
AAAP in the Media
Displaying 1 - 12 of 14
Experts share lessons learned on gender-responsive climate action during Commonwealth NDC webinar
This year, Edith Ofwona Adera, Coordinator of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP) and the African Development Bank’s Regional Principal Officer for Climate Change and Green Growth, marked International Women’s Day in a special way.
Adera took part in a panel discussion organised by the Commonwealth Secretariat, reflecting this year’s theme: Gender equality today for a sustainable tomorrow.
The panel, hosted by Jennifer Namgyal of the Commonwealth Secretariat, brought together experts who shared their experiences and lessons learned on integrating gender equality in Nationally Determined Contributions, or NDCs, across their respective regions and institutions. NDCs are national plans highlighting climate actions, including targets, policies and measures that governments aim to implement.
Hannah Girardeau, of the NDC Partnership Support Unit, kicked off the session with a presentation on the findings of an analysis of gender considerations in revised NDCs of the partnership’s member countries. The assessment revealed that more countries had now included the fundamental building blocks of gender-responsive climate action in their policies and plans. Girardeau noted that there is a need to invest in other critical elements such as conducting gender analyses, developing indicators, and establishing gender-responsive budgets to complement progress achieved.
Adera agreed with her. “As climate change impacts affect people differently, the responses need to be differentiated, based on identified unique needs, informed by disaggregated data,” Adera added.
To address this challenge, the African Development Bank is supporting national statistical systems in five countries through a Capacity Building for Gender Statistics and Monitoring Systems project. The project aims to produce quality, comparable and regular gender statistics to address national data gaps, strengthen monitoring systems, and integrate gender indicators across sectors.
Bertha Chiudza of the Green Climate Fund said a key requirement for all its financed activities is to ensure gender considerations are included in the development of action plans and assessments. “For its support on Nationally Determined Contributions, the Green Climate Fund ensures that gender considerations are brought in from planning and design, implementation and reporting across the sectors prioritized by countries, while ensuring inclusive stakeholder consultations,” Chiudza stated.
Sasha Jattansingh, the Commonwealth Climate Finance Adviser, gave insights into Antigua and Barbuda’s actions to mainstream gender equality into Nationally Determined Contributions. The country recognized equity issues and committed to a just energy transition with a strong focus on gender, Jattansingh noted. Antigua and Barbuda is an example of a country that has made progress in developing an inclusive renewable energy strategy that promotes socially inclusive, gender-responsive, and accessible investment opportunities.
Anna Rojas of the International Union for Conservation of Nature also shared her experiences and lessons in integrating gender into Nationally Determined Contributions, pointing out that biodiversity issues are now being integrated more consistently in these plans. She called for local-level conversations with women to tap into their strengths and rich knowledge. “Engagement with women will avoid dismal adaptation because, the more we identify needs, strengths, and solutions, the better we will be prepared,” she emphasized.
The African Development Bank is rolling out a detailed analysis of climate-gender hotspots in Rwanda. Adera said it would highlight real gender gaps and deep vulnerabilities, and how best climate interventions can address these gender issues.
Finance also emerged as one of the vital tools to promote gender equality in Nationally Determined Contributions. Innovative financial instruments and solutions must come into play when addressing gender inequalities for climate change interventions, noted Unnikrishnan Nair of the Commonwealth Secretariat.
African Youth Adaptation Solutions Challenge – Cycle 1
Through the African Youth Adaptation Solutions (YouthADAPT) Challenge, the AAAP aims to inspire and support the commercialisation of climate change adaptation solutions, driven by African youth entrepreneurs. The YouthADAPT Challenge is open to solutions (products, services, tools, or ideas) targeted at climate change adaptation and increasing resilience.
Admissible solutions can represent:
- An adaptation solutions business that has not been scaled and is not in widespread use
- An existing resilience and adaptation solutions business or product
- A commercially viable means to raise awareness or scale uptake of specific adaptation solutions.
Applicants must be 18–35 years old and registered and operating in Africa. Their venture must be youth-led while delivering climate adaptation or resilience solutions addressing a real-life challenge. 50% of the finalists will be women-owned or women-led enterprises. Winners will receive a business grant of up to $100,000 and the opportunity to further develop their ventures through business support and acceleration.
The Cycle 1 (2021) winners were unveiled at COP26 in Glasgow, United Kingdom, in a ceremony held at the Africa Pavilion. They include Mumita Holdings Limited, Cameroon, Salubata Technological Innovations Limited, Nigeria, Sustainable Builders, Zambia, Global Farms and Trading Company Limited, Ghana, Miama General Dealers Limited, Zambia, Kimplanter Seedling and Nurseries Limited, Kenya, Irri Hub Ke Limited, Kenya, Soupah Farm en- Market Limited, Nigeria, Simkay Green Global Ventures, Nigeria and Bleaglee Waste Management Limited, Cameroon.
The YouthADAPT Challenge aims to support youth-led enterprises to accelerate and scale-up innovative solutions for climate adaptation and resilience that will also lead to decent jobs for youth. The solutions target key environmental, social, and economic sectors affected by climate change, with a clear value proposition to scale up for greater impact and to create specified direct jobs.
The Challenge aims to strengthen inclusive growth and broaden investment and economic opportunities for youth in Africa through entrepreneurial skills development by providing training, mentorship, and financing to youth-led businesses (50% women-owned). The first edition of the awards was launched on 06 September 2021.
- Provide a financial contribution to cover the cost of program implementation and 50% of grant funding
- Participate in project missions and field visits to review progress with select beneficiary enterprises
- Support the project team to provide clarity on climate change adaptation and resilience in the training component, including tracking the creation of adaptation jobs
- Coordinate project monitoring and evaluation.
- The most innovative youth-owned enterprises on the continent are scaled up
- The viability of selected businesses is improved, to help sustain their impact on climate change adaptation
- Inclusiveness promoted through 50% of the selected businesses being led by women.
- Young innovators and MSMEs equipped with customised business development skills and resources;
- The short-term growth of youth-owned enterprises supported, with links to private equity and loan products for longer term growth.
- Expansion of partnership, knowledge sharing, exchange and learning created through a network of youth entrepreneurs in Africa.
