20.56 million to further upgrade Banjul port
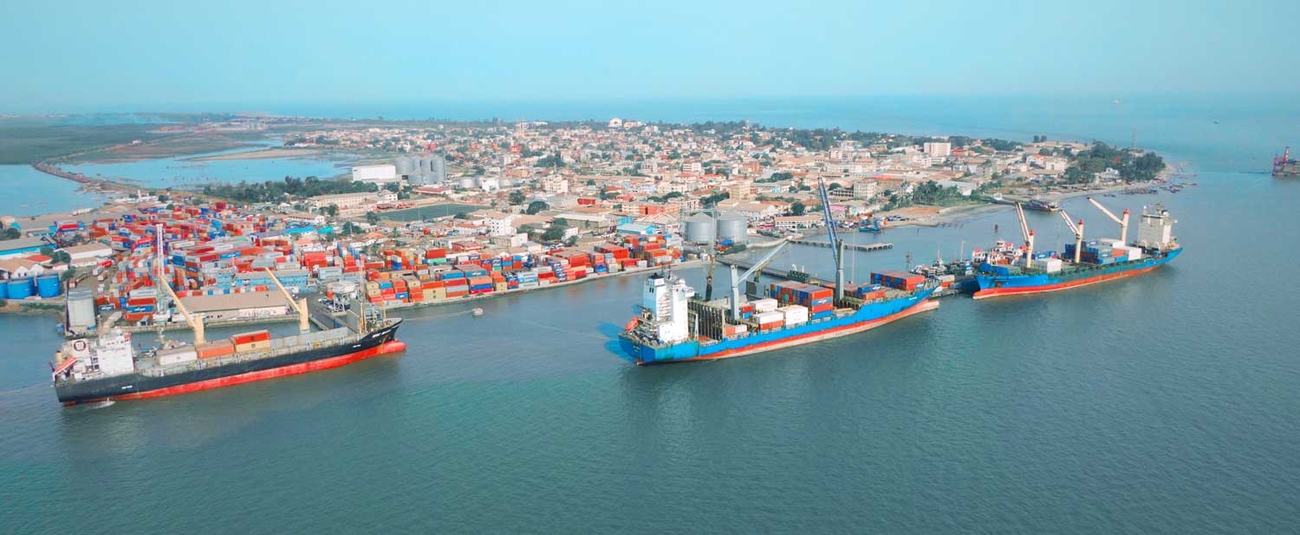

The Board of Directors of the African Development Fund (ADF), the concessional window of the African Development Bank Group, on Thursday approved grants worth $20.56 million to finance the fourth expansion of Banjul Port in The Gambia.
The funding comprises an ADF grant of $13.71 million and another $6.85 million grant from the Transition Support Facility window. The project will also receive a $450,000 grant from the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Programme (AAAP) a joint initiative of the African Development Bank and the Global Centre on Adaptation, for technical assistance to mainstream climate resilience into the expansion. AAAP will use cutting-edge climate analytics to identify and quantify the impacts of physical climate risk on the port infrastructure and provide adaptation investment options to climate-proof it.
The expansion will be financed in parallel with a private investor who will be selected competitively by the Gambian government. The World Bank and the African Development Bank supported the Banjul Port’s previous expansions.
The fourth expansion program entails an extension of the port jetty by 345 meters to accommodate up to three ships simultaneously instead of one currently. It also provides for the expansion of the container terminal area by 22,000 m2 to create space for unloading ships, replacement of a non-functioning ferry plying the Banjul and Bara crossing and widening port access roads by 3km to ease congestion. Information and communication processing systems will also be procured for efficient linkages between customs and the terminal operating system.
Upgrading the port will significantly reduce ship turnaround time and cut costly congestion and surcharges, enabling reductions in sea freight costs and demurrage payments. The works will boost the facility’s capacity to meet growing traffic and improve efficiency in operations and management as it digitizes its procedures. The introduction of green and low-carbon emission ferries will make the port infrastructure more climate-friendly and climate-resilient. The project is also expected to empower women's groups through gender-sensitive procurement and provide jobs, especially for the youth.
At the end of November 2022, the Bank Group had 12 active operations in The Gambia, valued at $166.6 million. Eighty percent (80%) of these are financed through its ADF window. The transport sector represents 55.6% of the portfolio, the largest share, followed by agriculture and rural development with 24%. Energy sector projects constitute 12% of the portfolio.
Contact:
Kwasi Kpodo, Communication and External Relations Department, African Development Bank, email: media@afdb.org(link sends e-mail)
GAMBIA National Transport Risk and Resilience Assessment
Transport systems are a key enabler for trans-sectorial development in The Gambia. The Gambia has a land area that stretches 450 km along the Gambia River, dividing the South and the North banks of the river, and is surrounded by the Senegal except for its 60 km Atlantic Ocean front. The national transport system contributes to geographical integration across the banks of the river and facilitates cross-border Nort-South traffic within Senegal. Strengthening the transport system will therefore also strengthen essential commercial links and reinforce access to social and economic facilities.
