AAAP in the Media
Displaying 1 - 12 of 17
Can today’s Adaptation Action minimize future losses and damages in Africa?

On the sidelines of the 2022 edition of Africa Climate Week(link is external), a session titled Limiting Loss and Damage through Enhanced Adaptation Action in Africa featured vibrant and timely discussion of an aspect of climate change that typically receives little attention: capturing and assessing the costs and damages associated with climate change.
The African Development Bank and Germany’s Konrad Adenauer Foundation hosted the event, which provided a forum for panelists and participants to discuss the importance of defining and evaluating such losses and damages of properties, economies, lives and livelihoods due to climate disasters. Africa is acknowledged to be the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
Moderator Olufunso Somorin, a Regional Principal Officer at the African Development Bank, opened the discussion. He pointed out that it is important for African countries to measure climate-change related loss and damage to enable appropriate quantification and well-designed responses best suited to country context. It was also important to capture those losses occurred even in instances where preventive climate adaptation actions had been taken, he added.
Fatten Agad, Africa Climate Foundation’s Senior Advisor on Climate Diplomacy and Geopolitics, called for production of a report that would serve as guidance and baseline for evaluating climate related losses and damage. “It has already been demonstrated that the socio-economic impact faced by African countries in coping with the Covid-19 crisis has been very high, and adding a burden of financing something such as loss and damage would be unfair,” she said.
Anja Beretta, Konrad Adenauer’s Director for Energy Security and Climate Change in Africa, urged African countries to integrate mechanisms to address losses and damage into their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs). She also called for designated institutions and functioning structures to ensure the efficient and effective use of climate finance to advance the discussion on financial flows into loss and damage.
Stephane Bonamy, Head of the Regional Delegation for the International Committee of the Red Cross in Cameroon, said, for countries that face both conflict and climate change impacts, it is imperative that preventive measures are put in place early enough to reduce the extent of loss and damage faced and lessen the burden on communities.” He noted that 14 of the 25 most vulnerable countries to climate change impacts worldwide also face some form of conflict.
Dr Olumide Abimbola, the Executive Director of the Africa Policy Research Institute in Berlin reiterated the need for more African examples of past and current loss and damage to be incorporated into textbooks and journals.
There was agreement among the participants on the need for Africa to prioritize timely, comprehensive and large-scale adaptation action to avert or minimize future losses and damages.
There was also consensus on the urgent need to scale up financial flows from public and private sources into adaptation action across Africa. They cited the African Development Bank’s Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program, a joint initiative with the Global Center on Adaptation, as a positive example. The program seeks to mobilize $25 billion over five years to accelerate and scale climate adaptation actions across the continent.
Participants also called for new strategic partnerships to drive adaptation policies, plans and investments in Africa through the implementation of NDCs and tapping synergies with such initiatives as the Africa Disaster Risk Financing program.
About the African Climate Week (ACW)
ACW is an annual event that engages and empowers stakeholders to drive climate action across countries, communities and economies. The event is organized by UN Climate Change in collaboration with global partners UN Development Programme, UN Environment Programme and the World Bank Group. Partners in the region include the Africa Union, the Africa Development Bank, the UN Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA). ACW 2022 was hosted in Gabon.
Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision at the Africa Climate Week
What: Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision
When: 31 August 09:30 - 10:30 CAT
Where: Libreville, Gabon
Who: Global Center on Adaptation; Africa Adaptation Initiative (Chaired by Gabon); African Development Bank
Despite contributing the least to global warming, Africa finds itself on the frontline of the climate emergency, with the impacts of external shocks exacerbating these vulnerabilities. Indeed, large portions of Africa—particularly the drylands that cover three-fifths of the continent—are warming at a rate twice the global average, putting half a billion people at risk.
Chaired by Gabon, the Africa Adaptation Initiative (AAI) aims to strengthen collaboration on adaptation across the continent. To implement this vision, the Global Center on Adaptation and the African Development Bank have jointly developed the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program – AAAP. This Africa-led, Africa-owned response is mobilizing $25 billion for climate adaptation investments in the continent over five years. This event will review progress of the AAAP and how it is contributing to narrowing the finance gap, thus accelerating the implementation of AAI.