- Inclusive growth, investment and economic opportunities for youth are strengthened through entrepreneurial skills development;
- Adaptation, innovation and jobs integrated and for jobs;
USD 1,000,000
Insurance Technical Support to Africa Adaptation Acceleration Programme (AAAP)
Countries in the Horn of Africa (HoA) are vulnerable to climatic shocks and their impact can have a devastating effect on agricultural production. The most vulnerable regions are arid and semi-arid areas that receive low rainfall and depend on pastoralism as the main economic activity. Elevated levels of food insecurity and conflict resulting from increased competition for pasture and water among pastoral communities is a concern for governments of HoA countries.
Strategies for increasing resilience need to be customized to different sub-regions and microclimates. Initiated in 2019, The Horn of Africa Initiative brings together 6 countries – Djibouti, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia and Sudan – to deepen economic integration and promote regional cooperation. The countries agreed that regional cooperation and economic integration should remain key to the overall recovery efforts of the sub-region.
The project described here focused on “Identifying Climate-Smart Digital Opportunities with Scaling Potential under the Horn of Africa Initiative”.
The findings in this report will contribute towards achieving the objectives of the HoA programme, which include:
-
Strengthening the resilience of pastoral and agro-pastoral production systems to climate change
-
Enhancing agribusiness and enterprise across value chains
-
Strengthening climate services and applications for enhanced adaptive capacity
This report was intended to contribute to the project design by ensuring that activities supporting investments under the HoA programme maximize complementarity around the application of digital technology to ensure efficiency, quality and real-time exchange of data, advisories and related services.
The report was also designed to produce a number of recommendations towards the identification of climate-smart digital opportunities; for example, the importance of establishing strong coordination mechanisms to implement digital solutions at a regional scale.
An in-depth understanding of the existing climate-smart digital opportunities with scaling potential under the HoA Initiative, including (but not limited to):
-
Emerging insurance innovations
-
Mainstreaming digital solutions to climate risk finance into country programmes
-
Application of digital technology to solve challenges in delivering agricultural insurance
-
Critical success factors for a successful regional drought insurance scheme
The output of this report advances the objectives of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Programme (AAAP) of GCA and the African Development Bank, which was developed to help implement the vision of the Africa Union’s Adaptation Initiative. To accelerate adaptation, the AAAP will use a triple-win approach and implement climate resilience activities that address COVID-19, climate change and the economy. AAAP intends to mobilize over US$25 billion to support adaptation between 2020–2025.
N/A
Inclusive Insurance for Smallholder Farmers in Africa
Rising average temperatures, longer heat waves, more extreme precipitation events and locust invasions are just some of the adverse effects of climate change that will impact agriculture in Africa. Climate change is expected to cause a decrease in crop productivity due to increased heat and drought. Some crops are likely to be particularly at risk, such as cotton in Côte d'Ivoire or Ghana. This phenomenon will directly impact the population, with greater consequences for the most vulnerable famers.
In the face of rising climate risk across Africa, insurance is a key adaptation measure to strengthen food security and ensure climate resilience. However, the agricultural insurance market is nascent, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, where less than 3% of farmers are protected.
The underdevelopment of agricultural insurance in Africa is due to a variety of factors, including the lack of organization in local value chains, the low profitability potential of programmes, and a general lack of financial resources and knowledge about insurance. Also, farmers do not consider agricultural insurance to be a priority.
The key aim of the landscape study on Inclusive Insurance for Smallholder Farmers in Africa was to clarify the pathway for the Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) to enter the agriculture insurance market in Africa. The study will contribute to defining the insurance toolkit included in the Smallholder Adaptation Accelerator (SAA) from the Climate Smart Digital Agriculture Pillar of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP), a joint programme in cooperation with the African Development Bank (AfDB).
The landscape study, completed in December 2021, describes the current state of the agricultural insurance market in Africa and considers (i) the various approaches available to scale up agricultural insurance; (ii) the types of insurance product that could be created; (iii) whether insurance premiums should be subsidized; and (iv) how digital technologies and effective relationships with local partners could be leveraged to facilitate product design and distribution.
This landscape study aimed to achieve:
- A synthesis of market knowledge, including key trends in the African insurance market and the challenges to development of the market
- In-depth product knowledge, including of parametric insurance and digital innovations
- An understanding of the various potential insurance schemes and an awareness of the challenges in distribution
- A clear set of recommendations for the creation of an insurance product for smallholder farmers.
The outcomes of this landscape study should contribute to:
- The identification of priority countries to launch a pilot for a smallholder insurance product.
- The involvement of GCA either as a partner in an existing programme insuring smallholders in a country in sub-Saharan Africa, where the population is connected and digitally active, with a stable government willing to support an insurance programme; or as the catalyst for a new agricultural parametric insurance programme.
- The initiation of a four-step workplan: (i) a feasibility study; (ii) a business agreement; (iii) product design and validation; and (iv) enrolment of farmers into the scheme.
- Once established, the evolution of the insurance cover and type of product over time; for example, from drought index insurance for maize, to a hybrid product for maize, to a hybrid product for maize and cassava.
100000
African Youth Adaptation Solutions Challenge – Cycle 2
YouthADAPT is an annual competition that invites young entrepreneurs and micro, small, and medium enterprises in Africa to submit innovative solutions and business ideas that have the potential to drive climate change adaptation and resilience across the continent.
Through YouthADAPT, the AAAP aims to inspire and support the commercialisation of climate change adaptation solutions, driven by African youth entrepreneurs. The YouthADAPT Challenge is open to solutions targeted at climate change adaptation and increasing resilience.
Solutions can represent:
- An adaptation solutions business that has not been scaled and is not in widespread use
- An existing resilience and adaptation solutions business or product
- A commercially viable means to raise awareness or scale uptake of specific adaptation solutions.
The second edition of the African Youth Adaptation Solutions (YouthADAPT) Challenge was launched in September 2022. Winners will receive a business grant of up to $100,000 and the opportunity to further develop their ventures through business support and acceleration.
The YouthADAPT Challenge aims to support youth-led enterprises to accelerate and scale-up innovative solutions for climate adaptation and resilience. The solutions target key environmental, social, and economic sectors affected by climate change, with a clear value proposition to scale up for greater impact and to create specified direct jobs.