The country’s transport system relies on: (i) roads (primary inter-urban trunk roads, secondary gravel surfaces roads, urban roads mainly in the Greater Banjul area), (ii) air transport with the Banjul International Airport, and (iii) maritime and fluvial transport with the Port of Banjul and the river. The Gambia National Transport Policy (2018 – 2027) highlights the key objectives for the development of the transport sector:
- Improving access to Isolated Regions within the country,
- Addressing the mobility needs of the growing population while urbanization rate is increasing,
- Improving integration across transportation modes,
- Reestablishing the river, currently under-utilized, as a backbone component of the National Transport System,
- Overall, reinforcing safety-systems, regulations, institutional capacity fostering transport infrastructure financing and private sector involvement.
The National Transport Policy links investments in transport with other sectoral outcomes around Trade, Agriculture, Tourism, and public / private sector relations policies.
The project aims to quantify transport infrastructure adaptation needs and provide a prioritized and evidence-based list of adaptation and resilience solutions that could be integrated in the upcoming transport infrastructure development investments.
Learning from the implementation in Ghana, the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program will provide technical assistance to include climate adaptation and resilience solutions in the Integrated Transport Master Plan.
- Data collection and analysis for transport assets and existing services (including spatial data on trade flows, access to healthcare, and other social and economic factors)
- High resolution spatial analysis and climate modelling of transportation infrastructure and expected hazards in different climate scenarios
- Climate Risks assessment with direct and indirect damages caused by projected climate change. This assessment will quantify financial, economic, and social damages, including impacts on women and vulnerable communities.
- Identify, appraise, and prioritize adaptation and resilience options
- Prioritized and financed pipeline of climate resilient transport infrastructure projects in the Gambia
- Identified wins for transport sector investments that can be linked to planned investments
- A strong basis for developing tools and methodologies that can be scaled up more rapidly by other partners, including MDBs
- Assessed and quantified climate risk for transport infrastructure, mentorship, and resources to thrive
- Identified, appraised, and prioritized adaptation and resilience options
- Link the national assessment with MDB investment planning cycles and other downstream investment planning opportunities
3000,000 Euros (AAAP Upstream Facility)
African Development Bank, Global Center on Adaptation host dialogue to look at climate risks facing Gambia’s Port of Banjul Fourth Expansion Project

The African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation hosted a virtual dialogue on Monday last week to discuss climate adaptation related to the Port of Banjul Fourth Expansion Project in Gambia.
The proposed project will increase cargo handling and storage capacity of the terminal in order to cope with increasing cargo volumes and trade.
The dialogue was attended by officials from Gambia’s Port Authority, the National Environment Agency, the National Roads Authority, the Department of Fisheries, the Department of Parks and Wildlife Management, the Department of Water Resources, Maersk Line Gambia, clearing and forwarding agency HM Trading, the Great Institute and civil society. The discussions centered on the climate hazards the Port of Banjul is exposed to, and the impact of these hazards on the Port’s assets, operations, and services.
The African Development Bank and European Investment Bank are considering financing the proposed expansion of the Port of Banjul, estimated at $114 million. To this end, the African Development Bank has committed $531,275 to the Gambia Port Authority to finance a feasibility assessment and investment preparation studies to lay the groundwork for the project.
Within the framework of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP) – a partnership between the African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation (GCA), GCA is providing technical
assistance worth around €200,000 to mainstream climate resilience into the Expansion Project, utilizing cutting-edge climate analytics to identify and quantify the impacts of physical climate risk on the investment and provide adaptation investment options to climate-proof the investment.
The findings from the climate analytics revealed that climate hazards could lead to cumulative economic damage to the Port of Banjul estimated at $27 million over the next 30 years. This is about 23% of the estimated investment required to upgrade the Port of Banjul. It also emerged that the Port could lose up to 3% of its revenue annually due to the impacts of physical climate risks.
Gambia - Banjul Port 4th Expansion Project
The Banjul Port 4th Expansion Project aims to enhance port infrastructure capacity, facilitate trade facilitation and regional connectivity in the West African sub-region. This regional infrastructure project will enhance economic growth and poverty reduction whilst reducing the transaction costs associated with regional trade. The proposed Banjul Port expansion and modernization Project will also serve as a catalyst for strengthening The Gambia’s position as a major trade and transport corridor hub within the West Africa sub region.
The Port expansion aims to support the economic development of The Gambia, by enhancing its strategic position and competitiveness as a transit and trans-shipment hub in the wider West Africa region.
