AAAP in the Media
Displaying 1 - 12 of 21
Experts share lessons learned on gender-responsive climate action during Commonwealth NDC webinar
This year, Edith Ofwona Adera, Coordinator of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP) and the African Development Bank’s Regional Principal Officer for Climate Change and Green Growth, marked International Women’s Day in a special way.
Adera took part in a panel discussion organised by the Commonwealth Secretariat, reflecting this year’s theme: Gender equality today for a sustainable tomorrow.
The panel, hosted by Jennifer Namgyal of the Commonwealth Secretariat, brought together experts who shared their experiences and lessons learned on integrating gender equality in Nationally Determined Contributions, or NDCs, across their respective regions and institutions. NDCs are national plans highlighting climate actions, including targets, policies and measures that governments aim to implement.
Hannah Girardeau, of the NDC Partnership Support Unit, kicked off the session with a presentation on the findings of an analysis of gender considerations in revised NDCs of the partnership’s member countries. The assessment revealed that more countries had now included the fundamental building blocks of gender-responsive climate action in their policies and plans. Girardeau noted that there is a need to invest in other critical elements such as conducting gender analyses, developing indicators, and establishing gender-responsive budgets to complement progress achieved.
Adera agreed with her. “As climate change impacts affect people differently, the responses need to be differentiated, based on identified unique needs, informed by disaggregated data,” Adera added.
To address this challenge, the African Development Bank is supporting national statistical systems in five countries through a Capacity Building for Gender Statistics and Monitoring Systems project. The project aims to produce quality, comparable and regular gender statistics to address national data gaps, strengthen monitoring systems, and integrate gender indicators across sectors.
Bertha Chiudza of the Green Climate Fund said a key requirement for all its financed activities is to ensure gender considerations are included in the development of action plans and assessments. “For its support on Nationally Determined Contributions, the Green Climate Fund ensures that gender considerations are brought in from planning and design, implementation and reporting across the sectors prioritized by countries, while ensuring inclusive stakeholder consultations,” Chiudza stated.
Sasha Jattansingh, the Commonwealth Climate Finance Adviser, gave insights into Antigua and Barbuda’s actions to mainstream gender equality into Nationally Determined Contributions. The country recognized equity issues and committed to a just energy transition with a strong focus on gender, Jattansingh noted. Antigua and Barbuda is an example of a country that has made progress in developing an inclusive renewable energy strategy that promotes socially inclusive, gender-responsive, and accessible investment opportunities.
Anna Rojas of the International Union for Conservation of Nature also shared her experiences and lessons in integrating gender into Nationally Determined Contributions, pointing out that biodiversity issues are now being integrated more consistently in these plans. She called for local-level conversations with women to tap into their strengths and rich knowledge. “Engagement with women will avoid dismal adaptation because, the more we identify needs, strengths, and solutions, the better we will be prepared,” she emphasized.
The African Development Bank is rolling out a detailed analysis of climate-gender hotspots in Rwanda. Adera said it would highlight real gender gaps and deep vulnerabilities, and how best climate interventions can address these gender issues.
Finance also emerged as one of the vital tools to promote gender equality in Nationally Determined Contributions. Innovative financial instruments and solutions must come into play when addressing gender inequalities for climate change interventions, noted Unnikrishnan Nair of the Commonwealth Secretariat.
African Youth Adaptation Solutions Challenge – Cycle 1
Through the African Youth Adaptation Solutions (YouthADAPT) Challenge, the AAAP aims to inspire and support the commercialisation of climate change adaptation solutions, driven by African youth entrepreneurs. The YouthADAPT Challenge is open to solutions (products, services, tools, or ideas) targeted at climate change adaptation and increasing resilience.
Admissible solutions can represent:
- An adaptation solutions business that has not been scaled and is not in widespread use
- An existing resilience and adaptation solutions business or product
- A commercially viable means to raise awareness or scale uptake of specific adaptation solutions.
Applicants must be 18–35 years old and registered and operating in Africa. Their venture must be youth-led while delivering climate adaptation or resilience solutions addressing a real-life challenge. 50% of the finalists will be women-owned or women-led enterprises. Winners will receive a business grant of up to $100,000 and the opportunity to further develop their ventures through business support and acceleration.