YouthADAPT aims to strengthen inclusive growth and broaden investment and economic opportunities for youth in Africa through entrepreneurial skills development by providing training, mentorship, and financing to youth-led businesses (50% women-owned). The first edition of the awards was launched on 06 September 2021.
- Provide a financial contribution to cover the cost of program implementation and 50% of grant funding
- Participate in project missions and field visits to review progress with select beneficiary enterprises
- Support the project team to provide clarity on climate change adaptation and resilience in the training component, including tracking the creation of adaptation jobs
- Coordinate project monitoring and evaluation.
- The most innovative youth-owned enterprises on the continent are scaled up
- The viability of selected businesses is improved, to help sustain their impact on climate change adaptation
- 50% of the selected businesses are led by women.
- Young innovators and MSMEs equipped with customised business development skills and resources.
- The short-term growth of youth-owned enterprises is supported, with links to private equity and loan products for longer term growth.
- Expansion of partnership, knowledge sharing, exchange and learning through a network of youth entrepreneurs in Africa.
- Inclusive growth, investment and economic opportunities for youth;
- Adaptation, innovation and jobs integrated and for jobs;
Total: USD 1,400,000
Budget for Knowledge Partner (Project Implementation Cost) - USD 400,000
Grant Awards (50% of total grant awards) – USD 1,000,000
2022 Disbursement:
60% Disbursement of Project Implementation Cost to Knowledge Partner – USD 240,000
50% of Grant Awards – USD 500,000
Staple Crops Processing Zone (SCPZ): funding proposal to the Green Climate Fund
The target countries of Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Togo and Zambia are regions experiencing high deforestation, poor agriculture yield and increasing poverty exacerbated by climate change. Across all four countries, climate variability and change has become a major threat to sustainable development.
As part of efforts to address these challenges, the four countries are implementing national projects to establish Staple Crops Processing Zones: initiatives designed to concentrate agro-processing activities within areas of high agricultural potential to boost productivity and integrate production, processing and marketing of selected commodities. These initiatives are purposely built shared facilities, to enable agricultural producers, processors, aggregators and distributors to operate in the same vicinity to reduce transaction costs and share business development services for increased productivity and competitiveness.
Developing adequate infrastructure (energy, water, roads, ICT) in rural areas of high agricultural potential should attract investments from private agro-industrialists/entrepreneurs to contribute to the economic and social development of rural areas.
The Staple Crops Processing Zone (SCPZ) development program aims to transform agriculture production in regions experiencing high deforestation, poor agriculture yield and increasing poverty exacerbated by climate change, including the target countries of Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Togo and Zambia.
The specific objectives of SCPZ are: (i) improving access to seed capital through grants and matching grants; (ii) supporting productivity enhancement through introduction of new technologies and agricultural inputs; (iii) improving access to infrastructure by supporting investment; (iv) improving the capacity of producer cooperative through training and TA, especially for targeted women and youth groups; (v) facilitating market linkages throughout-growers’ schemes; and (vi) facilitating on-farm value addition by targeting limited value chains and linking farmers to the supply chain.
GCF financing is sought to strengthen one of the project components of SCPZ in Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Togo and Zambia.
- Through the technical assistance program, AAAPwill accelerate the mobilization of adaptation finance.
- Increased carbon sinks in soil and above-ground biomass
- Reduced carbon dioxide/other greenhouse gas emissions from farms due to efficient energy use
- Increased renewable energy production from biomass, either as a substitute for fossil fuels or as a replacement for burning of fuel wood or crop residues
- Fewer incidents of bare soils, reduced soil erosion and increased water percolation.
- Reduced emissions through low-emission energy access and power generation
- Reduced emissions due to improved waste management, including by recycling waste and use of waste in biogas systems
- Reduction of emissions from land use and deforestation, and enhancement of forest carbon stocks.
-
Increased resilience, including to extreme events such as droughts and floods, and enhanced livelihood of about 55% of highly vulnerable people and communities
-
Increased access to better health and wellbeing, and food and water security to over 100,000 beneficiaries, in addition to provision of alternative sources of energy
-
Increased resilience of ecosystems and ecosystem services in forests and savannas
USD 427 million:
- Funding proposal to GCF seeking USD 174.02 million (USD 130.02 million grant and USD 44 million loan)
- AfDB providing USD 111.2 million (USD 85.2 million loan and USD 26 million grant)
- Co-financiers:
European Union, USD 10.4 million (grant)
BOAD, USD 17.6 million (loan)
Korea Exim Bank, USD 50 million (loan)
Korea Fund, USD 5 million (grant)
Islamic Development Bank, USD 31 million (loan)
Governments of target countries, USD 28 million (counterpart financing)
Global Center on Adaptation, AfDB host regional forum on the future of resilient food systems in Africa
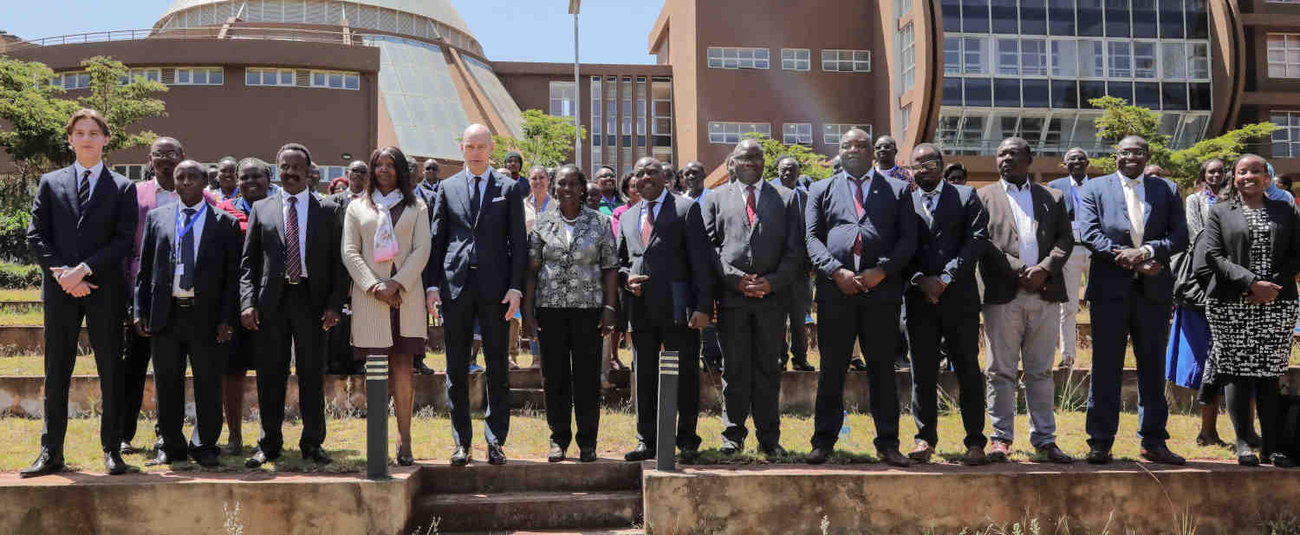

The Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) in collaboration with the African Development Bank and the Wangari Mathai Institute have concluded a three-day regional forum on the future of resilient food systems in Africa.