- Utilizing cutting-edge climate analytics to identify and quantify the impacts of physical climate risk on the investment
- Delivering high resolution climate risks assessments, adaptation and resilience investment options to climate-proof the investment against the impacts of physical climate risks
- Extension of the port jetty by 345 meters to accommodate up to three ships simultaneously instead of one currently
- Provide for the expansion of the container terminal area by 22,000 m2 to create space for unloading ships
- Replacement of a non-functioning ferry plying the Banjul and Bara crossing and widening port access roads by 3km to ease congestion
- Complete and widen the Bund Road access to facilitate traffic flow in and around the access roads leading to the Port of Banjul
- Relocate its current Head Office Complex away from the main operational zone
- Construct a new Container Terminal
- Procurement of Information and communication processing systems for efficient linkages between customs and the terminal operating system
- Significantly reduced ship turnaround time and cut costly congestion and surcharges, enabling reductions in sea freight costs and demurrage payments
- Boost the facility’s capacity to meet growing traffic and improve efficiency in operations and management as it digitizes its procedures
- Climate-friendly and climate-resilient port infrastructure by introduction of green and low-carbon emission ferries
- Empower women's groups through gender-sensitive procurement and provide jobs, especially for the youth
AfDB Investment of USD 44.5 Million of total USD 115 Million
Reinforcing Resilience to Food and Nutrition Insecurity in the Sahel (P2-P2RS)
The Sahel, which lies between the Sahara Desert to the north and tropical savannas to the south, is one of the largest semi-arid/arid sub-regions globally. As such, the region is highly vulnerable to climate change and other uncertainties. The impacts of climate change may have critical socio-economic consequences for the Sahel, including poor agricultural yields, increased frequency of natural disasters. Already, the number of people in the Sahel suffering from chronic food and nutrition insecurity, poverty and vulnerability to the effects of climate change is rising steadily.
A lasting solution to food and nutrition insecurity in the Sahel requires building resilience to climate change, long-term agricultural sector financing and developing trade and regional integration. Sustained, longer-term investments in household resilience can significantly reduce the cost of emergency assistance, ultimately breaking the cycle of recurring famine. This is the most cost-effective intervention option which meets the basic needs and preserves the dignity of the populations of the Sahel. This idea is central to the Programme to Build Resilience to Food and Nutrition Insecurity in the Sahel (P2RS)
The overall objective of the P2-P2RS is to contribute to the substantial improvement of the living conditions and the food and nutritional security of the populations of the Sahel region.
Specifically, the program aims to i) strengthen the resilience to climate change of agro-sylvo-pastoral producers, including through promotion of climate-smart agricultural technologies in the Sahel and the development of climate intelligent villages; ii) develop the agro-sylvo-pastoral value chains, including through the development and improvement of hydro, meteorology and climate services; and iii) support regional institutions (CILSS, APGMV, CCRS) to strengthen adaptive capacity in the Sahel.
- Design digital adaptation solutions (Digital Climate Advisory Services, DCAS) for the Sahel context
- Investment readiness and infrastructure, institutional and farmer capacity needs for DCAS
- Feasibility study to integrate DCAS into agricultural extension and agrometeorological advisory to smallholder farmers and pastoralists
- 1 million rural households have access to digital or data-enabled climate-smart technologies
- 500,000 smallholders have adopted adaptation practices
- 5 million smallholders have access to climate services;
- Development and improvement of hydro, meteorology and climate services
- The development of climate-intelligent villages
- Promotion of climate-smart agricultural technologies in the Sahel
- Resilience to food and nutrition security built for the targeted populations
USD 300 million
Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program showcases African youths driving climate innovation

The Africa Adaptation Acceleration program (AAAP) – a joint initiative of the African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation – recently showcased its initiative to harness the dynamism and leadership of Africa’s youth to drive climate adaption innovation.
On the side-lines of the recent 3rd Gobeshona Global Conference(link is external), AAAP brought together participants in its YouthADAPT program to share their experiences with the program as well as strategies to scale up youth-led approaches to adaptation
In his opening remarks, Dr. Kevin Kariuki, African Development Bank Vice President for Power, Energy, and Climate & Green Growth underscored young people’s integral role in Africa’s sustainable development.
“Youth form the backbone of Africa’s population, constituting over 60% of the population. The continent’s sustainable development hinges on harnessing this demographic dividend,” Kariuki said. “The AAAP, through its YouthADAPT pillar, has so far supported 35 youth-led enterprises in 14 African countries with $3.5 million to drive climate actions in sectors such as agriculture, waste management, renewable energy, water and sanitation,” Kariuki added. YouthADAPT is one of AAAPs four pillars for accelerating climate adaptation.