The Cycle 1 (2021) winners were unveiled at COP26 in Glasgow, United Kingdom, in a ceremony held at the Africa Pavilion. They include Mumita Holdings Limited, Cameroon, Salubata Technological Innovations Limited, Nigeria, Sustainable Builders, Zambia, Global Farms and Trading Company Limited, Ghana, Miama General Dealers Limited, Zambia, Kimplanter Seedling and Nurseries Limited, Kenya, Irri Hub Ke Limited, Kenya, Soupah Farm en- Market Limited, Nigeria, Simkay Green Global Ventures, Nigeria and Bleaglee Waste Management Limited, Cameroon.
The YouthADAPT Challenge aims to support youth-led enterprises to accelerate and scale-up innovative solutions for climate adaptation and resilience that will also lead to decent jobs for youth. The solutions target key environmental, social, and economic sectors affected by climate change, with a clear value proposition to scale up for greater impact and to create specified direct jobs.
The Challenge aims to strengthen inclusive growth and broaden investment and economic opportunities for youth in Africa through entrepreneurial skills development by providing training, mentorship, and financing to youth-led businesses (50% women-owned). The first edition of the awards was launched on 06 September 2021.
- Provide a financial contribution to cover the cost of program implementation and 50% of grant funding
- Participate in project missions and field visits to review progress with select beneficiary enterprises
- Support the project team to provide clarity on climate change adaptation and resilience in the training component, including tracking the creation of adaptation jobs
- Coordinate project monitoring and evaluation.
- The most innovative youth-owned enterprises on the continent are scaled up
- The viability of selected businesses is improved, to help sustain their impact on climate change adaptation
- Inclusiveness promoted through 50% of the selected businesses being led by women.
- Young innovators and MSMEs equipped with customised business development skills and resources;
- The short-term growth of youth-owned enterprises supported, with links to private equity and loan products for longer term growth.
- Expansion of partnership, knowledge sharing, exchange and learning created through a network of youth entrepreneurs in Africa.
- Inclusive growth, investment and economic opportunities for youth are strengthened through entrepreneurial skills development;
- Adaptation, innovation and jobs integrated and for jobs;
USD 1,000,000
Insurance Technical Support to Africa Adaptation Acceleration Programme (AAAP)
Countries in the Horn of Africa (HoA) are vulnerable to climatic shocks and their impact can have a devastating effect on agricultural production. The most vulnerable regions are arid and semi-arid areas that receive low rainfall and depend on pastoralism as the main economic activity. Elevated levels of food insecurity and conflict resulting from increased competition for pasture and water among pastoral communities is a concern for governments of HoA countries.
Strategies for increasing resilience need to be customized to different sub-regions and microclimates. Initiated in 2019, The Horn of Africa Initiative brings together 6 countries – Djibouti, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia and Sudan – to deepen economic integration and promote regional cooperation. The countries agreed that regional cooperation and economic integration should remain key to the overall recovery efforts of the sub-region.
The project described here focused on “Identifying Climate-Smart Digital Opportunities with Scaling Potential under the Horn of Africa Initiative”.
The findings in this report will contribute towards achieving the objectives of the HoA programme, which include:
-
Strengthening the resilience of pastoral and agro-pastoral production systems to climate change
-
Enhancing agribusiness and enterprise across value chains
-
Strengthening climate services and applications for enhanced adaptive capacity
This report was intended to contribute to the project design by ensuring that activities supporting investments under the HoA programme maximize complementarity around the application of digital technology to ensure efficiency, quality and real-time exchange of data, advisories and related services.
The report was also designed to produce a number of recommendations towards the identification of climate-smart digital opportunities; for example, the importance of establishing strong coordination mechanisms to implement digital solutions at a regional scale.
An in-depth understanding of the existing climate-smart digital opportunities with scaling potential under the HoA Initiative, including (but not limited to):
-
Emerging insurance innovations
-
Mainstreaming digital solutions to climate risk finance into country programmes
-
Application of digital technology to solve challenges in delivering agricultural insurance
-
Critical success factors for a successful regional drought insurance scheme
The output of this report advances the objectives of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Programme (AAAP) of GCA and the African Development Bank, which was developed to help implement the vision of the Africa Union’s Adaptation Initiative. To accelerate adaptation, the AAAP will use a triple-win approach and implement climate resilience activities that address COVID-19, climate change and the economy. AAAP intends to mobilize over US$25 billion to support adaptation between 2020–2025.
