
AAAP in the Media
Displaying 1 - 12 of 12
Experts share lessons learned on gender-responsive climate action during Commonwealth NDC webinar
This year, Edith Ofwona Adera, Coordinator of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP) and the African Development Bank’s Regional Principal Officer for Climate Change and Green Growth, marked International Women’s Day in a special way.
Adera took part in a panel discussion organised by the Commonwealth Secretariat, reflecting this year’s theme: Gender equality today for a sustainable tomorrow.
The panel, hosted by Jennifer Namgyal of the Commonwealth Secretariat, brought together experts who shared their experiences and lessons learned on integrating gender equality in Nationally Determined Contributions, or NDCs, across their respective regions and institutions. NDCs are national plans highlighting climate actions, including targets, policies and measures that governments aim to implement.
Hannah Girardeau, of the NDC Partnership Support Unit, kicked off the session with a presentation on the findings of an analysis of gender considerations in revised NDCs of the partnership’s member countries. The assessment revealed that more countries had now included the fundamental building blocks of gender-responsive climate action in their policies and plans. Girardeau noted that there is a need to invest in other critical elements such as conducting gender analyses, developing indicators, and establishing gender-responsive budgets to complement progress achieved.
Adera agreed with her. “As climate change impacts affect people differently, the responses need to be differentiated, based on identified unique needs, informed by disaggregated data,” Adera added.
To address this challenge, the African Development Bank is supporting national statistical systems in five countries through a Capacity Building for Gender Statistics and Monitoring Systems project. The project aims to produce quality, comparable and regular gender statistics to address national data gaps, strengthen monitoring systems, and integrate gender indicators across sectors.
Bertha Chiudza of the Green Climate Fund said a key requirement for all its financed activities is to ensure gender considerations are included in the development of action plans and assessments. “For its support on Nationally Determined Contributions, the Green Climate Fund ensures that gender considerations are brought in from planning and design, implementation and reporting across the sectors prioritized by countries, while ensuring inclusive stakeholder consultations,” Chiudza stated.
Sasha Jattansingh, the Commonwealth Climate Finance Adviser, gave insights into Antigua and Barbuda’s actions to mainstream gender equality into Nationally Determined Contributions. The country recognized equity issues and committed to a just energy transition with a strong focus on gender, Jattansingh noted. Antigua and Barbuda is an example of a country that has made progress in developing an inclusive renewable energy strategy that promotes socially inclusive, gender-responsive, and accessible investment opportunities.
Anna Rojas of the International Union for Conservation of Nature also shared her experiences and lessons in integrating gender into Nationally Determined Contributions, pointing out that biodiversity issues are now being integrated more consistently in these plans. She called for local-level conversations with women to tap into their strengths and rich knowledge. “Engagement with women will avoid dismal adaptation because, the more we identify needs, strengths, and solutions, the better we will be prepared,” she emphasized.
The African Development Bank is rolling out a detailed analysis of climate-gender hotspots in Rwanda. Adera said it would highlight real gender gaps and deep vulnerabilities, and how best climate interventions can address these gender issues.
Finance also emerged as one of the vital tools to promote gender equality in Nationally Determined Contributions. Innovative financial instruments and solutions must come into play when addressing gender inequalities for climate change interventions, noted Unnikrishnan Nair of the Commonwealth Secretariat.
African Youth Adaptation Solutions Challenge – Cycle 1
Through the African Youth Adaptation Solutions (YouthADAPT) Challenge, the AAAP aims to inspire and support the commercialisation of climate change adaptation solutions, driven by African youth entrepreneurs. The YouthADAPT Challenge is open to solutions (products, services, tools, or ideas) targeted at climate change adaptation and increasing resilience.
Admissible solutions can represent:
- An adaptation solutions business that has not been scaled and is not in widespread use
- An existing resilience and adaptation solutions business or product
- A commercially viable means to raise awareness or scale uptake of specific adaptation solutions.
Applicants must be 18–35 years old and registered and operating in Africa. Their venture must be youth-led while delivering climate adaptation or resilience solutions addressing a real-life challenge. 50% of the finalists will be women-owned or women-led enterprises. Winners will receive a business grant of up to $100,000 and the opportunity to further develop their ventures through business support and acceleration.
