AAAP in the Media
Displaying 1 - 8 of 8
Global Center on Adaptation, AfDB host regional forum on the future of resilient food systems in Africa
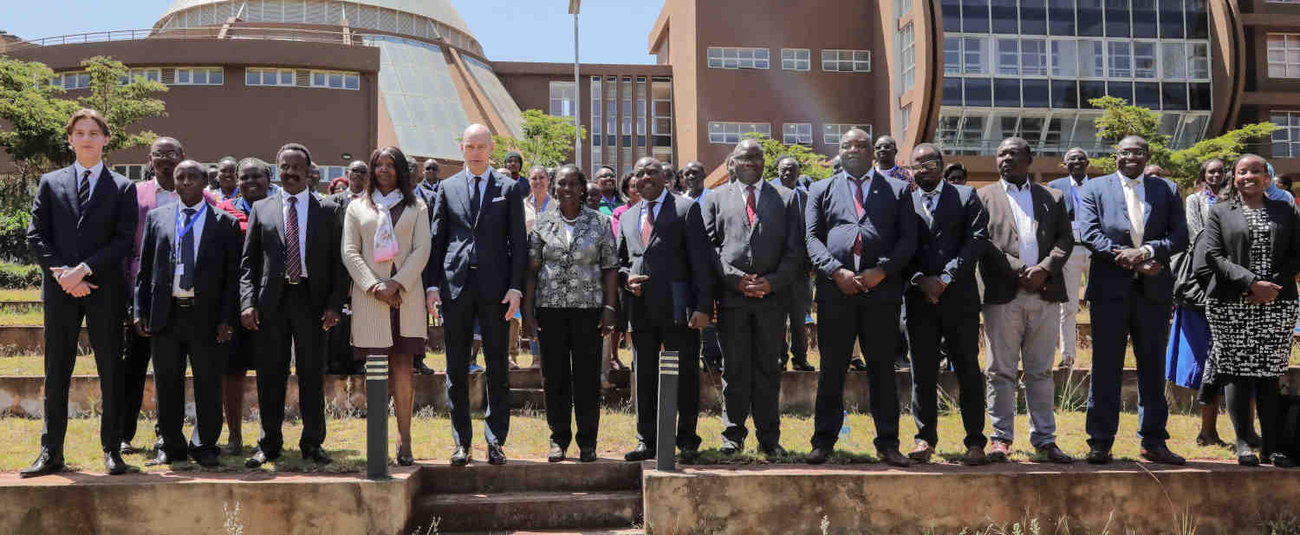

The Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) in collaboration with the African Development Bank and the Wangari Mathai Institute have concluded a three-day regional forum on the future of resilient food systems in Africa.
The Forum, called the Future of Resilient Food Systems in Africa – AAAP Digital Solutions for a Changing Climate provided training aimed at strengthening the capacity of stakeholders from across Eastern Africa to design and implement solutions to improve food security and climate resilience and to facilitate knowledge sharing among farmers on approaches to scale up the use of Digital climate-informed advisory services, or DCAS.
Digital climate-informed advisory services are tools and platforms that integrate climate information into agricultural decision-making. These services range from digital mobile apps, radio, and online platforms to digitally enabled printed bulletins based on climate models and extension services that utilize climate information platforms.
DCAS offers crucial opportunities to build the resilience of small-scale producers in the face of worsening climate change impacts. From seasonal forecasts to pest advisories, effectively designed services provide producers with the resources to adapt to climate shocks and plan for new climate conditions.
Globally, more than 300 million small-scale agricultural producers have limited or no access to such services because service provision is still fragmented, unsustainable beyond project cycles, and not reaching the last mile.
Speaking at the opening ceremony of the forum, Professor Patrick Verkooijen, CEO of Global Center on Adaptation called for urgent financial support to put Africa on the path of food sovereignty.
“Africa needs urgent support to scale up the implementation of adaptation solutions that are already yielding good results for irrigation, developing drought-resistant seeds, crops and livestock diversification, “ he said.
“Through the African Adaptation Acceleration Programme, AAAP, we are rolling out a $350 million project to build resilience for food and nutrition security in the Horn of Africa towards mobilising new digital climate technology for market information, insurance products, financial services that can and must be tailored to smallholder farmers’ needs”, he added.
Speaking on behalf of the African Development Bank’s East Africa Regional Director General, Nnenna Nwabufo, Dr Pascal Sanginga, Regional Sector Manager for Agriculture and Agro-Industries noted that the forum was timely, coming hot on the heels of the recently concluded Dakar 2 Feed Africa-Food Sovereignty and Resilience summit , organised by the African Development Bank.
“The Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP) is already contributing to closing Africa’s adaptation gap by supporting African countries to make a transformational shift in their development pathways by putting climate adaptation and resilience at the center of their policies, programs, and institutions. There is no doubt that AAAP will be a strong component of the Country Food and Agricultural Delivery Compacts to accelerate the transformation of Africa’s food systems and build a more resilient Africa”, he said.