Caroline Mukuhi Mwangi, founder of Kimplanter Seedling(link is external) and Nurseries Limited, said her company was already seeing the benefits of participation in the program. Kimplanter provides drought resistant seedlings that boost food production and food security in Kenya.
Mwangi said, “We have ventured into new markets in semi-arid regions and expanded our seedling varieties, increasing our revenue by 36% as a result of AAAP support. Our customer base has also grown from 8,000 to 16,000 farmers and we have increased our staff from 17 to 32, all of whom are women or youth.”
Aramide Abe, the Program Lead of Jobs for Youth & Entrepreneurship at the Global Center on Adaptation(link is external) confirmed that participating enterprises have already begun to show results. She said some have seen revenues rise by up to 50 percent. A fifth have ventured into new markets and have raised over $106,000 in additional funding from different sources.
Juveline Ngum, the founder of Bleaglee Waste Management Limited, a Cameroon-based start-up company using drone technology to tackle waste disposal, also stressed the benefits of participating in YouthADAPT.
“We have expanded our waste disposal management solution from west Cameroon into Douala, effectively using drones to detect clogged drainages and utilizing data for demand driven waste management,” Ngum said. Now, we aim to expand across national borders into Dakar, Senegal.”
Noël N'guessan’s Cote d’Ivoire-based company, LONO(link is external) – a winner of the 2022 YouthADAPT challenge – has patented technology for the production of organic fertilizer. The company has also introduced modular and mobile bio digesters for the agri-food sector. Biodigesters use microbes and other bacteria to break down organic waste including fat, greases, and even animal manure.
Still, Nguessan said challenges remained. “The cost of prototyping hardware equipment can be prohibitively high, resulting in lengthy project development cycles, “he said. He pointed to financial management training as vital for youth-led businesses.
The session also featured presentations by African Development Bank partners and other global organizations that have rolled out similar initiatives to YouthAdapt.
