
AAAP in the Media
Displaying 1 - 7 of 7
Can today’s Adaptation Action minimize future losses and damages in Africa?

On the sidelines of the 2022 edition of Africa Climate Week(link is external), a session titled Limiting Loss and Damage through Enhanced Adaptation Action in Africa featured vibrant and timely discussion of an aspect of climate change that typically receives little attention: capturing and assessing the costs and damages associated with climate change.
The African Development Bank and Germany’s Konrad Adenauer Foundation hosted the event, which provided a forum for panelists and participants to discuss the importance of defining and evaluating such losses and damages of properties, economies, lives and livelihoods due to climate disasters. Africa is acknowledged to be the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
Moderator Olufunso Somorin, a Regional Principal Officer at the African Development Bank, opened the discussion. He pointed out that it is important for African countries to measure climate-change related loss and damage to enable appropriate quantification and well-designed responses best suited to country context. It was also important to capture those losses occurred even in instances where preventive climate adaptation actions had been taken, he added.
Fatten Agad, Africa Climate Foundation’s Senior Advisor on Climate Diplomacy and Geopolitics, called for production of a report that would serve as guidance and baseline for evaluating climate related losses and damage. “It has already been demonstrated that the socio-economic impact faced by African countries in coping with the Covid-19 crisis has been very high, and adding a burden of financing something such as loss and damage would be unfair,” she said.
Anja Beretta, Konrad Adenauer’s Director for Energy Security and Climate Change in Africa, urged African countries to integrate mechanisms to address losses and damage into their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs). She also called for designated institutions and functioning structures to ensure the efficient and effective use of climate finance to advance the discussion on financial flows into loss and damage.
Stephane Bonamy, Head of the Regional Delegation for the International Committee of the Red Cross in Cameroon, said, for countries that face both conflict and climate change impacts, it is imperative that preventive measures are put in place early enough to reduce the extent of loss and damage faced and lessen the burden on communities.” He noted that 14 of the 25 most vulnerable countries to climate change impacts worldwide also face some form of conflict.
Dr Olumide Abimbola, the Executive Director of the Africa Policy Research Institute in Berlin reiterated the need for more African examples of past and current loss and damage to be incorporated into textbooks and journals.
There was agreement among the participants on the need for Africa to prioritize timely, comprehensive and large-scale adaptation action to avert or minimize future losses and damages.
There was also consensus on the urgent need to scale up financial flows from public and private sources into adaptation action across Africa. They cited the African Development Bank’s Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program, a joint initiative with the Global Center on Adaptation, as a positive example. The program seeks to mobilize $25 billion over five years to accelerate and scale climate adaptation actions across the continent.
Participants also called for new strategic partnerships to drive adaptation policies, plans and investments in Africa through the implementation of NDCs and tapping synergies with such initiatives as the Africa Disaster Risk Financing program.
About the African Climate Week (ACW)
ACW is an annual event that engages and empowers stakeholders to drive climate action across countries, communities and economies. The event is organized by UN Climate Change in collaboration with global partners UN Development Programme, UN Environment Programme and the World Bank Group. Partners in the region include the Africa Union, the Africa Development Bank, the UN Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA). ACW 2022 was hosted in Gabon.
Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision at the Africa Climate Week
What: Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision
When: 31 August 09:30 - 10:30 CAT
Where: Libreville, Gabon
Who: Global Center on Adaptation; Africa Adaptation Initiative (Chaired by Gabon); African Development Bank
Despite contributing the least to global warming, Africa finds itself on the frontline of the climate emergency, with the impacts of external shocks exacerbating these vulnerabilities. Indeed, large portions of Africa—particularly the drylands that cover three-fifths of the continent—are warming at a rate twice the global average, putting half a billion people at risk.
Chaired by Gabon, the Africa Adaptation Initiative (AAI) aims to strengthen collaboration on adaptation across the continent. To implement this vision, the Global Center on Adaptation and the African Development Bank have jointly developed the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program – AAAP. This Africa-led, Africa-owned response is mobilizing $25 billion for climate adaptation investments in the continent over five years. This event will review progress of the AAAP and how it is contributing to narrowing the finance gap, thus accelerating the implementation of AAI.