N/A
Inclusive Insurance for Smallholder Farmers in Africa
Rising average temperatures, longer heat waves, more extreme precipitation events and locust invasions are just some of the adverse effects of climate change that will impact agriculture in Africa. Climate change is expected to cause a decrease in crop productivity due to increased heat and drought. Some crops are likely to be particularly at risk, such as cotton in Côte d'Ivoire or Ghana. This phenomenon will directly impact the population, with greater consequences for the most vulnerable famers.
In the face of rising climate risk across Africa, insurance is a key adaptation measure to strengthen food security and ensure climate resilience. However, the agricultural insurance market is nascent, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, where less than 3% of farmers are protected.
The underdevelopment of agricultural insurance in Africa is due to a variety of factors, including the lack of organization in local value chains, the low profitability potential of programmes, and a general lack of financial resources and knowledge about insurance. Also, farmers do not consider agricultural insurance to be a priority.
The key aim of the landscape study on Inclusive Insurance for Smallholder Farmers in Africa was to clarify the pathway for the Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) to enter the agriculture insurance market in Africa. The study will contribute to defining the insurance toolkit included in the Smallholder Adaptation Accelerator (SAA) from the Climate Smart Digital Agriculture Pillar of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP), a joint programme in cooperation with the African Development Bank (AfDB).
The landscape study, completed in December 2021, describes the current state of the agricultural insurance market in Africa and considers (i) the various approaches available to scale up agricultural insurance; (ii) the types of insurance product that could be created; (iii) whether insurance premiums should be subsidized; and (iv) how digital technologies and effective relationships with local partners could be leveraged to facilitate product design and distribution.
This landscape study aimed to achieve:
- A synthesis of market knowledge, including key trends in the African insurance market and the challenges to development of the market
- In-depth product knowledge, including of parametric insurance and digital innovations
- An understanding of the various potential insurance schemes and an awareness of the challenges in distribution
- A clear set of recommendations for the creation of an insurance product for smallholder farmers.
The outcomes of this landscape study should contribute to:
- The identification of priority countries to launch a pilot for a smallholder insurance product.
- The involvement of GCA either as a partner in an existing programme insuring smallholders in a country in sub-Saharan Africa, where the population is connected and digitally active, with a stable government willing to support an insurance programme; or as the catalyst for a new agricultural parametric insurance programme.
- The initiation of a four-step workplan: (i) a feasibility study; (ii) a business agreement; (iii) product design and validation; and (iv) enrolment of farmers into the scheme.
- Once established, the evolution of the insurance cover and type of product over time; for example, from drought index insurance for maize, to a hybrid product for maize, to a hybrid product for maize and cassava.
100000
African Youth Adaptation Solutions Challenge – Cycle 2
YouthADAPT is an annual competition that invites young entrepreneurs and micro, small, and medium enterprises in Africa to submit innovative solutions and business ideas that have the potential to drive climate change adaptation and resilience across the continent.
Through YouthADAPT, the AAAP aims to inspire and support the commercialisation of climate change adaptation solutions, driven by African youth entrepreneurs. The YouthADAPT Challenge is open to solutions targeted at climate change adaptation and increasing resilience.
Solutions can represent:
- An adaptation solutions business that has not been scaled and is not in widespread use
- An existing resilience and adaptation solutions business or product
- A commercially viable means to raise awareness or scale uptake of specific adaptation solutions.
The second edition of the African Youth Adaptation Solutions (YouthADAPT) Challenge was launched in September 2022. Winners will receive a business grant of up to $100,000 and the opportunity to further develop their ventures through business support and acceleration.
The YouthADAPT Challenge aims to support youth-led enterprises to accelerate and scale-up innovative solutions for climate adaptation and resilience. The solutions target key environmental, social, and economic sectors affected by climate change, with a clear value proposition to scale up for greater impact and to create specified direct jobs.