The Forum, called the Future of Resilient Food Systems in Africa – AAAP Digital Solutions for a Changing Climate provided training aimed at strengthening the capacity of stakeholders from across Eastern Africa to design and implement solutions to improve food security and climate resilience and to facilitate knowledge sharing among farmers on approaches to scale up the use of Digital climate-informed advisory services, or DCAS.
Digital climate-informed advisory services are tools and platforms that integrate climate information into agricultural decision-making. These services range from digital mobile apps, radio, and online platforms to digitally enabled printed bulletins based on climate models and extension services that utilize climate information platforms.
DCAS offers crucial opportunities to build the resilience of small-scale producers in the face of worsening climate change impacts. From seasonal forecasts to pest advisories, effectively designed services provide producers with the resources to adapt to climate shocks and plan for new climate conditions.
Globally, more than 300 million small-scale agricultural producers have limited or no access to such services because service provision is still fragmented, unsustainable beyond project cycles, and not reaching the last mile.
Speaking at the opening ceremony of the forum, Professor Patrick Verkooijen, CEO of Global Center on Adaptation called for urgent financial support to put Africa on the path of food sovereignty.
“Africa needs urgent support to scale up the implementation of adaptation solutions that are already yielding good results for irrigation, developing drought-resistant seeds, crops and livestock diversification, “ he said.
“Through the African Adaptation Acceleration Programme, AAAP, we are rolling out a $350 million project to build resilience for food and nutrition security in the Horn of Africa towards mobilising new digital climate technology for market information, insurance products, financial services that can and must be tailored to smallholder farmers’ needs”, he added.
Speaking on behalf of the African Development Bank’s East Africa Regional Director General, Nnenna Nwabufo, Dr Pascal Sanginga, Regional Sector Manager for Agriculture and Agro-Industries noted that the forum was timely, coming hot on the heels of the recently concluded Dakar 2 Feed Africa-Food Sovereignty and Resilience summit , organised by the African Development Bank.
“The Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP) is already contributing to closing Africa’s adaptation gap by supporting African countries to make a transformational shift in their development pathways by putting climate adaptation and resilience at the center of their policies, programs, and institutions. There is no doubt that AAAP will be a strong component of the Country Food and Agricultural Delivery Compacts to accelerate the transformation of Africa’s food systems and build a more resilient Africa”, he said.
Professor Stephen Kiama Gitahi, Vice Chancellor of the University of Nairobi, reiterated the relevance of the forum pointing out that 70% of the population in Eastern Africa live in rural areas and depend on agriculture for their livelihoods. He encouraged the trainers to simplify the modules in a manner that removes the fear for technology and accelerate adaptation for rural farmers. Citing the legacy of late Professor Wangari Maathai he stated:
“We acknowledge that gaps exist on climate adaptation in the rural communities and those can be smartly bridged with the use of digital smart agriculture and climate innovations to create great conservation impact in our region.”
The forum brought together stakeholders from ministries of agriculture, related government agencies, public research institutions, farmer organizations, universities and non-profit organizations working on climate adaptation for food security in Eastern Africa. These included participants from Djibouti, Eritrea, South Sudan, Burundi, Rwanda, Mauritius, Tanzania, Seychelles, Sudan, Ethiopia, Rwanda and Kenya.
About Global Center on Adaptation
The Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) is an international organization which works as a solutions broker to accelerate action and support for adaptation solutions, from the international to the local, in partnership with the public and private sector. Founded in 2018, GCA operates from its headquarters in the largest floating office in the world, located in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. GCA has a worldwide network of regional offices in Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire; Dhaka, Bangladesh and Beijing, China.
About the Wangari Maathai Institute, University of Nairobi
The Wangari Maathai Institute (WMI) for peace and environmental studies is a global centre for teaching and research on environmental management, governance, peace and conflicts and the nexus between peace and democracy. The centre was founded in 2009 with the support of the Government of Kenya (GoK), the African Union(AU) and the African Development Bank(AfDB) to celebrate and immortalize the work of the late Nobel Laurete
Prof.Wangari Maathai who was a global champion on environmental conservation and governance. The centre trains future leaders and Champions for environment. The Centre is located in the serene environment in Upper Kabete suburb of Nairobi City.
Ethiopia: African Development Fund approves $13.95 million grant for Borana Resilient Water Development for Improved livelihoods program

The Board of Directors of the African Development Fund has approved a $13.95 million grant to the Government of Ethiopia to implement the first phase of a livelihood improvement project for pastoralist communities in Ethiopia’s drylands.
The Borana Resilient Water Development for Improved Livelihoods Program will enhance access to climate-resilient, gender-sensitive integrated and sustainable water and sanitation services. Phase one of the program will focus on developing well-field infrastructure and a transmission pipeline to a storage tank.
The Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) will contribute €300,000 to the program to strengthen adaptation and resilience, under the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program, a partnership with the African Development Bank.
GCA will provide technical assistance for the development of an in-depth understanding of climate related risks to improve the climate resilience of the catchments. It will also design a strategy and approach to involve local communities, and carry out a gender climate vulnerability and resilience assessment as an integral part of climate adaptation.
The scheme will bolster access to water supplies in Elweya, Dubluk, and Yabel districts, covering 62 rural villages and 12 towns with an estimated population of 308,576 people—half of them women – and 975,750 livestock.