Professor Stephen Kiama Gitahi, Vice Chancellor of the University of Nairobi, reiterated the relevance of the forum pointing out that 70% of the population in Eastern Africa live in rural areas and depend on agriculture for their livelihoods. He encouraged the trainers to simplify the modules in a manner that removes the fear for technology and accelerate adaptation for rural farmers. Citing the legacy of late Professor Wangari Maathai he stated:
“We acknowledge that gaps exist on climate adaptation in the rural communities and those can be smartly bridged with the use of digital smart agriculture and climate innovations to create great conservation impact in our region.”
The forum brought together stakeholders from ministries of agriculture, related government agencies, public research institutions, farmer organizations, universities and non-profit organizations working on climate adaptation for food security in Eastern Africa. These included participants from Djibouti, Eritrea, South Sudan, Burundi, Rwanda, Mauritius, Tanzania, Seychelles, Sudan, Ethiopia, Rwanda and Kenya.
About Global Center on Adaptation
The Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) is an international organization which works as a solutions broker to accelerate action and support for adaptation solutions, from the international to the local, in partnership with the public and private sector. Founded in 2018, GCA operates from its headquarters in the largest floating office in the world, located in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. GCA has a worldwide network of regional offices in Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire; Dhaka, Bangladesh and Beijing, China.
About the Wangari Maathai Institute, University of Nairobi
The Wangari Maathai Institute (WMI) for peace and environmental studies is a global centre for teaching and research on environmental management, governance, peace and conflicts and the nexus between peace and democracy. The centre was founded in 2009 with the support of the Government of Kenya (GoK), the African Union(AU) and the African Development Bank(AfDB) to celebrate and immortalize the work of the late Nobel Laurete
Prof.Wangari Maathai who was a global champion on environmental conservation and governance. The centre trains future leaders and Champions for environment. The Centre is located in the serene environment in Upper Kabete suburb of Nairobi City.
20 young African entrepreneurs bag $100,000 each to boost their climate adaptation businesses
UK gives Africa $197 million to mitigate climate change
EAC Railway Rehabilitation Support Project - Refurbishment of Kampala-Malaba Meter-Gauge-Railway
Railway lines are critical to opening up the heartland of Africa, where there is immense agricultural and economic potential. The Kampala-Malaba Meter Gauge Railway (MGR) in Uganda is part of the East African Community’s Northern Corridor. It links Ugandan capital Kampala to Kenyan coastal city Mombasa. The East African Community Railway Rehabilitation Support Project will strengthen rail services and lower transport costs in a region rich in agricultural land, manufacturing and minerals and petroleum production. The work will consist of the immediate rehabilitation of 265km of MGR railway tracks between Malaba and Mukono. This includes the line to Jinja Pier and Port Bell on Lake Victoria.
The objective of the project is to improve rail transport services on the Northern Corridor and to lower transportation costs to enhance trade competitiveness for Uganda and the EAC region. The project will add to the transport infrastructure stock in the East African Community (EAC) region and in particular Uganda to support production in agro-processing, mining, timber, petroleum, and manufacturing industries.
The East African Community Railway Rehabilitation Support Project also advances the African Union’s Agenda 2063 and three of the African Development Bank’s High 5 operational priorities: Integrate Africa, Industrialise Africa and Improve the Quality of Life for the People of Africa.
- Conduct high-resolution, asset-level climate risk and vulnerability assessment to quantify key climate risk hazards and associated risks to the planned railway line.
- Adaptation and resilience investment options appraisal to identify and appraise adaptation and resilience options, focusing on integration of nature-based solutions (NBS)
- Structuring the NBS investment options depending on the scale of NBS options in partnership with the World Wide Fund
- Capacity enhancement for resilient railway project planning and management under the AAAP Masterclass on Climate Resilient infrastructure in partnership with University of Nairobi
- Improve maritime transportation on Lake Victoria through the acquisition of new wagon ferries and construction of spurs to Port Bell and Jinja port
- Promote trade, spur industrial development and create jobs
- Stimulate growth and enhance regional integration in Eastern Africa
- Design for the Kampala multimodal hub and refurbishment of Kampala-Namanve and Tororo-Malaba sections totalling 28 kilometres.