YouthADAPT aims to strengthen inclusive growth and broaden investment and economic opportunities for youth in Africa through entrepreneurial skills development by providing training, mentorship, and financing to youth-led businesses (50% women-owned). The first edition of the awards was launched on 06 September 2021.
- Provide a financial contribution to cover the cost of program implementation and 50% of grant funding
- Participate in project missions and field visits to review progress with select beneficiary enterprises
- Support the project team to provide clarity on climate change adaptation and resilience in the training component, including tracking the creation of adaptation jobs
- Coordinate project monitoring and evaluation.
- The most innovative youth-owned enterprises on the continent are scaled up
- The viability of selected businesses is improved, to help sustain their impact on climate change adaptation
- 50% of the selected businesses are led by women.
- Young innovators and MSMEs equipped with customised business development skills and resources.
- The short-term growth of youth-owned enterprises is supported, with links to private equity and loan products for longer term growth.
- Expansion of partnership, knowledge sharing, exchange and learning through a network of youth entrepreneurs in Africa.
- Inclusive growth, investment and economic opportunities for youth;
- Adaptation, innovation and jobs integrated and for jobs;
Total: USD 1,400,000
Budget for Knowledge Partner (Project Implementation Cost) - USD 400,000
Grant Awards (50% of total grant awards) – USD 1,000,000
2022 Disbursement:
60% Disbursement of Project Implementation Cost to Knowledge Partner – USD 240,000
50% of Grant Awards – USD 500,000
Global Leaders Rally Support and Finance for the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program to Tackle Climate Change in Africa
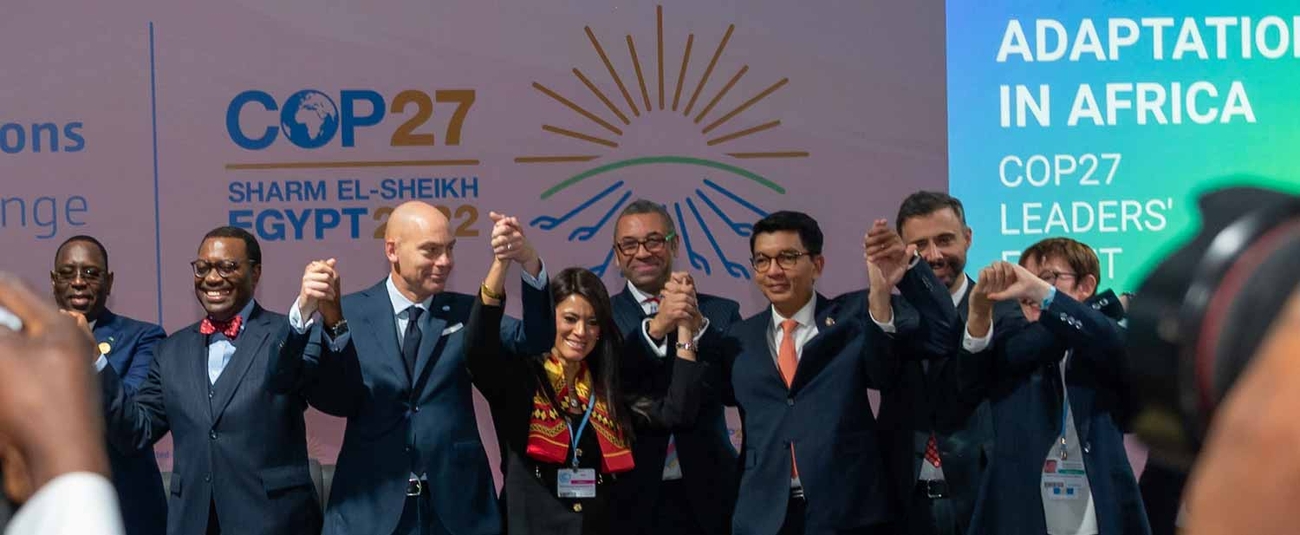

Global leaders on Tuesday rallied around climate adaptation for Africa. They attended the Africa Adaptation Leaders’ Event, convened by African Union Chair President Macky Sall of Senegal, Global Center on Adaptation CEO Patrick Verkooijen, and African Development Bank Group President Akinwumi Adesina.