Osward Chanda, Director of Water Development and Sanitation at the African Development Bank, said: “The Bank’s support is a coordinated response with the Government of Ethiopia to mitigate water, sanitation and climate challenges, develop sustainable water structures, and improve socioeconomic outcomes in Borana.”
Phase one of the program will be implemented over four years. The Borana Resilient Water Development for Improved Livelihoods Program will lead to improved health outcomes, nutrition and food security.
In the last 15 years, Ethiopia has suffered eight major droughts with adverse consequences for its economy and the livelihoods of its people, resulting in forced migration and displacement of humans and livestock. Droughts in the Borana area have been linked to increased violent conflict and boundary disputes, and unsafe drinking water, and inadequate sanitation, which remain critical health concerns in the Ethiopian lowlands.
The Borana program aligns with the Bank’s Strategy for Addressing Fragility and Building Resilience in Africa as well as its Gender Strategy, Jobs for Youth in Africa Strategy, Multi-Sectoral Nutrition Action Plan, and the Bank’s Climate Change Policy which seeks to invest in programs which boost climate resilience and adaptation.
Contact:
Olufemi Terry, Département de la communication et des relations extérieures, medias@afdb.org(link sends e-mail)
Ethiopia Wheat Value Chain Development Project (EWVCDP)
The wheat demand gap in Ethiopia is 0.6 million MT per year and is growing. As a result, the country is faced with a huge import bill estimated to be USD 540 million annually to satisfy the local demand for wheat. In addition, wheat productivity is only at 3.0 MT/ha. Increasing wheat production is a core part of Ethiopia’s Ten-Year Development Plan (2021-2030) to accelerate economic progress and ensure national food security.
To achieve self-sufficiency and be a net exporter by 2025/26, the Government of Ethiopia launched the National Wheat Flagship Program (NWFP) for wheat self-sufficiency and import substitution, a program to expand and promote irrigated wheat production on a total area of one million Ha in 2022/23 season and expand it by 5-10% annually. To support achieve this target, the African Development Bank financed the Ethiopia Wheat Value Chain Development Project (EWVCDP) to contribute to meeting Ethiopia’s wheat demands, sustain the import substitution goal and produce surplus for export.
The objective is to improve production and productivity of wheat in Ethiopia with the aim of promoting national wheat self-sufficiency, regional trade, and exports, at the same time, increase incomes and improved livelihoods for wheat value-chain actors.
- Conduct a suitability analysis to assess local climatic conditions and food security, the structure of the local economy and access to resources, and to identify parts of the country that are performing below potential in terms of agricultural productivity
- Using a hybrid of climate risk assessment tools to generate micro-region climate risk maps and information to highlight local enabling conditions for particular interventions to accelerate adaptation in agriculture
- Facilitate the production of a feasibility and blueprint of the integration of digital adaptation solutions
- Integrate digital climate adaptation solutions in the wheat farmer registration system
- Support capacity building of extension agents and stakeholders to deploy digital climate advisory services and digital adaptation solutions in the delivery and implementation of agricultural extension services
- Facilitate access to farm inputs (seeds and fertiliser)
- Improve the efficiency of existing irrigation schemes through rehabilitation and maintenance of infrastructure –desilting, drainage, extend canals
- Strengthened and established full package mechanization service centres in the wheat growing areas
- Delivered extension and advisory services to farmers on agricultural practices (soil, crop and water management packages, disease and pest management and post-harvest handling)
- Increased wheat production through mechanisation, extension and advisory services
- Enabled market linkages, Agri-Finance and private investments
- Rehabilitated and expanded Irrigation Infrastructure by increasing the efficiency of existing irrigation schemes
AfDB Investment USD 54 million
Total of USD 94.30 Million
AAAP webinar: Innovation essential for climate-smart future, but it's not enough
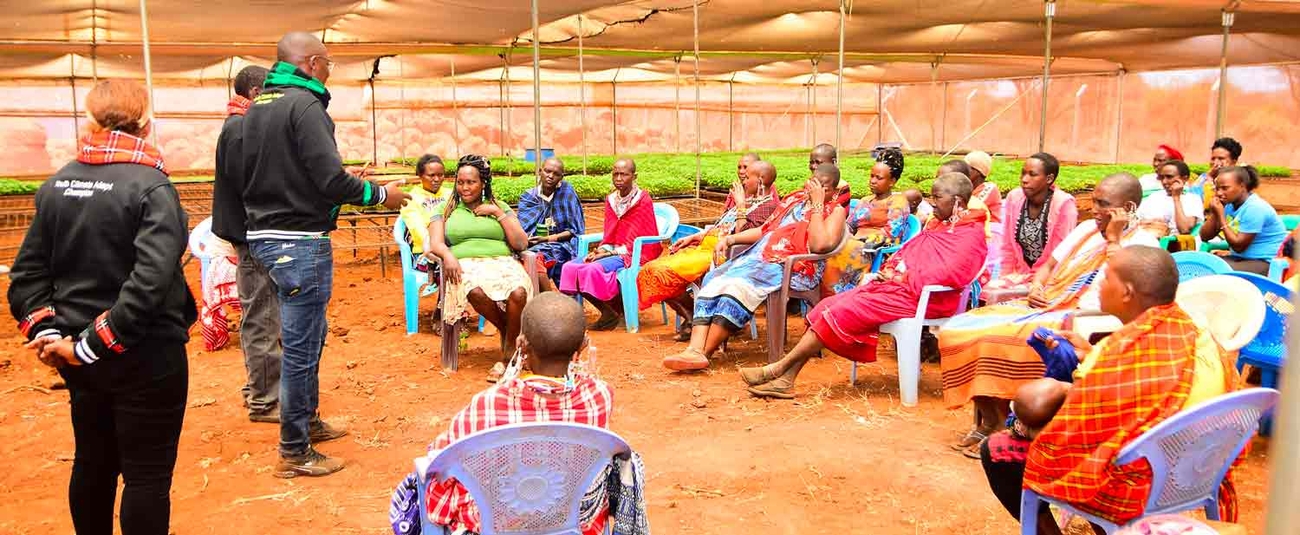

The 2022 United Nations Climate Change Conference, COP27, is dubbed ‘African COP’ as the impact of climate change on African countries will be a key theme of discussions. Agriculture and food systems will also be a critical focus of COP27, with Saturday, 12 November, dedicated to both themes, in addition to adaptation. Also high on the climate agenda is the role of the youth, as 10 November is dedicated to their participation.