Program
- Welcome Remarks by the Moderator
Davinah Milenge Uwella – Principal Programme Coordinator, African Development Bank
- Opening Video
- Opening Remarks
Dr. Kevin Kariuki – Vice President, Power, Energy, Climate Change and Green Growth, AfDB
- Framing remarks: The Africa Adaptation Initiative and the AAA
Tanguy Gahouma-Bekale – Special Advisor to His Excellency Ali Bongo Ondimba, President of the Gabonese Republic, Permanent Secretary of the National Climate Council
- The AAAP as the vehicle to implement the AAI vision
Prof. Anthony Nyong – Senior Director, and Africa Regional Director, Global Center on Adaptation
AAAP voices from the field
- AAAP partners and beneficiaries
Moderated discussion with participants
- Wrap up by the Moderator
Multi-Stakeholder Dialogue on Climate Risk Assessment and adaptation options prioritization for the Transgabonaise road corridor PPP project
What: This is a private event
Where: Global - Virtual
When: 19 April 2023, 0:00
This first Multi-Stakeholder Climate Risk Dialogue will present the preliminary results of the high-resolution climate hazard modelling outcomes, and vulnerability assessment of the road corridor project.
Event description:
As part of the Global Center on Adaptation’s support to the Transgabonaise road corridor project under the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP), a Multi-Stakeholder Climate Risk Dialogue was organized to present results from the climate risk assessment with the African Development Bank, and project partners including the Societe Autiroutiere du Gabon (SAG), and the government of Gabon’s departments of Environment, Weather, and transport.
Historical weather trends, in Gabon, show an increase in mean annual temperatures of +1ºC since 1981, and decrease in mean annual rainfall, at an average rate of 3.8 mm per month per decade since 1960, with regional disparities. The technical assistance provided by the GCA will support an in-depth understanding of future climate hazards under different climate change scenarios, and across the different regions crossed by the 900km road corridor, and led to identify and provide a cost-benefit analysis of adaptation and resilience options to mitigate these current and future climate hazards.
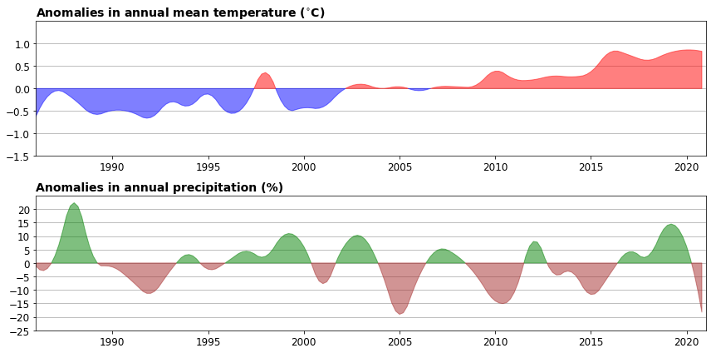
Figure 1: Climatology in Gabon: Historic evolution and trends, Source GCA – study from Royal Haskoning, Lobelia Earth, April 2023.
This First Multi-Stakeholder Climate Risk Dialogue will present the preliminary results of the high-resolution climate hazard modelling outcomes, and vulnerability assessment of the road corridor project. Especially, the project stakeholders will discuss the main climate hazards that have been highlighted, including extreme temperatures, extreme precipitation, drought intensity, and how these climate events might impact the assets and transport services. The discussion with local stakeholders will contribute to ensure robustness of the project outcomes.
Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision

What: Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision
When: 31 August 09:30 - 10:30 CAT
Where: Libreville, Gabon
Who: Global Center on Adaptation; Africa Adaptation Initiative (Chaired by Gabon); African Development Bank
Despite contributing the least to global warming, Africa finds itself on the frontline of the climate emergency, with the impacts of external shocks exacerbating these vulnerabilities. Indeed, large portions of Africa—particularly the drylands that cover three-fifths of the continent—are warming at a rate twice the global average, putting half a billion people at risk.
Chaired by Gabon, the Africa Adaptation Initiative (AAI) aims to strengthen collaboration on adaptation across the continent. To implement this vision, the Global Center on Adaptation and the African Development Bank have jointly developed the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program – AAAP. This Africa-led, Africa-owned response is mobilizing $25 billion for climate adaptation investments in the continent over five years. This event will review progress of the AAAP and how it is contributing to narrowing the finance gap, thus accelerating the implementation of AAI.