The event took place at the global climate summit (COP27) in Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt. It underscored the critical need for climate adaptation in Africa and responded to the call for the capitalization of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP).
“This is a pivotal step in the fight against climate change,” African Union Chair President Macky Sall said. “The commitments made by Africa’s partners will give the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program the boost that it needs to transform the development trajectory of the world’s most climate exposed continent. I am confident in the ability of the AAAP to deliver results for Africa.”
The Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program is an Africa-owned and Africa-led initiative developed by the Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) and the African Development Bank (AfDB) in close collaboration with the African Union. It serves as the implementation of the Africa Adaptation Initiative (AAI) to mobilize $25 billion to implement, scale and accelerate climate adaptation across the Africa. Since 2021, AAAP has mainstreamed climate adaptation in over$3.5 billion of investments in 19 countries.
United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres said: “I want to express my total solidarity for the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program […] I urge the international community to support Africa to mobilize the technical & financial resources for scaling up transformative adaptation.”
“With this innovative program, Africa has developed a plan to grow, create jobs and opportunities for people, and to be resilient against the climate crisis,” said President Akufo-Addo of Ghana. “AAAP’s singular focus on the issue of climate adaptation will also contribute to greater stability and progress in Africa and around the world. AAAP is aligned with Ghana’s plans to address climate change as it chairs the Climate Vulnerability Forum (CVF) to lead efforts from the world’s most climate vulnerable countries to spur and mobilize investment through the Climate Prosperity Plans."
James Cleverly, Secretary of State for Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Affairs of the United Kingdom announced that the UK will provide £200 million to the African Development Bank’s Climate Action Window. This is in addition to the £20 million announced at COP26 in Glasgow to the AAAP Upstream Financing Facility.
Cleverly noted: “Climate change is having a devastating impact on countries in Sub-Saharan Africa facing drought and extreme weather patterns, which have historically received a tiny proportion of climate finance. This new mechanism […] will see vital funds delivered to those most affected by the impacts of climate change, much more quickly.”
Prime Minister Mark Rutte of the Netherlands followed through on the commitment made at the Africa Adaptation Summit held at the Global Center on Adaptation in September to confirm that the Netherlands will contribute EUR110 million to the AAAP, with EUR10 million in support for the Upstream Financing Facility hosted by GCA and EUR 100 million for the Climate Action Window of the African Development Fund at the African Development Bank as part of the Netherlands’ commitment to dedicate half of its climate funding, fully grant based, to climate adaptation, with a focus on Africa.
Norwegian Prime Minister Jonas Gahr Støre echoed African leaders’ calls for countries to rapidly scale up finance for climate adaptation, stating: “The climate crisis is here and now. Years of progress are at risk.”
“The AAAP Upstream Financing Facility is the delivery mechanism of adaptation and will use millions to leverage the billions that is required for adaptation,” he continued. “AAAP projects will generate effective climate adaptation outcomes. Adaptation is a growth agenda. A jobs agenda. And a prosperity agenda. On behalf of Norway, I am looking forward to continuing this partnership, investing in it, and supporting it with the Global Center on Adaptation.”
International Monetary Fund Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva emphasized the need to accelerate adaptation in Africa, stating: “It is paramount to support Africa’s adaptation because Africa will not reach its tremendous potential without it. AAAP complements the IMF’s Resilience and Sustainability Trust, which helps countries address external shocks such as climate change and ensure sustainable growth that can give Africa a chance to leapfrog outdated development models.”
African Development Bank Group President Dr. Akinwumi Adesina said: “Africa is suffering from the devastating effects of climate change. Our continent is being short changed by climate finance. The contributions towards the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program’s Upstream Financing Facility and the Climate Action Window – which the African Development Bank manages – will help capitalize the program. With increased capital, we can better deliver the investment needed to bridge the adaptation finance gap. We want to ensure that the most vulnerable communities can benefit from a sustainable and prosperous future.”
Endorsing the outcomes of the high-level meeting, Patrick Verkooijen, CEO of the Global Center on Adaptation, closed with a statement emphasizing the AAAP’s impact to date, noting that “there is no pause button on the climate crisis. Africa must adapt to the threat of climate change, and it must adapt now.”