Program
- Welcome Remarks by the Moderator
Davinah Milenge Uwella – Principal Programme Coordinator, African Development Bank
- Opening Video
- Opening Remarks
Dr. Kevin Kariuki – Vice President, Power, Energy, Climate Change and Green Growth, AfDB
- Framing remarks: The Africa Adaptation Initiative and the AAA
Tanguy Gahouma-Bekale – Special Advisor to His Excellency Ali Bongo Ondimba, President of the Gabonese Republic, Permanent Secretary of the National Climate Council
- The AAAP as the vehicle to implement the AAI vision
Prof. Anthony Nyong – Senior Director, and Africa Regional Director, Global Center on Adaptation
AAAP voices from the field
- AAAP partners and beneficiaries
Moderated discussion with participants
- Wrap up by the Moderator
Multi-Stakeholder Dialogue on Climate Risk Assessment and adaptation options prioritization for the Transgabonaise road corridor PPP project
What: This is a private event
Where: Global - Virtual
When: 19 April 2023, 0:00
This first Multi-Stakeholder Climate Risk Dialogue will present the preliminary results of the high-resolution climate hazard modelling outcomes, and vulnerability assessment of the road corridor project.
Event description:
As part of the Global Center on Adaptation’s support to the Transgabonaise road corridor project under the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP), a Multi-Stakeholder Climate Risk Dialogue was organized to present results from the climate risk assessment with the African Development Bank, and project partners including the Societe Autiroutiere du Gabon (SAG), and the government of Gabon’s departments of Environment, Weather, and transport.
Historical weather trends, in Gabon, show an increase in mean annual temperatures of +1ºC since 1981, and decrease in mean annual rainfall, at an average rate of 3.8 mm per month per decade since 1960, with regional disparities. The technical assistance provided by the GCA will support an in-depth understanding of future climate hazards under different climate change scenarios, and across the different regions crossed by the 900km road corridor, and led to identify and provide a cost-benefit analysis of adaptation and resilience options to mitigate these current and future climate hazards.
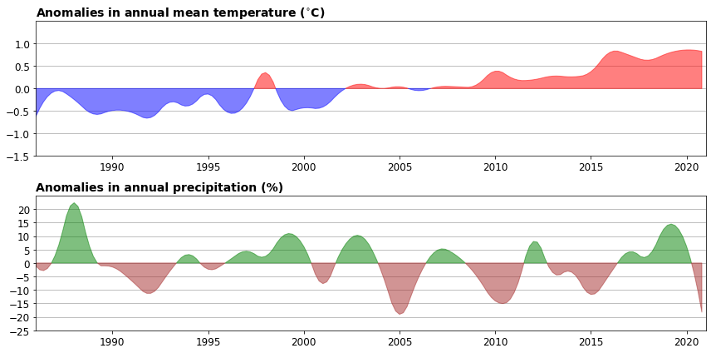
Figure 1: Climatology in Gabon: Historic evolution and trends, Source GCA – study from Royal Haskoning, Lobelia Earth, April 2023.
This First Multi-Stakeholder Climate Risk Dialogue will present the preliminary results of the high-resolution climate hazard modelling outcomes, and vulnerability assessment of the road corridor project. Especially, the project stakeholders will discuss the main climate hazards that have been highlighted, including extreme temperatures, extreme precipitation, drought intensity, and how these climate events might impact the assets and transport services. The discussion with local stakeholders will contribute to ensure robustness of the project outcomes.
Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision

What: Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision
When: 31 August 09:30 - 10:30 CAT
Where: Libreville, Gabon
Who: Global Center on Adaptation; Africa Adaptation Initiative (Chaired by Gabon); African Development Bank
Despite contributing the least to global warming, Africa finds itself on the frontline of the climate emergency, with the impacts of external shocks exacerbating these vulnerabilities. Indeed, large portions of Africa—particularly the drylands that cover three-fifths of the continent—are warming at a rate twice the global average, putting half a billion people at risk.
Chaired by Gabon, the Africa Adaptation Initiative (AAI) aims to strengthen collaboration on adaptation across the continent. To implement this vision, the Global Center on Adaptation and the African Development Bank have jointly developed the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program – AAAP. This Africa-led, Africa-owned response is mobilizing $25 billion for climate adaptation investments in the continent over five years. This event will review progress of the AAAP and how it is contributing to narrowing the finance gap, thus accelerating the implementation of AAI.
Program
- Welcome Remarks by the Moderator
Davinah Milenge Uwella – Principal Programme Coordinator, African Development Bank
- Opening Video
- Opening Remarks
Dr. Kevin Kariuki – Vice President, Power, Energy, Climate Change and Green Growth, AfDB
- Framing remarks: The Africa Adaptation Initiative and the AAA
Tanguy Gahouma-Bekale – Special Advisor to His Excellency Ali Bongo Ondimba, President of the Gabonese Republic, Permanent Secretary of the National Climate Council
- The AAAP as the vehicle to implement the AAI vision
Prof. Anthony Nyong – Senior Director, and Africa Regional Director, Global Center on Adaptation
AAAP voices from the field
- AAAP partners and beneficiaries
Moderated discussion with participants
- Wrap up by the Moderator
Gabon –The Transgabonaise Road Project
With improvements to the road, rail, shipping and aviation networks a key government goal, Gabon’s transport sector is undergoing a major transformation. While population pressure is modest, with around 1.7m people in the country, existing links are limited; the two largest cities, Libreville and Port-Gentil, had, until work began on one recently, no road connection.