The Cycle 1 (2021) winners were unveiled at COP26 in Glasgow, United Kingdom, in a ceremony held at the Africa Pavilion. They include Mumita Holdings Limited, Cameroon, Salubata Technological Innovations Limited, Nigeria, Sustainable Builders, Zambia, Global Farms and Trading Company Limited, Ghana, Miama General Dealers Limited, Zambia, Kimplanter Seedling and Nurseries Limited, Kenya, Irri Hub Ke Limited, Kenya, Soupah Farm en- Market Limited, Nigeria, Simkay Green Global Ventures, Nigeria and Bleaglee Waste Management Limited, Cameroon.
The YouthADAPT Challenge aims to support youth-led enterprises to accelerate and scale-up innovative solutions for climate adaptation and resilience that will also lead to decent jobs for youth. The solutions target key environmental, social, and economic sectors affected by climate change, with a clear value proposition to scale up for greater impact and to create specified direct jobs.
The Challenge aims to strengthen inclusive growth and broaden investment and economic opportunities for youth in Africa through entrepreneurial skills development by providing training, mentorship, and financing to youth-led businesses (50% women-owned). The first edition of the awards was launched on 06 September 2021.
- Provide a financial contribution to cover the cost of program implementation and 50% of grant funding
- Participate in project missions and field visits to review progress with select beneficiary enterprises
- Support the project team to provide clarity on climate change adaptation and resilience in the training component, including tracking the creation of adaptation jobs
- Coordinate project monitoring and evaluation.
- The most innovative youth-owned enterprises on the continent are scaled up
- The viability of selected businesses is improved, to help sustain their impact on climate change adaptation
- Inclusiveness promoted through 50% of the selected businesses being led by women.
- Young innovators and MSMEs equipped with customised business development skills and resources;
- The short-term growth of youth-owned enterprises supported, with links to private equity and loan products for longer term growth.
- Expansion of partnership, knowledge sharing, exchange and learning created through a network of youth entrepreneurs in Africa.
- Inclusive growth, investment and economic opportunities for youth are strengthened through entrepreneurial skills development;
- Adaptation, innovation and jobs integrated and for jobs;
USD 1,000,000
Insurance Technical Support to Africa Adaptation Acceleration Programme (AAAP)
Countries in the Horn of Africa (HoA) are vulnerable to climatic shocks and their impact can have a devastating effect on agricultural production. The most vulnerable regions are arid and semi-arid areas that receive low rainfall and depend on pastoralism as the main economic activity. Elevated levels of food insecurity and conflict resulting from increased competition for pasture and water among pastoral communities is a concern for governments of HoA countries.
Strategies for increasing resilience need to be customized to different sub-regions and microclimates. Initiated in 2019, The Horn of Africa Initiative brings together 6 countries – Djibouti, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia and Sudan – to deepen economic integration and promote regional cooperation. The countries agreed that regional cooperation and economic integration should remain key to the overall recovery efforts of the sub-region.
The project described here focused on “Identifying Climate-Smart Digital Opportunities with Scaling Potential under the Horn of Africa Initiative”.
The findings in this report will contribute towards achieving the objectives of the HoA programme, which include:
-
Strengthening the resilience of pastoral and agro-pastoral production systems to climate change
-
Enhancing agribusiness and enterprise across value chains
-
Strengthening climate services and applications for enhanced adaptive capacity
This report was intended to contribute to the project design by ensuring that activities supporting investments under the HoA programme maximize complementarity around the application of digital technology to ensure efficiency, quality and real-time exchange of data, advisories and related services.
The report was also designed to produce a number of recommendations towards the identification of climate-smart digital opportunities; for example, the importance of establishing strong coordination mechanisms to implement digital solutions at a regional scale.
An in-depth understanding of the existing climate-smart digital opportunities with scaling potential under the HoA Initiative, including (but not limited to):
-
Emerging insurance innovations
-
Mainstreaming digital solutions to climate risk finance into country programmes
-
Application of digital technology to solve challenges in delivering agricultural insurance
-
Critical success factors for a successful regional drought insurance scheme
The output of this report advances the objectives of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Programme (AAAP) of GCA and the African Development Bank, which was developed to help implement the vision of the Africa Union’s Adaptation Initiative. To accelerate adaptation, the AAAP will use a triple-win approach and implement climate resilience activities that address COVID-19, climate change and the economy. AAAP intends to mobilize over US$25 billion to support adaptation between 2020–2025.