- Directly benefit close to 1.2 million people with 40% being women
- Deepened trade and transforming East Africa into a globally competitive upper-middle-income region
- Support production in agro-processing, mining, timber, petroleum, and manufacturing industries in Uganda
- Reduced travel cost and improved on road traffic safety
- Efficient and effective transportation system
- Reduce transport GHG emissions and road maintenance costs
- Create jobs for both men and women
- Build capacity of Uganda Railway Authority
AfDB investment of USD 290.6 million, of a total of USD 397.7 million
Uganda - Water Supply and Sanitation Programme Phase III (WSSP III)
Uganda recognizes the cross-benefits of access to safe drinking water and improved sanitation and has made substantial access increase over the last decades. This has raised coverage to safe drinking water from 42% in 1991 to 64 % in 2014 and access to adequate sanitation from 51% in 2001 to 74.6% in 2014. The current coverage of water supply and sanitation in Uganda’s Central Region remains low and is constrained by the rapid population growth and increased urbanization (5.5%) linked to proximity to Kampala, the capital city.
The objective of the project is to improve the health and productivity of Uganda’s population through provision of safe water and sanitation services to target a population of 1.43m people (51.4 % women)
- Identify WSS schemes with significant capital investments that are situated in regions that are highly exposed to climate-related risks such as floods
- Carry out climate risk assessment for a select number of schemes that are highly ex-posed to floods and provide technical assistance on increasing the flood resilience of these water service provision assets including design and operation and maintenance
- Provide technical assistance to design climate related risk reduction measures through a combination of grey and green investments
- To understand the how the regional hydrological system influence on local hydrological system, a rapid desk assessment – based on globally available data - will be undertaken to identify climate hotspots. This scan will also identify existing good practices in Uganda
- Collaborate closely with focal agencies of the client government to build their capacity
- Build resilience into infrastructure projects and assets, prioritizing nature-based solutions by understanding climate risks to WSSS service delivery assets and increase flood resilience of these assets
- 5 large rural gravity-flow water system schemes (4 new and 1 rehabilitated) covering a target population of about 170,000 people
- 6 urban water supply schemes in secondary cities, targeting a population of 500,000 people
- 20 solar powered rural water supply schemes for high yielding boreholes for small communities of 1,000 - 2,000 households each
- Improved water resources management, environmental protection and catchment management
- Implementation of rural water supply infrastructure, including large gravity flow schemes (LGFS) and solar powered water schemes
- Promotion and implementation of sanitation and hygiene development
- Construction of water for production storage infrastructure comprising of earth dams and valley tanks
- Implement catchment management and environmental protection activities
USD 60 Million
African Development Bank Group approves $379.6 million Desert to Power financing facility for the G5 Sahel countries

The Board of Directors of the African Development Bank Group has approved the Desert to Power G5 Sahel Financing Facility, covering Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania, and Niger. The Bank envisages to commit up to $379.6 million in financing and technical assistance for the facility over the next seven years.
The Desert to Power G5 Financing Facility aims to assist the G5 Sahel countries to adopt a low-emission power generation pathway by making use of the region’s abundant solar potential. The facility will focus on utility-scale solar generation through independent power producers and energy storage solutions. These investments will be backed by a technical assistance component to enhance implementation capacity, strengthen the enabling environment for private sector investments, and ensure gender and climate mainstreaming.
The facility is expected to result in 500 MW of additional solar generation capacity and facilitate electricity access to some 695,000 households. Over the lifespan of the project, it is expected to reduce carbon emissions by over 14.4 million tons of carbon dioxide equivalent.
The Board of the Green Climate Fund approved $150 million in concessional resources in October 2021 for the facility, which is expected to leverage around $437 million in additional financing from other development finance institutions, commercial banks and private sector developers. The Global Center on Adaptation is providing technical assistance to strengthen adaptation and resilience measures undertaken in the facility as part of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program in partnership with the African Development Bank.
The African Development Bank’s Vice President for Power, Energy, Climate Change and Green Growth, Dr. Kevin Kariuki said: “The innovative blended finance approach of the Desert to Power G5 Sahel Facility will de-risk, and therefore catalyze, private sector investment in solar power generation in the region. This will lead to transformational energy generation and bridge the energy access deficit in some of Africa’s most fragile countries.”
Dr. Daniel Schroth, the Bank’s Acting Director for Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency, added: “The facility will also support the integration of larger shares of variable renewables in the region’s power systems, notably through the deployment of innovative battery storage solutions and grid investments.”
The facility will be implemented as part of the broader Desert to Power initiative, a flagship program led by the African Development Bank. The objective is to light up and power the Sahel region by adding 10 GW of solar generation capacity and providing electricity to around 250 million people in the 11 Sahelian countries by 2030.
.embed-container { position: relative; padding-bottom: 56.25%; height: 0; overflow: hidden; max-width: 100%; } .embed-container iframe, .embed-container object, .embed-container embed { position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; }
.embed-container { position: relative; padding-bottom: 56.25%; height: 0; overflow: hidden; max-width: 100%; } .embed-container iframe, .embed-container object, .embed-container embed { position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; }
.embed-container { position: relative; padding-bottom: 56.25%; height: 0; overflow: hidden; max-width: 100%; } .embed-container iframe, .embed-container object, .embed-container embed { position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; }