“Through the AAAP,” he continued, “Africa has charted its path towards a climate-resilient future for its youth, its economic growth, and for its prosperity.”
About the Global Center on Adaptation
The Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) is an international organization which works as a solutions broker to accelerate action and support for adaptation solutions, from the international to the local, in partnership with the public and private sector, to ensure we learn from each other and work together for a climate-resilient future. Founded in 2018, GCA is hosted by the Netherlands, working from its headquarters in Rotterdam with a knowledge and research hub based in Groningen. GCA has a worldwide network of regional offices in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, Dhaka, Bangladesh and Beijing, China. Through this evolving network of offices and global and regional GCA teams, the organization engages in high-level policy activities, new research contributions, communications, and technical assistance to governments and the private sector.
About the African Development Bank
The African Development Bank Group is Africa’s premier development organization. Its overarching objective is to spur sustainable economic development and social progress in its regional member countries, thus contributing to poverty reduction across the continent.
The Bank Group achieves this objective by mobilizing and allocating resources for investment in African countries and providing policy advice and technical assistance to support development efforts.
In 2015, all multilateral development institutions agreed on the same set of objectives, the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Learn more: https://www.afdb.org/
About the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program
The Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP) is a joint initiative of the African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation (GCA). It aims to mobilize $25 billion, over five years, to accelerate and scale climate adaptation action across the continent. This ambition is delivered through the AAAP Upstream Financing Facility managed by the Global Center on Adaptation and the African Development Bank’s climate action window in the ADF replenishment. AAAP works across four pillars to achieve transformational results: Climate-Smart Digital Technologies for Agriculture and Food Security; African Infrastructure Resilience Accelerator; Youth Empowerment for Entrepreneurship and Job Creation in Climate Adaptation and Resilience and Innovative Financial Initiatives for Africa. AAAP has already guided over $3.5 billion of upstream investments in 19 countries with every dollar spent influencing $100 downstream.
COP27 - COP27 Leaders' Event, Accelerating Adaptation in Africa (DAY 2)
Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program showcases African youths driving climate innovation

The Africa Adaptation Acceleration program (AAAP) – a joint initiative of the African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation – recently showcased its initiative to harness the dynamism and leadership of Africa’s youth to drive climate adaption innovation.
On the side-lines of the recent 3rd Gobeshona Global Conference(link is external), AAAP brought together participants in its YouthADAPT program to share their experiences with the program as well as strategies to scale up youth-led approaches to adaptation
In his opening remarks, Dr. Kevin Kariuki, African Development Bank Vice President for Power, Energy, and Climate & Green Growth underscored young people’s integral role in Africa’s sustainable development.
“Youth form the backbone of Africa’s population, constituting over 60% of the population. The continent’s sustainable development hinges on harnessing this demographic dividend,” Kariuki said. “The AAAP, through its YouthADAPT pillar, has so far supported 35 youth-led enterprises in 14 African countries with $3.5 million to drive climate actions in sectors such as agriculture, waste management, renewable energy, water and sanitation,” Kariuki added. YouthADAPT is one of AAAPs four pillars for accelerating climate adaptation.
Caroline Mukuhi Mwangi, founder of Kimplanter Seedling(link is external) and Nurseries Limited, said her company was already seeing the benefits of participation in the program. Kimplanter provides drought resistant seedlings that boost food production and food security in Kenya.
Mwangi said, “We have ventured into new markets in semi-arid regions and expanded our seedling varieties, increasing our revenue by 36% as a result of AAAP support. Our customer base has also grown from 8,000 to 16,000 farmers and we have increased our staff from 17 to 32, all of whom are women or youth.”
Aramide Abe, the Program Lead of Jobs for Youth & Entrepreneurship at the Global Center on Adaptation(link is external) confirmed that participating enterprises have already begun to show results. She said some have seen revenues rise by up to 50 percent. A fifth have ventured into new markets and have raised over $106,000 in additional funding from different sources.
Juveline Ngum, the founder of Bleaglee Waste Management Limited, a Cameroon-based start-up company using drone technology to tackle waste disposal, also stressed the benefits of participating in YouthADAPT.