The 828 km long Transgabonaise road is key as it connects Libreville (the capital and coastal city) and Franceville (third Gabonese city after Port-Gentil). It comprises several segments of the Routes Nationales (RN) 1 to 4. Despite its strategic importance, the road has suffered from substantial deterioration due to a lack of maintenance and increased traffic over the last decade, caused by the increase of population and lumbering.
The projects is supporting the rehabilitation of a succession of national roads in Gabon to make it a more efficient logistics axis.
Transgabonaise Road Project is divided into three stages:
- Libreville -AlembéStage
- Alembé -Mikouyi (via Lalara, Koumameyong, Booué, Carrefour Leroy)
- Mikouyi -Franceville
- High-resolution, asset-level climate risk and vulnerability assessments to quantify key climate hazards and associated risks to the road infrastructure assets along the entire road corridor
- Innovative solutions for climate smart transport asset management: Based on specific hazards identified including nature-based solutions (NBS) to optimize the resilience of the assets
- Operational performance metrics and standards for the service level agreement (SLA) based on the direct and indirect climate-related damages identified
- Improvement in the capacity and quality of the road infrastructure
- Creation of over 1,000 direct jobs and over 9,000 indirect jobs
- Saving on operational costs and travel time impacting both households and private sector development though lower transport costs
- Generation of safety benefits and lower greenhouse gas emissions
- Additional 200 billion CFA (or $302.4 million) to Gabon’s GDP (equivalent to ~1.9% according to the 2021 GDP)
- Increased connectivity within Gabon and with neighboring countries such as Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea and Congo-Brazzaville
- Promote economic growth through ease of transportation of goods and services efficiently, allowing businesses to access larger markets and expand their operations
- increased trade, investment, and tourism, stimulating economic development in both urban and rural areas in Gabon
- Enhances regional integration and cooperation by facilitating the movement of people, goods, and services across borders, fostering trade relationships and cultural exchange
- Improve accessibility to remote areas, providing people with better opportunities for education, healthcare, employment, and social services
USD 99.2 million
Project to Support a Resilient Agriculture Value Chain Development in Congo and DRC (PRAFS)
The Republic of Congo (ROC) and the Democratic Republic of Congo(DRC) are 2 of the 6 countries that make up the Congo Basin – an area with the second largest tropical rainforest in the world. These two countries are therefore, home to a huge diversity of plants and animals that span across a variety of landscapes (including a mosaic of rivers, forests, savannas, swamps and flooded forests). The area has a huge agrosylvo-pastoral and fishery production potential, and is a vector for the promotion of the agroindustry as well as for creating benefit leading to a strengthening of the rural economy.
The objective of this project is to ensure that the existing agricultural landscape is better able to support any potential increase in demand for land and water resources while simultaneously ensuring an effective resilience to climate change. This should minimise the need for expansion of farmland into existing forest landscapes thereby avoiding forest degradation, deforestation, thereby reducing emissions and enhancing forest carbon stocks. The project includes three main components: (i) Enhancing the sustainability of agricultural landscapes; (ii) Capacity building, awareness raising and dissemination; and (iii) project coordination and management.
- Feasibility study on integrating DCAS into agricultural extension and design of the agrometeorological advisory flow and required investments for successful scaling up of advisory to small-scale farmers
- Identification of capacity building and enabling interventions to ensure uptake by of DCAS
- Training of producer organisations in the appropriate use of selected technologies
- Collaborating with ICS producers within the country to train female producer organisations in the production and distribution of improved cooking stoves
- Pilot study undertaken to test the potential of developing smoke-flavored products working with the local fish research institute
- Provision of 15 solar drying systems to 15 improved maize planting material producer groups of to facilitate the post-harvest processing and storage
- Provide 100 cassava producer groups with solar drying systems to facilitate processing and storage and bio
- Training of 60 farmer field school facilitators
- Establishment and running of farmer field schools
- 2 355 000 beneficiaries, which make up 2.5% of the population
- Enhanced abilities of regional and local-level decision-makers to promote appropriate agroforestry-based climate resilient technologies
- Promotion of increased climate resilient agricultural production landscapes using innovative technologies
- Promotion of producers, women and youth’s organizations
- Capacity development of personnel involved at different levels of planning and execution of agroforestry schemes and the farmers
- Strengthened institutional capacities to improve ecosystem services through agroforestry and enhance the climate-resilience of production landscapes
- Local communities, farmers and farmer groups trained in the management of climate-resilient agroforestry landscapes
- Use of energy efficient technologies for post-harvest processing promoted
USD 217.6 Million