N/A
Inclusive Insurance for Smallholder Farmers in Africa
Rising average temperatures, longer heat waves, more extreme precipitation events and locust invasions are just some of the adverse effects of climate change that will impact agriculture in Africa. Climate change is expected to cause a decrease in crop productivity due to increased heat and drought. Some crops are likely to be particularly at risk, such as cotton in Côte d'Ivoire or Ghana. This phenomenon will directly impact the population, with greater consequences for the most vulnerable famers.
In the face of rising climate risk across Africa, insurance is a key adaptation measure to strengthen food security and ensure climate resilience. However, the agricultural insurance market is nascent, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, where less than 3% of farmers are protected.
The underdevelopment of agricultural insurance in Africa is due to a variety of factors, including the lack of organization in local value chains, the low profitability potential of programmes, and a general lack of financial resources and knowledge about insurance. Also, farmers do not consider agricultural insurance to be a priority.
The key aim of the landscape study on Inclusive Insurance for Smallholder Farmers in Africa was to clarify the pathway for the Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) to enter the agriculture insurance market in Africa. The study will contribute to defining the insurance toolkit included in the Smallholder Adaptation Accelerator (SAA) from the Climate Smart Digital Agriculture Pillar of the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP), a joint programme in cooperation with the African Development Bank (AfDB).
The landscape study, completed in December 2021, describes the current state of the agricultural insurance market in Africa and considers (i) the various approaches available to scale up agricultural insurance; (ii) the types of insurance product that could be created; (iii) whether insurance premiums should be subsidized; and (iv) how digital technologies and effective relationships with local partners could be leveraged to facilitate product design and distribution.
This landscape study aimed to achieve:
- A synthesis of market knowledge, including key trends in the African insurance market and the challenges to development of the market
- In-depth product knowledge, including of parametric insurance and digital innovations
- An understanding of the various potential insurance schemes and an awareness of the challenges in distribution
- A clear set of recommendations for the creation of an insurance product for smallholder farmers.
The outcomes of this landscape study should contribute to:
- The identification of priority countries to launch a pilot for a smallholder insurance product.
- The involvement of GCA either as a partner in an existing programme insuring smallholders in a country in sub-Saharan Africa, where the population is connected and digitally active, with a stable government willing to support an insurance programme; or as the catalyst for a new agricultural parametric insurance programme.
- The initiation of a four-step workplan: (i) a feasibility study; (ii) a business agreement; (iii) product design and validation; and (iv) enrolment of farmers into the scheme.
- Once established, the evolution of the insurance cover and type of product over time; for example, from drought index insurance for maize, to a hybrid product for maize, to a hybrid product for maize and cassava.
100000
African Youth Adaptation Solutions Challenge – Cycle 2
YouthADAPT is an annual competition that invites young entrepreneurs and micro, small, and medium enterprises in Africa to submit innovative solutions and business ideas that have the potential to drive climate change adaptation and resilience across the continent.
Through YouthADAPT, the AAAP aims to inspire and support the commercialisation of climate change adaptation solutions, driven by African youth entrepreneurs. The YouthADAPT Challenge is open to solutions targeted at climate change adaptation and increasing resilience.
Solutions can represent:
- An adaptation solutions business that has not been scaled and is not in widespread use
- An existing resilience and adaptation solutions business or product
- A commercially viable means to raise awareness or scale uptake of specific adaptation solutions.
The second edition of the African Youth Adaptation Solutions (YouthADAPT) Challenge was launched in September 2022. Winners will receive a business grant of up to $100,000 and the opportunity to further develop their ventures through business support and acceleration.
The YouthADAPT Challenge aims to support youth-led enterprises to accelerate and scale-up innovative solutions for climate adaptation and resilience. The solutions target key environmental, social, and economic sectors affected by climate change, with a clear value proposition to scale up for greater impact and to create specified direct jobs.
YouthADAPT aims to strengthen inclusive growth and broaden investment and economic opportunities for youth in Africa through entrepreneurial skills development by providing training, mentorship, and financing to youth-led businesses (50% women-owned). The first edition of the awards was launched on 06 September 2021.