Ahead of COP27 and in line with their commitment to this youth agenda, the African Development Bank and the Global Center on Adaptation hosted a webinar to examine ways to make agriculture attractive to the youth.
The webinar titled, Are Climate-Smart and Digital Agriculture Solutions the Silver Bullet to Attract Youth, highlighted the potential of climate-smart and digital agriculture in attracting young people and thereby rejuvenating an aging global agricultural sector.
Dr. Kevin Kariuki, African Development Bank’s Vice President for Power Energy, Climate and Green Growth, pointed out the challenges the agriculture sector faces due to the changing climate change.
“Agriculture across most of sub-Saharan Africa is still predominantly rain-fed and therefore extremely vulnerable to both short-term fluctuations and long-term changes in climate conditions. It is the most exposed sector with estimates indicating that climate change will cause a decrease in yields of 8 – 22% for Africa’s rain-fed staple crops over the next 20 years,” Kariuki said.
Dr. Beth Dunford, African Development Bank’s Vice President for Agriculture, Human and Social Development, noted that while agriculture holds tremendous potential for job creation in Africa, its current traditional form is not attractive to young people for various reasons, including negative perceptions.
“Who wants to wear overalls, dig the field with a hoe or drive a tractor when we can do it in a suit and dust coat, right? However, technology makes agriculture cool enough to motivate them to use tech-enabled enterprises to be part of agricultural value chains,” Dunford said.
Prof. Anthony Nyong, Senior Director for Africa at the Global Centre on Adaptation, said: “There is a gap in the agriculture sector in Africa, and that is in the use of digital solutions.”
AAAP’s Climate Smart Digital Technologies for Agriculture and Food Security Pillar is scaling up access to digital technologies and associated data-driven agricultural and financial services for at least 30 million African farmers.
In the African Development Bank’s Program to Build Resilience for Food and Nutrition Security in the Horn of Africa (BREFONS), currently ongoing in Djibouti, Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, South Sudan, and Sudan, the AAAP is facilitating the integration of climate-smart digital technologies for adaptation and resilience.
“The project will increase the productivity of crops and livestock by 30%, reaching about 1.3 million farmers and pastoralists using climate services such as index insurance. About 55,000 additional jobs will be created for youth and women,” said Oluyede Ajayi, Africa Program Lead, Food Security and Rural Well Being, Global Centre on Adaptation.
Panelists said the youth must utilize their digital skills to accelerate the transformation of the agricultural sector, which forms the central pillar of Africa’s economy. They urged participants to contribute to solutions that enhance market linkages to promote agribusiness.
“Africa’s significant youth population faces rising unemployment with myriad negative consequences. These challenges are further exacerbated by climate shocks, skill gaps & limited preparedness to address the effects of climate change,” said Andre-Marie Taptue, Principal Economist at the African Development Bank's Jobs for Youth program.
AAAP’s YouthAdapt program promotes sustainable job creation through entrepreneurship in climate adaptation and resilience in Africa by unlocking $3 billion in credit for adaptation action.
Last year, the first set of ten young African entrepreneurs and Micro, Small, and Medium-sized Enterprises offering innovative solutions and business ideas that can drive climate change adaptation and resilience were awarded at COP26 in Glasgow. This year the Africa Youth Adaptation Competition 20 enterprises across Africa will each receive up to $100,000 in addition to mentorship and coaching to support their climate change adaptation innovation.
Panelists included Claude Migisha from the African Development Bank, Dr. Fleur Wouterse, and Aramide Abe from the Global Center of Adaptation. They shared their views on how AAAP was shaping and adding value to the Bank Digital Agriculture Flagship program, ways to accelerate investor engagement in agriculture adaptation, and how the YouthADAPT was moving the needle on entrepreneurship, unlocking finance and job creation.
Gislaine Matiedje Nkenmayi from Mumita Holdings, a recipient of the 2021 YouthADAPT Challenge award, shared her experience on how the $100,000 grant transformed her enterprise.
“With the grant, we were able to reach out to more than 10 cooperatives with a total of 257 smallholder farmers, to whom we offer free advisory services, low-cost greenhouses and solar-powered irrigation systems. We have been able to expand production from 100kg to 1000kg of fresh vegetables weekly,” Nkenmayi said.
In her concluding remarks, Edith Ofwona Adera, Principal Regional Climate Change Officer and AAAP coordinator at the Bank stressed the need to strengthen adaptation and resilience measures and expedite mainstreaming climate adaptation for transformation at scale. She called for the engagement of the private sector, given the role they can play in adapting to climate change, financing adaptation, and supporting others through products and services for resilience.
Speech by Dr. Akinwumi A. Adesina President, African Development Bank Group at the Thirty-Fifth Ordinary Session of the Assembly of the African Union Addis Ababa, 5-6 February 2022

-
Mobilizing Financing for Africa’s Accelerated Economic Recovery, Development and Integration
- Your Excellency Macky Sall, President of the Republic of Senegal and Chairperson of the African Union
- Your Excellency Abiy Ahmed, Prime Minister of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, Our Gracious Host
- Your Excellencies Heads of State and Government
- Your Excellency Moussa Faki Mahamat, Chairperson of the Africa Union Commission
- Your Excellency Amina Mohammed, Deputy Secretary General of the United Nations, Representing the Secretary General of the United Nations
- Your Excellency Monique Nsanzabaganwa, Deputy Chairperson of the African Union Commission
- Honorable Ministers
- Honorable Commissioners of the African Union Commission
- The Executive Secretary of the UN Economic Commission for Africa
- The Secretary General, the African Continental Free Trade Area Secretariat
- Heads of African Union Organs and Institutions
- Chief Executives and Heads of Regional Economic Communities
- Permanent Representatives to the African Union
- Members of the Diplomatic Corps
- Distinguished Ladies and Gentlemen
I deeply appreciate this honor and opportunity offered me by the Chairperson of the African Union Commission, the Deputy Chairperson, Commissioners, and the Permanent Representatives Committee.