“We have expanded our waste disposal management solution from west Cameroon into Douala, effectively using drones to detect clogged drainages and utilizing data for demand driven waste management,” Ngum said. Now, we aim to expand across national borders into Dakar, Senegal.”
Noël N'guessan’s Cote d’Ivoire-based company, LONO(link is external) – a winner of the 2022 YouthADAPT challenge – has patented technology for the production of organic fertilizer. The company has also introduced modular and mobile bio digesters for the agri-food sector. Biodigesters use microbes and other bacteria to break down organic waste including fat, greases, and even animal manure.
Still, Nguessan said challenges remained. “The cost of prototyping hardware equipment can be prohibitively high, resulting in lengthy project development cycles, “he said. He pointed to financial management training as vital for youth-led businesses.
The session also featured presentations by African Development Bank partners and other global organizations that have rolled out similar initiatives to YouthAdapt.
Sandra Simbiri, Program Specialist at UNICEF’s Generation Unlimited(link is external), said:
“Supporting entrepreneurs through STEM principles is key to preparing the young for technological innovations.”
Alfred Asiko, Senior Market Engagement Manager for the ClimateTech Programme at GSMA(link is external), a mobile technology association, said it has played a role in empowering youth to deploy such technologies as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence and blockchain to tackle climate challenges.
“Through our innovation fund, we offer grants to climate startups, with a focus on supporting resilient solutions that utilize frontier technologies. We also provide skills development and training to help entrepreneurs succeed in scaling their innovations,” Asiko said.
He said that venture capital (VCs) firms had a critical role to play. ”We need to see more VCs stepping up and taking over from development finance institutions (DFIs) in providing financing and support to youth-led businesses,” he added.
YouthADAPT targets reaching 10, 000 African youth-led enterprises by 2025, promoting innovation and inclusive growth for young people in climate resilient jobs and through youth enterprise development. The AAAP’s other three pillars are Climate-Smart Digital Technologies for Agriculture and Food Security; the African Infrastructure Resilience Accelerator and the Innovative Financial Initiatives for Africa
The third annual Gobeshona Global Conference, organized by the International Centre for Climate Change and Development, took place virtually from 10-16 March 2023. It focused on monitoring Locally- Led Adaptation (LLA) and resilience.
African Development Bank and Global Center on Adaptation work with partners to enhance capacity to access climate adaptation funding

The African Development Bank and Global Center on Adaptation today launched a new initiative under the Technical Assistant Programme of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program(link is external) to help African countries access more climate adaptation funding.
A climate rationale is the scientific basis of a project and describes the climate change scenario, outlining the climate problem in a particular country (e.g., flooding, droughts for an adaptation project) and region that the project will be implemented in. The rigorous requirement by Green Climate Fund for climate rationale based on 30 years of point-source climate data has led to a high attrition rate for funding proposals with an adaptation focus.
Through this new initiative, Direct Access Entities in Africa will receive additional support to enhance their capacity with regards to climate data, tools, and methodologies that help them meet the critical requirements of climate rationale for compelling funding proposals that could merit approval by the GCF Board.
The GCF is one of the mechanisms of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change to significantly contribute to the global efforts towards attaining the goals set by the international community to combat climate change. It supports developing countries to limit or reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to climate change impacts. For adaptation, it allocates resources based on: (i) the ability of a proposed activity to demonstrate its potential to adapt to the impacts of climate change by promoting sustainable development and a paradigm shift; (ii) the urgent and immediate needs of vulnerable countries, in particular, Least Developed Countries, Small Island Developing States and African States.
The African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation will work with their partners to select at least four proposals each year based on the pipeline of Direct Access Entities funding proposals that require additional technical assistance and guidance. Through its Technical Assistance Programme (TAP), the Global Center on Adaptation will provide technical assistance for a selected set of funding proposals.
The launch event for the new initiative took place in Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire, on the 6th and 7th of December with program partners including the Green Climate Fund (GCF), World Meteorological Organization (WMO), Africa Climate Change Fund, ClimDev Special Fund and Regional Climate Centers in Africa.