Sandra Simbiri, Program Specialist at UNICEF’s Generation Unlimited(link is external), said:
“Supporting entrepreneurs through STEM principles is key to preparing the young for technological innovations.”
Alfred Asiko, Senior Market Engagement Manager for the ClimateTech Programme at GSMA(link is external), a mobile technology association, said it has played a role in empowering youth to deploy such technologies as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence and blockchain to tackle climate challenges.
“Through our innovation fund, we offer grants to climate startups, with a focus on supporting resilient solutions that utilize frontier technologies. We also provide skills development and training to help entrepreneurs succeed in scaling their innovations,” Asiko said.
He said that venture capital (VCs) firms had a critical role to play. ”We need to see more VCs stepping up and taking over from development finance institutions (DFIs) in providing financing and support to youth-led businesses,” he added.
YouthADAPT targets reaching 10, 000 African youth-led enterprises by 2025, promoting innovation and inclusive growth for young people in climate resilient jobs and through youth enterprise development. The AAAP’s other three pillars are Climate-Smart Digital Technologies for Agriculture and Food Security; the African Infrastructure Resilience Accelerator and the Innovative Financial Initiatives for Africa
The third annual Gobeshona Global Conference, organized by the International Centre for Climate Change and Development, took place virtually from 10-16 March 2023. It focused on monitoring Locally- Led Adaptation (LLA) and resilience.
20 young African entrepreneurs bag $100,000 each to boost their climate adaptation businesses
Programme Showcases African youths driving climate novelty
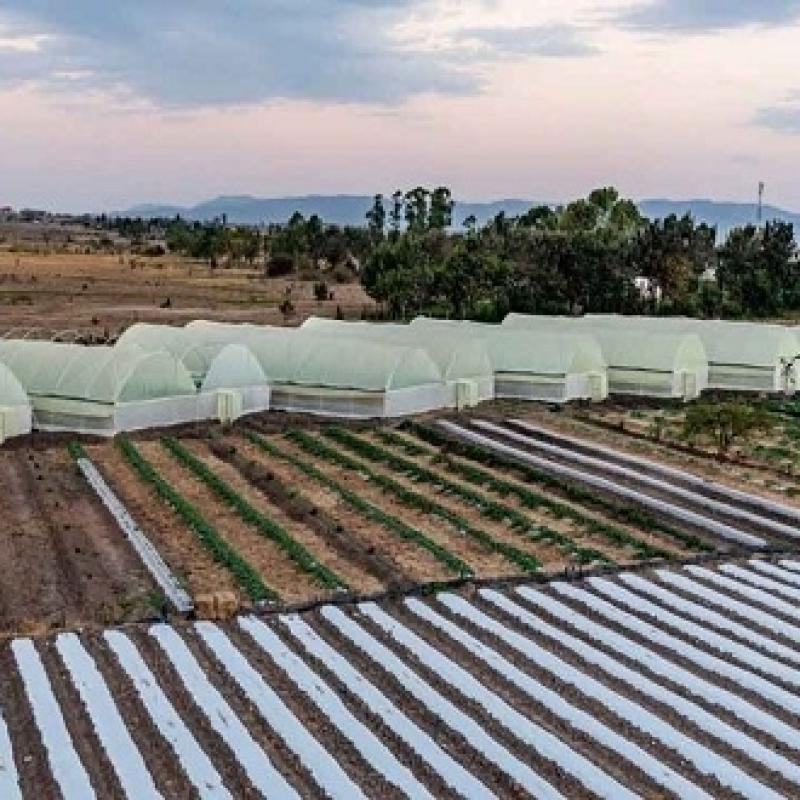
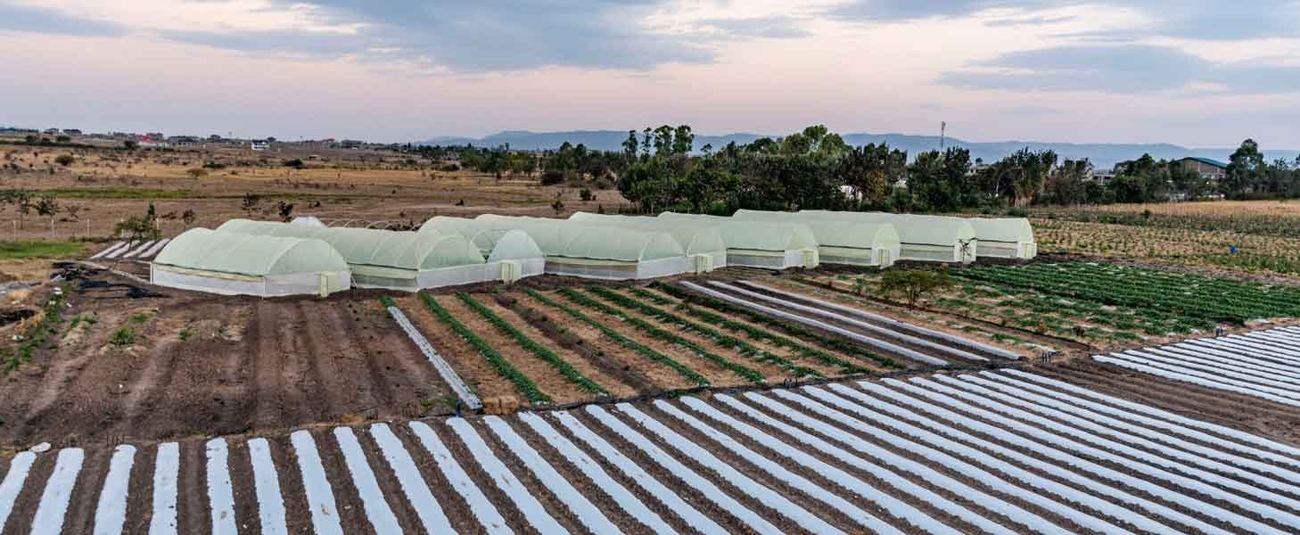
African Development Bank-supported Cameroonian start-up provides low-cost greenhouses, sustainable solutions to boost livelihoods
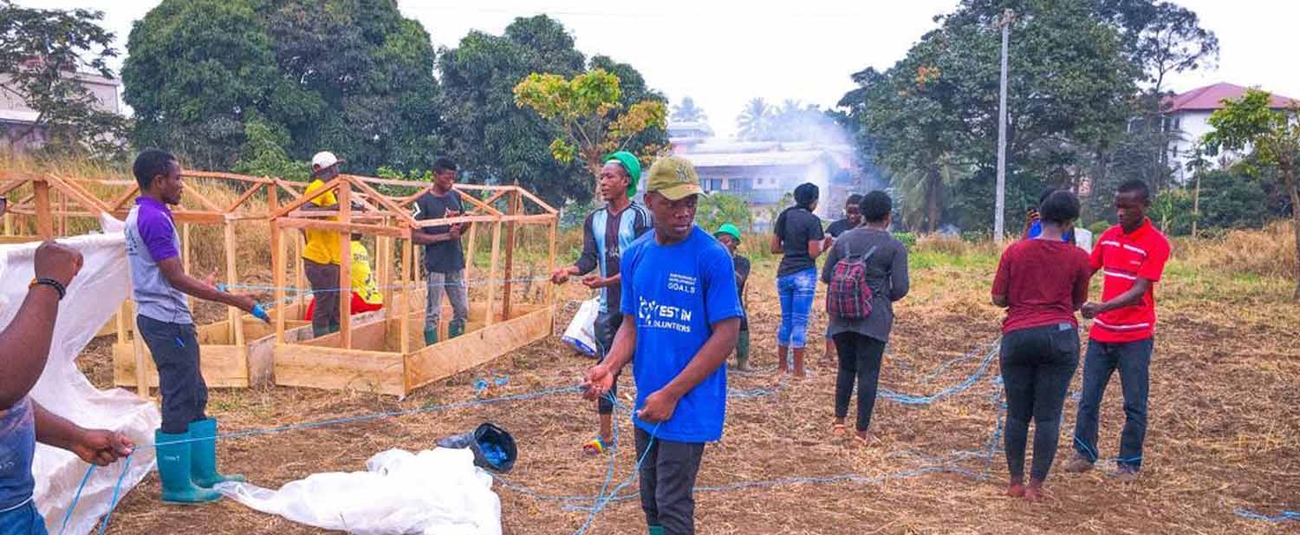

A youth-led agricultural start-up is supporting farmers in climate-vulnerable Cameroon to produce crops sustainably year-round using low-cost greenhouses and solar-powered irrigation.