Program
- Welcome Remarks by the Moderator
Davinah Milenge Uwella – Principal Programme Coordinator, African Development Bank
- Opening Video
- Opening Remarks
Dr. Kevin Kariuki – Vice President, Power, Energy, Climate Change and Green Growth, AfDB
- Framing remarks: The Africa Adaptation Initiative and the AAA
Tanguy Gahouma-Bekale – Special Advisor to His Excellency Ali Bongo Ondimba, President of the Gabonese Republic, Permanent Secretary of the National Climate Council
- The AAAP as the vehicle to implement the AAI vision
Prof. Anthony Nyong – Senior Director, and Africa Regional Director, Global Center on Adaptation
AAAP voices from the field
- AAAP partners and beneficiaries
Moderated discussion with participants
- Wrap up by the Moderator
Gabon –The Transgabonaise Road Project
With improvements to the road, rail, shipping and aviation networks a key government goal, Gabon’s transport sector is undergoing a major transformation. While population pressure is modest, with around 1.7m people in the country, existing links are limited; the two largest cities, Libreville and Port-Gentil, had, until work began on one recently, no road connection.
The 828 km long Transgabonaise road is key as it connects Libreville (the capital and coastal city) and Franceville (third Gabonese city after Port-Gentil). It comprises several segments of the Routes Nationales (RN) 1 to 4. Despite its strategic importance, the road has suffered from substantial deterioration due to a lack of maintenance and increased traffic over the last decade, caused by the increase of population and lumbering.
The projects is supporting the rehabilitation of a succession of national roads in Gabon to make it a more efficient logistics axis.
Transgabonaise Road Project is divided into three stages:
- Libreville -AlembéStage
- Alembé -Mikouyi (via Lalara, Koumameyong, Booué, Carrefour Leroy)
- Mikouyi -Franceville
- High-resolution, asset-level climate risk and vulnerability assessments to quantify key climate hazards and associated risks to the road infrastructure assets along the entire road corridor
- Innovative solutions for climate smart transport asset management: Based on specific hazards identified including nature-based solutions (NBS) to optimize the resilience of the assets
- Operational performance metrics and standards for the service level agreement (SLA) based on the direct and indirect climate-related damages identified
- Improvement in the capacity and quality of the road infrastructure
- Creation of over 1,000 direct jobs and over 9,000 indirect jobs
- Saving on operational costs and travel time impacting both households and private sector development though lower transport costs
- Generation of safety benefits and lower greenhouse gas emissions
- Additional 200 billion CFA (or $302.4 million) to Gabon’s GDP (equivalent to ~1.9% according to the 2021 GDP)
- Increased connectivity within Gabon and with neighboring countries such as Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea and Congo-Brazzaville
- Promote economic growth through ease of transportation of goods and services efficiently, allowing businesses to access larger markets and expand their operations
- increased trade, investment, and tourism, stimulating economic development in both urban and rural areas in Gabon
- Enhances regional integration and cooperation by facilitating the movement of people, goods, and services across borders, fostering trade relationships and cultural exchange
- Improve accessibility to remote areas, providing people with better opportunities for education, healthcare, employment, and social services
USD 99.2 million
Staple Crops Processing Zone (SCPZ): funding proposal to the Green Climate Fund
The target countries of Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Togo and Zambia are regions experiencing high deforestation, poor agriculture yield and increasing poverty exacerbated by climate change. Across all four countries, climate variability and change has become a major threat to sustainable development.
As part of efforts to address these challenges, the four countries are implementing national projects to establish Staple Crops Processing Zones: initiatives designed to concentrate agro-processing activities within areas of high agricultural potential to boost productivity and integrate production, processing and marketing of selected commodities. These initiatives are purposely built shared facilities, to enable agricultural producers, processors, aggregators and distributors to operate in the same vicinity to reduce transaction costs and share business development services for increased productivity and competitiveness.
Developing adequate infrastructure (energy, water, roads, ICT) in rural areas of high agricultural potential should attract investments from private agro-industrialists/entrepreneurs to contribute to the economic and social development of rural areas.
The Staple Crops Processing Zone (SCPZ) development program aims to transform agriculture production in regions experiencing high deforestation, poor agriculture yield and increasing poverty exacerbated by climate change, including the target countries of Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Togo and Zambia.
The specific objectives of SCPZ are: (i) improving access to seed capital through grants and matching grants; (ii) supporting productivity enhancement through introduction of new technologies and agricultural inputs; (iii) improving access to infrastructure by supporting investment; (iv) improving the capacity of producer cooperative through training and TA, especially for targeted women and youth groups; (v) facilitating market linkages throughout-growers’ schemes; and (vi) facilitating on-farm value addition by targeting limited value chains and linking farmers to the supply chain.