- Provide a financial contribution to cover the cost of program implementation and 50% of grant funding
- Participate in project missions and field visits to review progress with select beneficiary enterprises
- Support the project team to provide clarity on climate change adaptation and resilience in the training component, including tracking the creation of adaptation jobs
- Coordinate project monitoring and evaluation.
- The most innovative youth-owned enterprises on the continent are scaled up
- The viability of selected businesses is improved, to help sustain their impact on climate change adaptation
- 50% of the selected businesses are led by women.
- Young innovators and MSMEs equipped with customised business development skills and resources.
- The short-term growth of youth-owned enterprises is supported, with links to private equity and loan products for longer term growth.
- Expansion of partnership, knowledge sharing, exchange and learning through a network of youth entrepreneurs in Africa.
- Inclusive growth, investment and economic opportunities for youth;
- Adaptation, innovation and jobs integrated and for jobs;
Total: USD 1,400,000
Budget for Knowledge Partner (Project Implementation Cost) - USD 400,000
Grant Awards (50% of total grant awards) – USD 1,000,000
2022 Disbursement:
60% Disbursement of Project Implementation Cost to Knowledge Partner – USD 240,000
50% of Grant Awards – USD 500,000
Can today’s Adaptation Action minimize future losses and damages in Africa?

On the sidelines of the 2022 edition of Africa Climate Week(link is external), a session titled Limiting Loss and Damage through Enhanced Adaptation Action in Africa featured vibrant and timely discussion of an aspect of climate change that typically receives little attention: capturing and assessing the costs and damages associated with climate change.
The African Development Bank and Germany’s Konrad Adenauer Foundation hosted the event, which provided a forum for panelists and participants to discuss the importance of defining and evaluating such losses and damages of properties, economies, lives and livelihoods due to climate disasters. Africa is acknowledged to be the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
Moderator Olufunso Somorin, a Regional Principal Officer at the African Development Bank, opened the discussion. He pointed out that it is important for African countries to measure climate-change related loss and damage to enable appropriate quantification and well-designed responses best suited to country context. It was also important to capture those losses occurred even in instances where preventive climate adaptation actions had been taken, he added.
Fatten Agad, Africa Climate Foundation’s Senior Advisor on Climate Diplomacy and Geopolitics, called for production of a report that would serve as guidance and baseline for evaluating climate related losses and damage. “It has already been demonstrated that the socio-economic impact faced by African countries in coping with the Covid-19 crisis has been very high, and adding a burden of financing something such as loss and damage would be unfair,” she said.
Anja Beretta, Konrad Adenauer’s Director for Energy Security and Climate Change in Africa, urged African countries to integrate mechanisms to address losses and damage into their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs). She also called for designated institutions and functioning structures to ensure the efficient and effective use of climate finance to advance the discussion on financial flows into loss and damage.
Stephane Bonamy, Head of the Regional Delegation for the International Committee of the Red Cross in Cameroon, said, for countries that face both conflict and climate change impacts, it is imperative that preventive measures are put in place early enough to reduce the extent of loss and damage faced and lessen the burden on communities.” He noted that 14 of the 25 most vulnerable countries to climate change impacts worldwide also face some form of conflict.
Dr Olumide Abimbola, the Executive Director of the Africa Policy Research Institute in Berlin reiterated the need for more African examples of past and current loss and damage to be incorporated into textbooks and journals.
There was agreement among the participants on the need for Africa to prioritize timely, comprehensive and large-scale adaptation action to avert or minimize future losses and damages.
There was also consensus on the urgent need to scale up financial flows from public and private sources into adaptation action across Africa. They cited the African Development Bank’s Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program, a joint initiative with the Global Center on Adaptation, as a positive example. The program seeks to mobilize $25 billion over five years to accelerate and scale climate adaptation actions across the continent.
Participants also called for new strategic partnerships to drive adaptation policies, plans and investments in Africa through the implementation of NDCs and tapping synergies with such initiatives as the Africa Disaster Risk Financing program.
About the African Climate Week (ACW)
ACW is an annual event that engages and empowers stakeholders to drive climate action across countries, communities and economies. The event is organized by UN Climate Change in collaboration with global partners UN Development Programme, UN Environment Programme and the World Bank Group. Partners in the region include the Africa Union, the Africa Development Bank, the UN Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA). ACW 2022 was hosted in Gabon.
Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision at the Africa Climate Week
What: Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision
When: 31 August 09:30 - 10:30 CAT
Where: Libreville, Gabon
Who: Global Center on Adaptation; Africa Adaptation Initiative (Chaired by Gabon); African Development Bank
Despite contributing the least to global warming, Africa finds itself on the frontline of the climate emergency, with the impacts of external shocks exacerbating these vulnerabilities. Indeed, large portions of Africa—particularly the drylands that cover three-fifths of the continent—are warming at a rate twice the global average, putting half a billion people at risk.
Chaired by Gabon, the Africa Adaptation Initiative (AAI) aims to strengthen collaboration on adaptation across the continent. To implement this vision, the Global Center on Adaptation and the African Development Bank have jointly developed the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program – AAAP. This Africa-led, Africa-owned response is mobilizing $25 billion for climate adaptation investments in the continent over five years. This event will review progress of the AAAP and how it is contributing to narrowing the finance gap, thus accelerating the implementation of AAI.
Program
- Welcome Remarks by the Moderator
Davinah Milenge Uwella – Principal Programme Coordinator, African Development Bank
- Opening Video
- Opening Remarks
Dr. Kevin Kariuki – Vice President, Power, Energy, Climate Change and Green Growth, AfDB
- Framing remarks: The Africa Adaptation Initiative and the AAA
Tanguy Gahouma-Bekale – Special Advisor to His Excellency Ali Bongo Ondimba, President of the Gabonese Republic, Permanent Secretary of the National Climate Council
- The AAAP as the vehicle to implement the AAI vision
Prof. Anthony Nyong – Senior Director, and Africa Regional Director, Global Center on Adaptation
AAAP voices from the field
- AAAP partners and beneficiaries
Moderated discussion with participants
- Wrap up by the Moderator
Multi-Stakeholder Dialogue on Climate Risk Assessment and adaptation options prioritization for the Transgabonaise road corridor PPP project
What: This is a private event
Where: Global - Virtual
When: 19 April 2023, 0:00
This first Multi-Stakeholder Climate Risk Dialogue will present the preliminary results of the high-resolution climate hazard modelling outcomes, and vulnerability assessment of the road corridor project.
Event description:
As part of the Global Center on Adaptation’s support to the Transgabonaise road corridor project under the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program (AAAP), a Multi-Stakeholder Climate Risk Dialogue was organized to present results from the climate risk assessment with the African Development Bank, and project partners including the Societe Autiroutiere du Gabon (SAG), and the government of Gabon’s departments of Environment, Weather, and transport.
Historical weather trends, in Gabon, show an increase in mean annual temperatures of +1ºC since 1981, and decrease in mean annual rainfall, at an average rate of 3.8 mm per month per decade since 1960, with regional disparities. The technical assistance provided by the GCA will support an in-depth understanding of future climate hazards under different climate change scenarios, and across the different regions crossed by the 900km road corridor, and led to identify and provide a cost-benefit analysis of adaptation and resilience options to mitigate these current and future climate hazards.
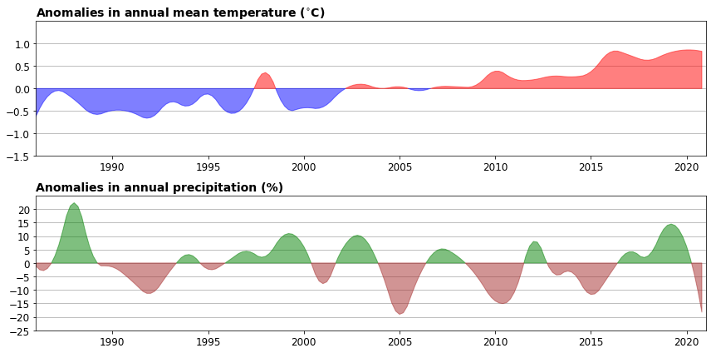
Figure 1: Climatology in Gabon: Historic evolution and trends, Source GCA – study from Royal Haskoning, Lobelia Earth, April 2023.
This First Multi-Stakeholder Climate Risk Dialogue will present the preliminary results of the high-resolution climate hazard modelling outcomes, and vulnerability assessment of the road corridor project. Especially, the project stakeholders will discuss the main climate hazards that have been highlighted, including extreme temperatures, extreme precipitation, drought intensity, and how these climate events might impact the assets and transport services. The discussion with local stakeholders will contribute to ensure robustness of the project outcomes.
Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision

What: Africa Adaptation Dialogue: implementing the vision
When: 31 August 09:30 - 10:30 CAT
Where: Libreville, Gabon
Who: Global Center on Adaptation; Africa Adaptation Initiative (Chaired by Gabon); African Development Bank
Despite contributing the least to global warming, Africa finds itself on the frontline of the climate emergency, with the impacts of external shocks exacerbating these vulnerabilities. Indeed, large portions of Africa—particularly the drylands that cover three-fifths of the continent—are warming at a rate twice the global average, putting half a billion people at risk.
Chaired by Gabon, the Africa Adaptation Initiative (AAI) aims to strengthen collaboration on adaptation across the continent. To implement this vision, the Global Center on Adaptation and the African Development Bank have jointly developed the Africa Adaptation Acceleration Program – AAAP. This Africa-led, Africa-owned response is mobilizing $25 billion for climate adaptation investments in the continent over five years. This event will review progress of the AAAP and how it is contributing to narrowing the finance gap, thus accelerating the implementation of AAI.
Program
- Welcome Remarks by the Moderator
Davinah Milenge Uwella – Principal Programme Coordinator, African Development Bank
- Opening Video
- Opening Remarks
Dr. Kevin Kariuki – Vice President, Power, Energy, Climate Change and Green Growth, AfDB
- Framing remarks: The Africa Adaptation Initiative and the AAA
Tanguy Gahouma-Bekale – Special Advisor to His Excellency Ali Bongo Ondimba, President of the Gabonese Republic, Permanent Secretary of the National Climate Council
- The AAAP as the vehicle to implement the AAI vision
Prof. Anthony Nyong – Senior Director, and Africa Regional Director, Global Center on Adaptation
AAAP voices from the field
- AAAP partners and beneficiaries
Moderated discussion with participants
- Wrap up by the Moderator
Gabon –The Transgabonaise Road Project
With improvements to the road, rail, shipping and aviation networks a key government goal, Gabon’s transport sector is undergoing a major transformation. While population pressure is modest, with around 1.7m people in the country, existing links are limited; the two largest cities, Libreville and Port-Gentil, had, until work began on one recently, no road connection.
The 828 km long Transgabonaise road is key as it connects Libreville (the capital and coastal city) and Franceville (third Gabonese city after Port-Gentil). It comprises several segments of the Routes Nationales (RN) 1 to 4. Despite its strategic importance, the road has suffered from substantial deterioration due to a lack of maintenance and increased traffic over the last decade, caused by the increase of population and lumbering.
The projects is supporting the rehabilitation of a succession of national roads in Gabon to make it a more efficient logistics axis.
Transgabonaise Road Project is divided into three stages:
- Libreville -AlembéStage
- Alembé -Mikouyi (via Lalara, Koumameyong, Booué, Carrefour Leroy)
- Mikouyi -Franceville
- High-resolution, asset-level climate risk and vulnerability assessments to quantify key climate hazards and associated risks to the road infrastructure assets along the entire road corridor
- Innovative solutions for climate smart transport asset management: Based on specific hazards identified including nature-based solutions (NBS) to optimize the resilience of the assets
- Operational performance metrics and standards for the service level agreement (SLA) based on the direct and indirect climate-related damages identified
- Improvement in the capacity and quality of the road infrastructure
- Creation of over 1,000 direct jobs and over 9,000 indirect jobs
- Saving on operational costs and travel time impacting both households and private sector development though lower transport costs
- Generation of safety benefits and lower greenhouse gas emissions
- Additional 200 billion CFA (or $302.4 million) to Gabon’s GDP (equivalent to ~1.9% according to the 2021 GDP)
- Increased connectivity within Gabon and with neighboring countries such as Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea and Congo-Brazzaville
- Promote economic growth through ease of transportation of goods and services efficiently, allowing businesses to access larger markets and expand their operations
- increased trade, investment, and tourism, stimulating economic development in both urban and rural areas in Gabon
- Enhances regional integration and cooperation by facilitating the movement of people, goods, and services across borders, fostering trade relationships and cultural exchange
- Improve accessibility to remote areas, providing people with better opportunities for education, healthcare, employment, and social services
USD 99.2 million