Mumita Holdings is a beneficiary of the African Development Bank’s investment into the channelling of private capital to young African entrepreneurs, who are seen as critical to unlocking innovative solutions to climate change and the continent’s energy transition.
Tackling climate change is an urgent global priority and perhaps more critical in Africa. The continent is home to nine of the ten countries most vulnerable to climate change worldwide. In response to this pressing challenge, the African Development Bank Group has committed to mobilize $25 billion in climate finance by 2025.
Mumita’s CEO, Matiedje Nkenmayi Gislaine, was among 15 winners of the 2021 African Youth Adaptation (YouthADAPT) Solutions Challenge, organized annually by the bank and the Global Centre on Adaptation as part of their joint Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP). Mumita received a development grant of $100,000 and participated in a 12-month business accelerator program to scale up the business, create more jobs and expand its impact.
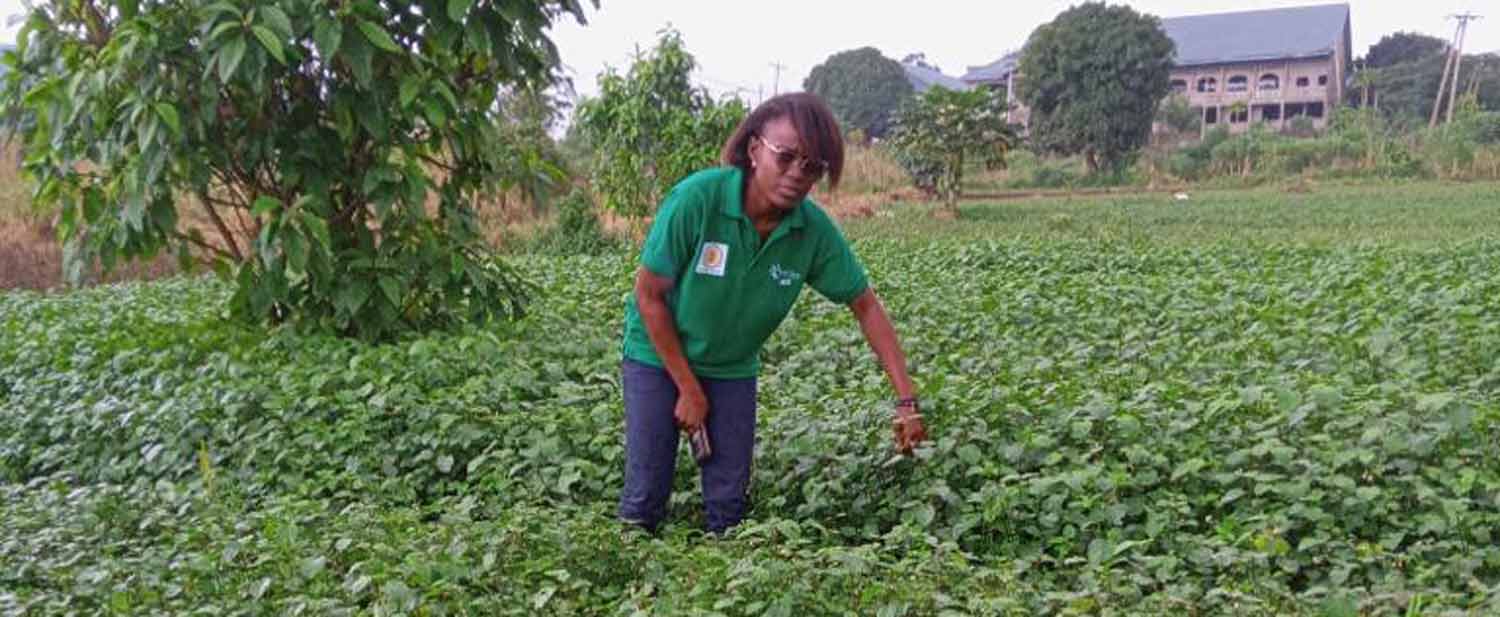

Mumita supports farmers in climate-vulnerable Cameroon to produce crops sustainably year-round using low-cost greenhouses and solar-powered irrigation. The firm mainly targets rural women farmers that cultivate African indigenous green leafy vegetables such as ndole and eru, or bitter leaf and wild spinach. These vegetables are an important source of revenue and nutrition. Demand for these leafy greens and tubers has increased, but production has not kept pace. At the same time, climate change impacts, including erratic rainfall patterns, have also hurt yields.