GCF financing is sought to strengthen one of the project components of SCPZ in Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Togo and Zambia.
- Through the technical assistance program, AAAPwill accelerate the mobilization of adaptation finance.
- Increased carbon sinks in soil and above-ground biomass
- Reduced carbon dioxide/other greenhouse gas emissions from farms due to efficient energy use
- Increased renewable energy production from biomass, either as a substitute for fossil fuels or as a replacement for burning of fuel wood or crop residues
- Fewer incidents of bare soils, reduced soil erosion and increased water percolation.
- Reduced emissions through low-emission energy access and power generation
- Reduced emissions due to improved waste management, including by recycling waste and use of waste in biogas systems
- Reduction of emissions from land use and deforestation, and enhancement of forest carbon stocks.
-
Increased resilience, including to extreme events such as droughts and floods, and enhanced livelihood of about 55% of highly vulnerable people and communities
-
Increased access to better health and wellbeing, and food and water security to over 100,000 beneficiaries, in addition to provision of alternative sources of energy
-
Increased resilience of ecosystems and ecosystem services in forests and savannas
USD 427 million:
- Funding proposal to GCF seeking USD 174.02 million (USD 130.02 million grant and USD 44 million loan)
- AfDB providing USD 111.2 million (USD 85.2 million loan and USD 26 million grant)
- Co-financiers:
European Union, USD 10.4 million (grant)
BOAD, USD 17.6 million (loan)
Korea Exim Bank, USD 50 million (loan)
Korea Fund, USD 5 million (grant)
Islamic Development Bank, USD 31 million (loan)
Governments of target countries, USD 28 million (counterpart financing)
Climate risk regulation in Africa’s financial sector and related private sector initiatives
Extreme weather phenomena such as rising temperatures and the increasing frequency of droughts and floods are affecting lives and livelihoods in Africa. According to the Global Climate Risk Index 2021,1 five African countries ranked among the 10 countries most affected by extreme weather in 2019: Mozambique (first), Zimbabwe (second), Malawi (fifth), South Sudan (eighth), and Niger (ninth).
Direct Access Modality to access the Green Climate Fund
Africa is under-served by adaptation finance. Africa received USD 7.9 billion of an annual average of USD 46 billion in adaptation finance for 2019 and 2020. There is a large disparity between climate finance pledged, finance approved, and finance disbursed by the multilateral climate funds. As of January 2022, only 9.23% of global climate financing was earmarked for sub-Saharan Africa for adaptation purposes. Almost one third of the Green Climate Fund’s (GCF's) Direct Access Entities (DAEs) are in Africa, but only 11 out of 54 countries have at least one national accredited entity. DAEs are only accredited for projects with budgets below USD 50 million and are therefore limited in their ability to access funding for larger projects.
This project will develop a concept note as a starting point for a full funding proposal to the GCF. To achieve this, actions will include a desk review of national climate-related development strategies and reference documents in the target country; identification of a promising project idea, in close collaboration with relevant stakeholders; and facilitation of a consultative workshop to discuss the project’s rationale, main intervention areas and implementation arrangements.
Through the Technical Assistance Program (TAP), the Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) will accelerate the mobilization of adaptation finance. Through the direct access modality, GCA will enhance local capacity to formulate robust concept notes for funding consideration by the Green Climate Fund.
AAAP will support the climate risk assessment studies requested by the GCF.
- Four robust project/program concept notes and pipeline developed, for Burkina Faso, Democratic Republic of Congo, Niger and Nigeria.
- For the Democratic Republic of Congo, new sources of climate finance for adaptation and resilience investments identified.
- Development of a roadmap with key actions to prepare the full funding proposal, including the necessary complementary studies, the evaluation of the cost of these studies and the cost of the full funding proposal.
- Relevant initiatives or projects planned or underway and implemented in the project intervention areas
- Development of a portfolio of paradigm-shifting adaptation projects and programs, i.e., development of concept notes, supporting and enhancing funding proposals.
- Building capacities for adaptation finance planning, mobilization and implementation, i.e., Climate Public Expenditure Reviews.
- Direct Access strengthening with the aim to diversify and to increase the delivery channels, i.e., New Accreditation and Accreditation upgrades.