I wish to congratulate His Excellency, President Macky Sall upon his election as the Chairperson of the African Union. Your Excellency, President Macky Sall, you have taken on the baton from His Excellency, President Felix Antoine Tshisekedi, with whom we have had the distinguished pleasure of working closely during his tenure as Chairperson.
Thank you, President Tshisekedi, for your remarkable leadership and outstanding service at the helm of our Union.
Your Excellencies, I will be speaking to you today on “Mobilizing Financing for Africa’s Accelerated Economic Recovery, Development and Integration”.
This is a very important and timely discussion, given that the African Development Bank has been given the mandate by a decision of the African Union to lead the mobilization of resources for Africa, to achieve Agenda 2063.
As this is the first time that I have had the opportunity to address you since my re- election, Your Excellencies, I wish to express to you, individually and collectively, my deep appreciation for your strong and unanimous support, and those of your Ministers of Finance and Foreign Affairs, for my re-election as President of the African Development Bank in August 2020. I thank H.E. President Muhammadu Buhari, my President, especially, for his trust, confidence, and unflinching support during this assignment which he sent me on to accomplish for Africa. I also wish to thank all our former heads of state for their steadfast support.
As always, I will continue to serve our beloved continent, and work with you to relentlessly accelerate the achievement of Agenda 2063: the Africa we want.
Your Excellencies, meeting today, physically, is itself an important milestone; a welcome relief following two years of the Covid-19 pandemic that has upended the world in an unprecedented manner.
It has been a global economic cyclone. Africa witnessed a decline in GDP growth of 2.1% in 2020, its lowest in twenty years. Africa’s GDP fell by $165 billion. Over 30 million jobs were lost and over 26 million people fell into extreme poverty.
I wish to commend the leadership efforts of the African Union, and our Heads of State and Government, for the critical roles you have played in dealing with the pandemic and the socio-economic challenges in its wake. Today, thanks to these efforts 11% of the population has been fully vaccinated, and another 16% has been partially vaccinated.
However, while developed countries have moved to booster shots, Africa is still struggling with basic shots.
Your Excellencies, we must learn from this experience. Africa can no longer outsource the security of the lives of its 1.4 billion people to the benevolence of others.
We must secure African lives!
It is time your Excellencies, to build Africa’s healthcare defense system. This must be based on three strategic priorities.
First, building Africa’s quality healthcare infrastructure. Second, building Africa’s pharmaceutical industry and Third, building Africa’s vaccine manufacturing capacity.
Africa needs $600 million to $1.3 billion to meet its goal of attaining 60% vaccine production by 2040. Investing in health is investing in national security.
The African Development Bank plans to invest $3 billion to support pharmaceutical and vaccines manufacturing capacity for Africa.
To address the socio-economic impacts of the pandemic and support economic recovery, Africa will need some $484 billion over the next 3 years. To eliminate extreme poverty by 2030, the continent will need $414 - $784 billion per year. Africa will need $7-$15 billion a year to deal with climate change. The continent will also need between $68 -$108 billion per year to fix the infrastructure financing gap.
Your Excellencies, we must drastically mobilize a lot more resources!
The African Development Bank, as the premier development financing institution in Africa, has been mobilizing resources to meet this challenge. Thanks to your support, the general capital of the Bank was increased in 2019 by 125%, rising from $93 billion to $208 billion, the highest since its establishment in 1964.
These resources have allowed the African Development Bank to scale up support to African economies to tackle the pandemic. The Board of Directors of the Bank approved a Crisis Response Facility of up to $10 Billion. The Bank also launched a $3 Billion Fight COVID-19 Social Bond on the international capital markets, which was the largest ever US- dollar denominated social bond in world history. The Bank provided $ 27 million as grants to the African Centers for Disease Control.
Your Excellencies, over the past six years, the African Development Bank has provided about $39 billion in financing to the continent in support of its High5 priorities to: light up and power Africa; feed Africa; integrate Africa; industrialize Africa; and improve the quality of life of the people of Africa.
These High5s are the accelerators for achieving Agenda 2063.
An assessment of these High5s by the United Nations Development Program indicated that the High5s would lead to the achievement of 90% of the Agenda 2063 goals and 90% of the Sustainable Development Goals targets.
Your Excellencies, so much has been achieved on the High5s. In the past five years, the work of the African Development Bank Group has impacted the lives of 335 million people – fast tracking the move towards achieving the Agenda 2063 goals. Close to 21 million people have gained access to electricity. Nearly 76 million people have benefitted from agricultural technologies for food security. More than 12 million people have gained access to finance through private sector investee companies. Over 69 million people have been provided with improved transport. And 50 million people have gained access to improved water and sanitation.
Your Excellencies, Feeding Africa remains a top priority. Our Technologies for African Agricultural Transformation which we call TAAT, has provided drought tolerant technologies for 12 million farmers across Africa. The Bank is supporting the creation of special agro-industrial processing zones in 18 countries to help drive the transformation of agriculture as a major source of wealth and jobs.
Your Excellencies, the African Development Bank, the International Fund for Agricultural Development, and the African Union Commission launched the Facility for African Food Security and Nutrition at the UN Food Systems Summit. Now dubbed Mission 1 for 200, this financing facility will help to mobilize $1 billion, provide climate resilient and nutrition-rich technologies for 40 million farmers, produce 100 million metric tons of food, and feed 200 million people. This will help to reduce food insecurity in Africa by 80%.
This is particularly crucial in 2022, the Year of Nutrition in Africa.
Your Excellencies, the Bank is investing heavily in renewable energy. This includes the world’s largest concentrated solar power system in Morocco and the Lake Turkana energy project, the largest windfarm in Africa. Together with Africa50, we have co-financed the 3,000 MW Ben Ban solar power project in Egypt. The Bank is also implementing a $20 billion Desert-to-Power initiative to develop 10,000 MW of solar power for the Sahelian zone of Africa, to provide electricity for 250 million people. This will become the largest solar zone in the world.
Your Excellencies, Africa faces a huge challenge with energy transition, and with climate change. The Bank is working to establish an African Just Energy Transition Facility that will support transition from coal and heavy fuel oil into clean energy. However,
Africa will need an energy mix that includes natural gas, to ensure stability of its energy systems, power industries, and ensure competitiveness.
Your Excellencies, we must go beyond “a just energy transition” to “a just energy system.”
Africa cannot be poor in an environmentally sustainable manner.