Mumita provides low-cost greenhouses that facilitate the year-round cultivation of vegetables. The greenhouses are made from materials such as wood, cement and mesh that are sourced locally from farmers. This has reduced the cost of building a greenhouse from $2,500 to about $500. The cost reduction has boosted yields and earnings. Mumita has also partnered with French company ASAP PROS1 to brand vegetable packaging with its own label.
For Nkenmayi, winning the YouthADAPT Challenge translated into multiple benefits for her business and rural communities in Cameroon.
“YouthADAPT funding has enabled us to construct two steel greenhouses in two cooperatives, as well as 10 wooden greenhouses, which has helped improve the capacity of vegetable nurseries from 1,500 seedlings to 25,000 seedlings,” Nkemanyi said. “We have also set up a processing unit, which can transform 1 tonne of dried vegetables per week, up from an initial 100 kg. We have also trained over 2,300 farmers in 10 villages in the southwest region, Mbanga in the Littoral region, Bamenda in the Northwest, and Boumnybel,” she added.
Currently, Mumita can supply indigenous dried vegetables in most of Cameroon but aims to expand coverage within and into other parts of sub-Saharan Africa.
The African Development Bank recognises the critical role of private investment, in closing financing gaps to drive green growth and build climate resilience. In line with this commitment, the bank is focusing on Mobilizing Private Sector Financing for Climate and Green Growth in Africa as the central theme of its 2023 Annual Meetings scheduled for 22-26 May in Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt
AAAP webinar: Innovation essential for climate-smart future, but it's not enough

The 2022 United Nations Climate Change Conference, COP27, is dubbed ‘African COP’ as the impact of climate change on African countries will be a key theme of discussions. Agriculture and food systems will also be a critical focus of COP27, with Saturday, 12 November, dedicated to both themes, in addition to adaptation. Also high on the climate agenda is the role of the youth, as 10 November is dedicated to their participation.
Ahead of COP27 and in line with their commitment to this youth agenda, the African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation hosted a webinar to examine ways to make agriculture attractive to the youth.
The webinar titled, Are Climate-Smart and Digital Agriculture Solutions the Silver Bullet to Attract Youth, highlighted the potential of climate-smart and digital agriculture in attracting young people and thereby rejuvenating an aging global agricultural sector.
Dr. Kevin Kariuki, African Development Bank’s Vice President for Power Energy, Climate and Green Growth, pointed out the challenges the agriculture sector faces due to the changing climate change.
“Agriculture across most of sub-Saharan Africa is still predominantly rain-fed and therefore extremely vulnerable to both short-term fluctuations and long-term changes in climate conditions. It is the most exposed sector with estimates indicating that climate change will cause a decrease in yields of 8 – 22% for Africa’s rain-fed staple crops over the next 20 years,” Kariuki said.
Dr. Beth Dunford, African Development Bank’s Vice President for Agriculture, Human and Social Development, noted that while agriculture holds tremendous potential for job creation in Africa, its current traditional form is not attractive to young people for various reasons, including negative perceptions.
“Who wants to wear overalls, dig the field with a hoe or drive a tractor when we can do it in a suit and dust coat, right? However, technology makes agriculture cool enough to motivate them to use tech-enabled enterprises to be part of agricultural value chains,” Dunford said.
Prof. Anthony Nyong, Senior Director for Africa at the Global Centre on Adaptation, said: “There is a gap in the agriculture sector in Africa, and that is in the use of digital solutions.”
AAAP’s Climate Smart Digital Technologies for Agriculture and Food Security Pillar is scaling up access to digital technologies and associated data-driven agricultural and financial services for at least 30 million African farmers.
In the African Development Bank’s Program to Build Resilience for Food and Nutrition Security in the Horn of Africa (BREFONS), currently ongoing in Djibouti, Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, South Sudan, and Sudan, the AAAP is facilitating the integration of climate-smart digital technologies for adaptation and resilience.