DRC: USD 58.75 million
Burkina Faso: USD 40 million
Niger: USD 50 million
Nigeria: USD 50 million
Total: USD 198.75 million
Global Center on Adaptation, AfDB host regional forum on the future of resilient food systems in Africa

The Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) in collaboration with the African Development Bank and the Wangari Mathai Institute have concluded a three-day regional forum on the future of resilient food systems in Africa.
The Forum, called the Future of Resilient Food Systems in Africa – AAAP Digital Solutions for a Changing Climate provided training aimed at strengthening the capacity of stakeholders from across Eastern Africa to design and implement solutions to improve food security and climate resilience and to facilitate knowledge sharing among farmers on approaches to scale up the use of Digital climate-informed advisory services, or DCAS.
Digital climate-informed advisory services are tools and platforms that integrate climate information into agricultural decision-making. These services range from digital mobile apps, radio, and online platforms to digitally enabled printed bulletins based on climate models and extension services that utilize climate information platforms.
DCAS offers crucial opportunities to build the resilience of small-scale producers in the face of worsening climate change impacts. From seasonal forecasts to pest advisories, effectively designed services provide producers with the resources to adapt to climate shocks and plan for new climate conditions.
Globally, more than 300 million small-scale agricultural producers have limited or no access to such services because service provision is still fragmented, unsustainable beyond project cycles, and not reaching the last mile.
Speaking at the opening ceremony of the forum, Professor Patrick Verkooijen, CEO of Global Center on Adaptation called for urgent financial support to put Africa on the path of food sovereignty.
“Africa needs urgent support to scale up the implementation of adaptation solutions that are already yielding good results for irrigation, developing drought-resistant seeds, crops and livestock diversification, “ he said.
“Through the African Adaptation Acceleration Programme, AAAP, we are rolling out a $350 million project to build resilience for food and nutrition security in the Horn of Africa towards mobilising new digital climate technology for market information, insurance products, financial services that can and must be tailored to smallholder farmers’ needs”, he added.
Speaking on behalf of the African Development Bank’s East Africa Regional Director General, Nnenna Nwabufo, Dr Pascal Sanginga, Regional Sector Manager for Agriculture and Agro-Industries noted that the forum was timely, coming hot on the heels of the recently concluded Dakar 2 Feed Africa-Food Sovereignty and Resilience summit , organised by the African Development Bank.
“The Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP) is already contributing to closing Africa’s adaptation gap by supporting African countries to make a transformational shift in their development pathways by putting climate adaptation and resilience at the center of their policies, programs, and institutions. There is no doubt that AAAP will be a strong component of the Country Food and Agricultural Delivery Compacts to accelerate the transformation of Africa’s food systems and build a more resilient Africa”, he said.
Professor Stephen Kiama Gitahi, Vice Chancellor of the University of Nairobi, reiterated the relevance of the forum pointing out that 70% of the population in Eastern Africa live in rural areas and depend on agriculture for their livelihoods. He encouraged the trainers to simplify the modules in a manner that removes the fear for technology and accelerate adaptation for rural farmers. Citing the legacy of late Professor Wangari Maathai he stated:
“We acknowledge that gaps exist on climate adaptation in the rural communities and those can be smartly bridged with the use of digital smart agriculture and climate innovations to create great conservation impact in our region.”
The forum brought together stakeholders from ministries of agriculture, related government agencies, public research institutions, farmer organizations, universities and non-profit organizations working on climate adaptation for food security in Eastern Africa. These included participants from Djibouti, Eritrea, South Sudan, Burundi, Rwanda, Mauritius, Tanzania, Seychelles, Sudan, Ethiopia, Rwanda and Kenya.
About Global Center on Adaptation
The Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) is an international organization which works as a solutions broker to accelerate action and support for adaptation solutions, from the international to the local, in partnership with the public and private sector. Founded in 2018, GCA operates from its headquarters in the largest floating office in the world, located in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. GCA has a worldwide network of regional offices in Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire; Dhaka, Bangladesh and Beijing, China.
About the Wangari Maathai Institute, University of Nairobi
The Wangari Maathai Institute (WMI) for peace and environmental studies is a global centre for teaching and research on environmental management, governance, peace and conflicts and the nexus between peace and democracy. The centre was founded in 2009 with the support of the Government of Kenya (GoK), the African Union(AU) and the African Development Bank(AfDB) to celebrate and immortalize the work of the late Nobel Laurete
Prof.Wangari Maathai who was a global champion on environmental conservation and governance. The centre trains future leaders and Champions for environment. The Centre is located in the serene environment in Upper Kabete suburb of Nairobi City.