To support Africa's adaption to climate change, the African Development Bank and the Global Centre for Adaptation have launched the African Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAA-P) with the goal of mobilizing $25 billion for climate adaptation for Africa.
We must revive the Lake Chad Basin!
We must save the Sahel from desertification! We must complete the Great Green Wall!
The African Development Bank has committed $6.5 billion towards the Great Green Wall. I would like to thank UN secretary General, Antonio Guterres, and my dear sister, Amina Mohammed, Deputy UN Secretary General, for their exceptional support for this initiative.
As we move from COP26 in Glasgow to COP27 in Sharm El Sheikh, to be hosted by President El Sisi, developed countries need to meet their $100 billion commitment on climate finance to support developing countries. This will help Africa.
Promises made must be promises kept.
The issuance of Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) of $650 billion by the International Monetary Fund has helped substantially, but Africa only received $33 billion worth of SDRs. African Heads of State at the Paris Summit on African Economies, with the strong support of President Emmanuel Macron, called for a re-allocation of $100 billion to Africa. You also asked that the re-allocated SDRs pass through the African Development Bank, as a prescribed holder of SDRs.
Your Excellencies, I will appreciate your continued strong support for this. Passing the re-allocated SDRs for Africa through the African Development Bank will serve Africa very well.
First, as a AAA-rated financial institution, the African Development Bank will be able to leverage the SDRs by 3-4 times. For example, a $50 billion re-allocation through the African Development Bank will be leveraged to deliver $200 billion to African economies.
Second, the African Development Bank will help to recapitalize other African financial institutions, many of which the Bank helped to establish, including the Afreximbank, the West African Development Bank, the East African Development Bank, the Development Bank of the Central African States, the Africa Guarantee Fund, Africa-Reinsurance Company, Shelter Afrique, Trade and Development Bank, Africa50, as well as the Development Bank of Southern Africa.
I wish to also use this platform to advocate for additional shareholder funding for these institutions to play their mandated roles.
Your Excellencies, to protect Africa from future economic shocks, it is now critical to establish an African Financial Stability Mechanism. Africa is the only region of the world that has no liquidity buffers to protect the continent against shocks. Europe has … Asia has… Latin America has … The Middle East has. These regions had more protection from the economic effects of the pandemic.
Africa did not.
This has led to widespread regional spill-over contagion effects, and instability.
African economies must be protected. The African Financial Stability Mechanism will protect African economies.
Your Excellencies, we need more resources to finance Africa’s low-income countries, especially those facing fragility. The African Development Fund, the concessional institution of the African Development Bank Group, has helped to support these countries with $8.5 billion in the past five years.
The African Development Fund has delivered impressive results. The Fund financed the landmark Senegambia bridge.
It financed the Rosso bridge between Mauritania and Senegal.
It financed Corridor 13 road between Central African Republic and the Republic of Congo.
It financed the road network rehabilitation project for Comoros. It financed the Revenue Authority project for Togo.
It financed the Bas Mangoky rice irrigation project for Madagascar.
The Fund is also financing the Kandadji multipurpose dam project for Niger. However, more resources are needed to meet the rising needs of low-income
countries. I wish to request the strong support of Your Excellencies, African Heads of State and Government, and of the African Union Commission, for the 16th Replenishment of the African Development Fund later this year.
Your Excellencies, with its $25 billion in equity, the African Development Fund can leverage up to $33 billion of additional financing for low-income countries. To achieve this, we need your support to change the article in the charter of the African Development Fund that does not allow it to go to market to leverage resources. This is top priority.
We are also leveraging private investments into Africa, in innovative ways. Your Excellencies, the Africa Investment Forum, established by the African Development Bank and its partners, has helped to secure investment interests worth more than $78 billion. This spectacular level of interest includes a $24 billion transaction for the liquefied natural gas project in Mozambique. We are proud that that this project will make Mozambique the third-largest producer of liquified natural gas in the world.
The project experienced challenges from insecurity, but thanks to your collective leadership, all is now back on track.
Your Excellencies, we must now link security, investment, growth, and development closely together. To enhance the security of Africa, the African Development Bank is currently developing Security Indexed Investment Bonds. Proceeds from these bonds, when developed, will support countries and regional economic communities to do four things. First, to upgrade security architecture. Second, to repair damaged infrastructure in conflict-affected zones. Third, to rebuild social infrastructure. And fourth, to protect zones with strategic investments.
Your Excellencies, we must build a better future for our youth. It is time to create youth- based wealth all across Africa. To boost financial support for the businesses of our youth, the African Development Bank Group is exploring with countries the establishment of Youth Entrepreneurship Investment Banks. They will be first rate financial institutions run by the youth for the youth.
Your Excellencies, to unleash the business potential of women, the Bank’s Affirmative Finance Action for Women in Africa (AFAWA) is mobilizing $5 billion for women businesses.
AFAWA is now working at scale. Over $425 million was disbursed in 2021 to banks for lending to women businesses. This year, we will disburse $500 million for women businesses.
Our vision is clear: When women win, Africa wins!
Your Excellencies, the African Continental Free Trade Area offers the continent incredible opportunities to accelerate Africa’s development. To achieve this goal, the African Development Bank has invested massively in infrastructure, from roads, transport corridors, airports, seaports, railways, and digital infrastructure. Over the past 10 years, we have invested over $40 billion in infrastructure. We are connecting nations, connecting businesses, connecting people.
Your Excellencies, with Agenda 2063, Africa’s glorious future beckons! Politically, we are ready.
Financially, we are strong and prepared.
Last year, the African Development Bank was ranked the Best Multilateral Financial Institution in the world by Global Finance, the leading US Financial Magazine.
The sun is shining!
Now let us surge forward, overcoming challenges in our way, with our eyes firmly focused on the goal: the Africa we want.
An Africa prosperous, peaceful, and stable. An Africa where the youth thrive and prosper.
An Africa where our women can reach their full potential. An Africa supported by strong financial institutions.
An Africa that develops with pride, looking inwards to mobilize domestic resources, and ending illicit capital flows.
Your Excellencies, with your bold and visionary leadership, a new Africa is emerging. Just as the eagle soars above the storms, so will Africa soar and achieve its destiny.
Africa is destined for greatness!
Thank you very much Your Excellencies.