23 Direct Access Entities accredited or at the final stage of accreditation to GCF participated in the two-day event with representatives of regional and international accredited entities, including the Development Bank of Southern Africa, the International Fund for Agricultural Development, the West African Development Bank, the Africa Finance Corporation and the United Nations Environment Program.
In opening remarks,Professor Anthony O. Nyong, Senior Director for Africa at the Global Center on Adaptation said , “Africa is on the frontline of our climate emergency. Through this new initiative, we aim to significantly increase the flow of adaptation finance to the region. Given the central role of the Green Climate Fund, the unprecedented volumes of funding it offers, the range of financial instruments it provides, and its different access modalities, we will initially focus this initiative on accessing GCF resources, but this is just the start of our long-term partnership with African countries to mobilize finance for climate adaptation across the continent. »
Dr. Al Hamndou Dorsouma, Acting Director of the Department of Climate Change and Green Growth at the African Development Bank, said, “climate rationale for GCF funding proposal is like the foundation of a building. A solid building should have a solid foundation and I am glad our bank has forged the collaboration with relevant regional and international institutions to help direct access entities secure approvals for more funding proposals on adaptation with strong climate rationale.”
Dr. Kevin Horsburgh, Lead Climate Scientist representing GCF, noted, “To promote transformational projects and catalyze climate finance at scale, GCF follows a four-pronged approach: transformational planning; catalyzing innovation; de-risking high impact projects; and aligning finance with sustainable development. Each step needs the best available information to assist decision-making. The GCF is pleased to be working with the WMO to create the bridge between climate information and all those who need to use it, to improve access to climate finance.”
Amir Delju, Senior Scientific Officer with the World Meteorological Organization, said, “Effective and progressive response to the urgent threat of climate change should be based on ‘the best available scientific knowledge.’ We recognize that it is very challenging for least developed countries to meet this requirement. As an expert service provider, WMO will continue providing the full value cycle of climate services, from data to analysis, information production, interpretation of the findings, and expert advice.”
Contact:
- Romaric OLLO HIEN, Communication and External Relations Department, African Development Bank, email: media@afdb.org(link sends e-mail)
- Technical Contact: Timothy Afful-Koomson, GCF Coordinator, African Development Bank, email: t.afful-koomson@afdb.org(link sends e-mail)
- Technical Contact: Ali Haider, Senior Program Officer, Climate Finance, Global Center on Adaptation, email: ali.haider@gca.org(link sends e-mail)
Africa Climate Change Fund launches Women and Youth Entrepreneurship Project
The Africa Climate Change Fund (ACCF) Secretariat has launched a scheme to support mechanisms for climate adaptation finance for women entrepreneurs and youth.
The scheme, “YouthADAPT: Empowering Women and Youth for Entrepreneurship and Job Creation in Climate Adaptation and Resilience,” will develop innovative, transformative climate-resilient bankable projects aligned with African countries’ Nationally Determined Contributions.
YouthADAPT is a flagship program under the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP), which is unlocking the untapped potential of youth in Africa to drive resilience and green enterprise.
The virtual launch followed the approval of a $1 million grant funding by the ACCF’s development partners for the project. The event rallied together stakeholders, including the project team, quality control, adaptation, gender, and communication experts, and climate change and green growth experts to share experiences.
ACCF Coordinator Rita Effah, and the Portfolio Officer, Lucy Debrion, explained the Fund’s operational guidelines on Bank-implemented projects.
AAAP Coordinator and Principal Climate Change Officer Edith Ofwona Adera said, "African youth are leading the way, not in talk, but in concrete climate action; as agents of change, innovators, and entrepreneurs.”
She said the scheme would support women-led local enterprises promoting adaptation solutions to create additional jobs.
Adera thanked the ACCF for collaborating on the projects. Adera also commended the Fund for its role in facilitating the production of proposals. “That makes our work easier,” she added.
Following the launch, the AAAP secretariat will regularly engage with the ACCF Secretariat on significant project milestones to ensure that the objective is fully accomplished.
Since 2017, the ACCF Governing Committees have approved 26 projects estimated at $15.87 million.
The AAAP will implement the project. For more information on ACCF and AAAP, please visit http://accf.afdb.org and www.afdb.org/aaap