“The project will increase the productivity of crops and livestock by 30%, reaching about 1.3 million farmers and pastoralists using climate services such as index insurance. About 55,000 additional jobs will be created for youth and women,” said Oluyede Ajayi, Africa Program Lead, Food Security and Rural Well Being, Global Centre on Adaptation.
Panelists said the youth must utilize their digital skills to accelerate the transformation of the agricultural sector, which forms the central pillar of Africa’s economy. They urged participants to contribute to solutions that enhance market linkages to promote agribusiness.
“Africa’s significant youth population faces rising unemployment with myriad negative consequences. These challenges are further exacerbated by climate shocks, skill gaps & limited preparedness to address the effects of climate change,” said Andre-Marie Taptue, Principal Economist at the African Development Bank's Jobs for Youth program.
AAAP’s YouthAdapt program promotes sustainable job creation through entrepreneurship in climate adaptation and resilience in Africa by unlocking $3 billion in credit for adaptation action.
Last year, the first set of ten young African entrepreneurs and Micro, Small, and Medium-sized Enterprises offering innovative solutions and business ideas that can drive climate change adaptation and resilience were awarded at COP26 in Glasgow. This year the Africa Youth Adaptation Competition 20 enterprises across Africa will each receive up to $100,000 in addition to mentorship and coaching to support their climate change adaptation innovation.
Panelists included Claude Migisha from the African Development Bank, Dr. Fleur Wouterse, and Aramide Abe from the Global Center of Adaptation. They shared their views on how AAAP was shaping and adding value to the Bank Digital Agriculture Flagship program, ways to accelerate investor engagement in agriculture adaptation, and how the YouthADAPT was moving the needle on entrepreneurship, unlocking finance and job creation.
Gislaine Matiedje Nkenmayi from Mumita Holdings, a recipient of the 2021 YouthADAPT Challenge award, shared her experience on how the $100,000 grant transformed her enterprise.
“With the grant, we were able to reach out to more than 10 cooperatives with a total of 257 smallholder farmers, to whom we offer free advisory services, low-cost greenhouses and solar-powered irrigation systems. We have been able to expand production from 100kg to 1000kg of fresh vegetables weekly,” Nkenmayi said.
In her concluding remarks, Edith Ofwona Adera, Principal Regional Climate Change Officer and AAAP coordinator at the Bank stressed the need to strengthen adaptation and resilience measures and expedite mainstreaming climate adaptation for transformation at scale. She called for the engagement of the private sector, given the role they can play in adapting to climate change, financing adaptation, and supporting others through products and services for resilience.
Winners of the 2021 YouthADAPT Challenge acquire skills to accelerate climate adaptation innovation and create green jobs
Winners of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program’s 2021 YouthADAPT Challenge have received training to equip them to produce and scale climate-related innovation and create green jobs.
The challenge competition awards business grants of up to $100,000 to young entrepreneurs and micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises in Africa to develop innovative solutions on climate adaptation and resilience.
During the three-day workshop, the 2021 winners – 10 representatives of enterprises from Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, Kenya and Zambia – received training in financial management and fundraising. Winning enterprises also received training on budgeting and cash flow projection, record keeping, and executing solid business plans.
The 10 entities are developing solutions in critical social and economic sectors affected by climate change, including agriculture; waste management; water resources and sanitation; renewable energy and energy efficiency; waste management and ecosystem restoration. Half of the enterprises are women-led businesses.
The training also instructed participants in how to position their enterprises in the market in order to offer an attractive funding proposition.
Ifeoluwa Olatayo of Soupah Farms-en-market in Nigeria, said she learned a lot during the training, including “how best to review the company’s finances and budget against unexpected shortfalls.”
Another participant, Juveline Ngum Ngwa of Mumita Holdings Limited in Cameroon, acknowledged the importance of budgeting in her enterprise’s overall success and security. “It allows us to better understand whether our business has enough revenue to pay its expenses,” Ngum Ngwa said.
Carolyne Mukuhi of Kimplanter Seedlings in Kenya said: “We look forward to this great journey towards a successful, impactful climate-adaptable business. A great world together.”
In addition to the training, the winning enterprises will be provided with mentorship and support to expand partnerships, knowledge sharing and learning through a network of young entrepreneurs in climate adaptation. The challenge also offers its winners an opportunity to participate in a 12-month business accelerator program to help them scale up their businesses, deepen their impact and create decent jobs.
An annual competition, the challenge falls under one of the pillars of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program, namely empowering youth for entrepreneurship and job creation in climate adaptation and resilience. The strategic goal is to strengthen inclusive growth and broaden investment and economic opportunities for youth in Africa by providing training, mentorship, and financing to youth-led businesses.
The Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program is a partnership between the African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation.
The African Development Bank’s contribution to the YouthAdapt Challenge was sourced from the Youth Entrepreneurship and Innovation Multi-donor Trust Fund.